The Union Cabinet, chaired by the PM Modi, has given its approval for ratification of the Kigali Amendment to the Montreal Protocol on Substances that Deplete the Ozone Layer for phase down of Hydroflurocarbons (HFCs) by India, adopted by the Parties to the Montreal Protocol on October, 2016 at 28th Meeting of the Parties to the Montreal Protocol held at Kigali, Rwanda.
The Montreal Protocol on Substances that Deplete the Ozone Layer, is an international environmental treaty for protection of the Ozone Layer by phasing out the production and consumption of man-made chemicals referred to as ozone depleting substances (ODS). The stratospheric ozone layer protects humans: and the environment from harmful levels of ultraviolet radiation from the sun.
India became a Party to the Montreal Protocol on Substances that Deplete the Ozone Layer on 19 June 1992 and since then has ratified the amendments to the Montreal Protocol. Additionally, India has successfully met the phase out targets of all the Ozone Depleting Substances as per the Montreal Protocol Schedule
After the present approval of the Cabinet, India will be ratifying the Kigali Amendment to the Montreal Protocol for phase down of HFC’s.
What are HFC ?
HFC or Hydrofluorocarbons are a type of gas, used widely for refrigeration. Three main HFCs used are HFC-23, HFC-134a and HFC152a.
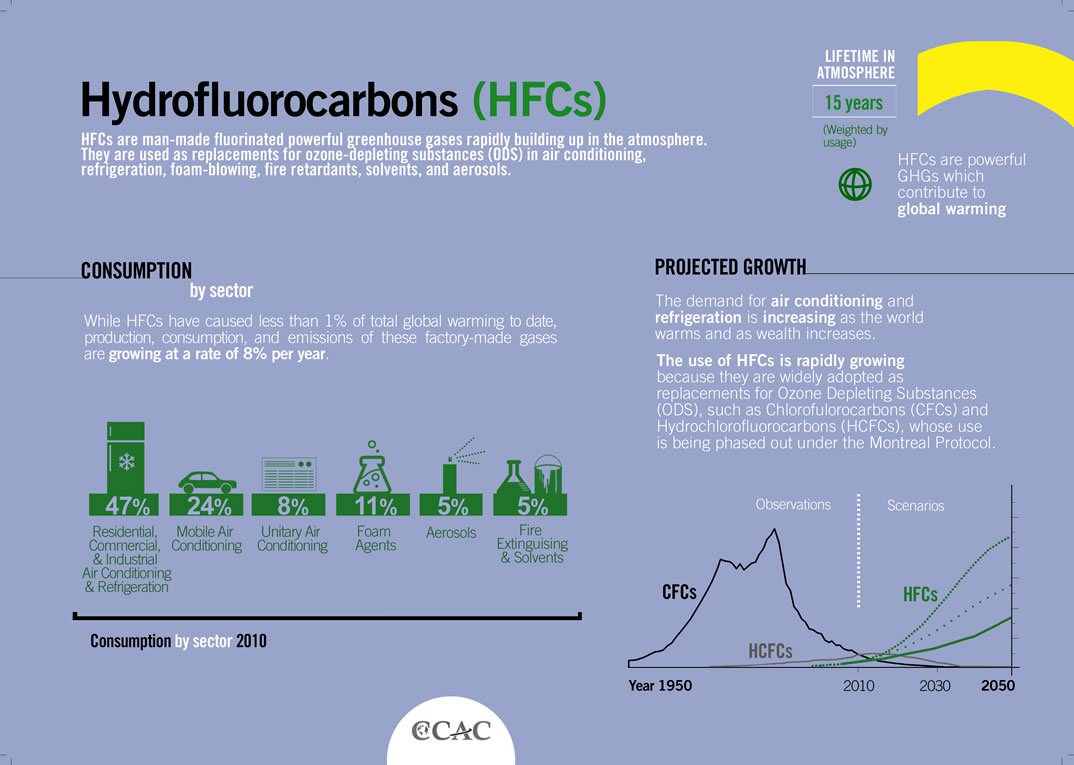
What is the issue with HFC ?
Initially HFC were not used for refrigeration, instead another gas CFC or Chlorofluorocarbons were used. But the problem with CFC was that it was causing depletion of ozone layer. Hence, use of CFC was banned and use new gas HFC was proposed.
Now, HFC was used as refrigeration gas, this gas did not cause depletion of ozone layer but it had another problem, it contributed to Global Warming. Hence the problem with HFC is, it is a powerful greenhouse gas with long atmospheric lifetimes (14 years).
Recognizing the growth in use of HFCs, especially in Refrigeration and Air-conditioning sector the Parties to the Montreal Protocol, reached agreement at their 28th Meeting of the Parties (MOP) held in October 2016 in Kigali, Rwanda to add HFCs to the list of controlled substances and approved a timeline for their gradual reduction by 80-85 per cent by the late 2040s.
India’s HFC Phase-down Strategy
India will complete its phase down of HFCs in 4 steps from 2032 onwards with cumulative reduction of 10% in 2032, 20% in 2037, 30% in 2042 and 80% in 2047. Further, a national strategy for phase down of Hydrofluorocarbons as per the applicable phase down schedule for India will be developed after required consultation with all the industry stakeholders by 2023.
Additionally, amendments to the existing legislation framework, the Ozone Depleting Substances (Regulation and Control) Rules to allow appropriate control of the production and consumption of Hydrofluorocarbons to ensure compliance with the Kigali Amendment will be done by mid-2024
Benefits of HFC Phasedown
HFC phasedown is expected to prevent the greenhouse gas emissions, helping prevent climate change and would benefit the people. The industry producing and consuming Hydrofluorocarbons will be phasing out Hydrofluorocarbons as per the agreed schedule under and transition to non-HFC and low global warming potential technologies.
Hydrofluorocarbons. phasedown is expected to prevent the emission of up to 105 million tonne of carbondioxide equivalent of greenhouse gases, helping to avoid up to 0.5 degree Celsius of global temperature rise by 2100, while continuing to protect the ozone layer.
Implementation of HFC phase down under the Kigali Amendment through the adoption of low-global warming potential and energy-efficient technologies will achieve energy efficiency gains^ and carbon dioxide emissions reduction – a “climate co-benefit”.
There would be scope for domestic manufacturing of equipment as well as alternative non-HFC and low-global warming potential chemicals to enable the industry to transition to the low global warming potential alternatives as per the agreed HFC phase down schedule. In addition, there would be opportunities to promote domestic innovation for new generation alternative refrigerants and related technologies.
Cabinet approves Ratification of Kigali Amendment to the Montreal Protocol – Source

