Ethical concern, dilemma and decision making in administration are key issues that shape the integrity and effectiveness of public service. In the subject Ethics, this topic highlights how administrators often face complex situations requiring a balance between personal values, public interest, and legal obligations. Understanding these aspects is essential for responsible and transparent governance.
Previous Year Questions
| Year | Question | Marks |
| 2021 | Explain the factors essential in “Ethical Decision “ making. In case of decisions being against administrative decisions, how will you harmonize them ? Explain with examples. | 10M |
| 2023 | What do you mean by moral dilemma? Should personal ethics take precedence over professional ethics in a situation of moral conflict? | 10M |
Understand ethical dilemma by A case study
(1)
(2)
(3)
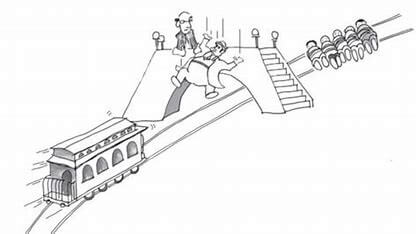
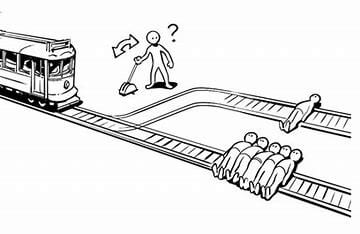
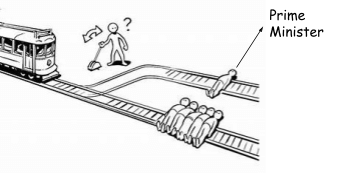
Above three images are related to a case study.
Image 1 –
- A train is coming and you are there on your duty. You observe that on one of the tracks, a single person is tied and on another track five people are tied. You have to pull the lever to give way to train on any particular track. What decision will you take ?
Image 2 –
- One side you find that the person is the prime minister of India and on the other track five common people are tied. Now what will be your decision ?
Image 3 –
- You see that a man is there on the bridge and he is the same man who tied all the people there. By throwing him in front of the train , the train can be stopped. What will be your decision now ? Will you throw that person or not ?
The situation arises in the above three cases, which put you in a doubt and make you think twice for your decision is the situation of ethical dilemma.
Ethical concern and Challenges in administration
Violation of ethical principles and deviation from what is morally right in administration is called ethical concern.
Various concerns and efforts to solve them
| Concern | Efforts to solve |
| Apathy and Lack of compassion | Field training, LBSNAA/RIPA Training, Guest lectures etc |
| Abuse of power and authority | 360 degree appraisal, Code of conduct, Code of ethics (Hota Committee), Citizen empowerment (RTI, Jan Sampark Portal) |
| Attitude – Risk Aversion attitude | Discretionary power (Specially joint secretary and above level), Protection of actions taken in good faith Bona fide action (Ex – Section 456 of the Companies Act, 2013 protects actions taken in good faith) |
| Corruption | PCA act 1988, K Santhanam Committee, e gov, CBI, CVC, Lokpal, RTI, PIL, NGOs and civil society (Ex – ADR), Social audit, Public Financial Management System (PFMS) software etc |
| Poor Transparency | e-Office, Citizen charter, Jan suchna portal |
| Insincerity (Violation of duty) | Aadhar enabled Biometric Attendance System |
| Lack of accountability | Streamlining the laws (Ex – IPC 1860, CrPC 1973 etc), In December 2023, the Indian Parliament passed a bill to repeal 76 obsolete laws |
| Political patronage and Cronyism | e-bidding, Civil services board (For promotion and transfers), Empowering The Central Administrative Tribunal (CAT) |
| Lack of integrity | Mission Karmyogi – The National Programme for Civil Services Capacity Building Introduction of ethics in entry level exams (UPSC and RPSC) |
| Modern concerns – Privacy | Digital Personal Data Protection Act, 2023 IT act 2000 (2021 amendment) |
| Poor Efficiency | Smart Performance Appraisal Report Recording Online Window (SPARROW) |
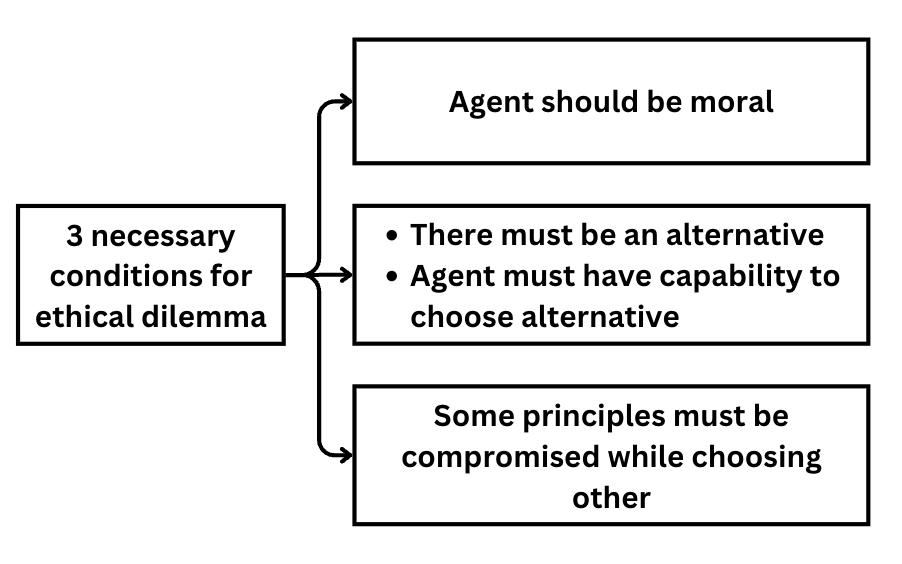
Ethical Dilemma
- Situation when there is conflict between two or more moral principles and moral agents need to pick one at the cost of another.
- Moral agents need to optimize the benefit.
Analogy
- You are an employee in a company and your boss leads the company to profit from losses. Your boss’s attitude towards his wife is very harsh and he does domestic violence. What decision will you take ? Will you directly complain to the police ?
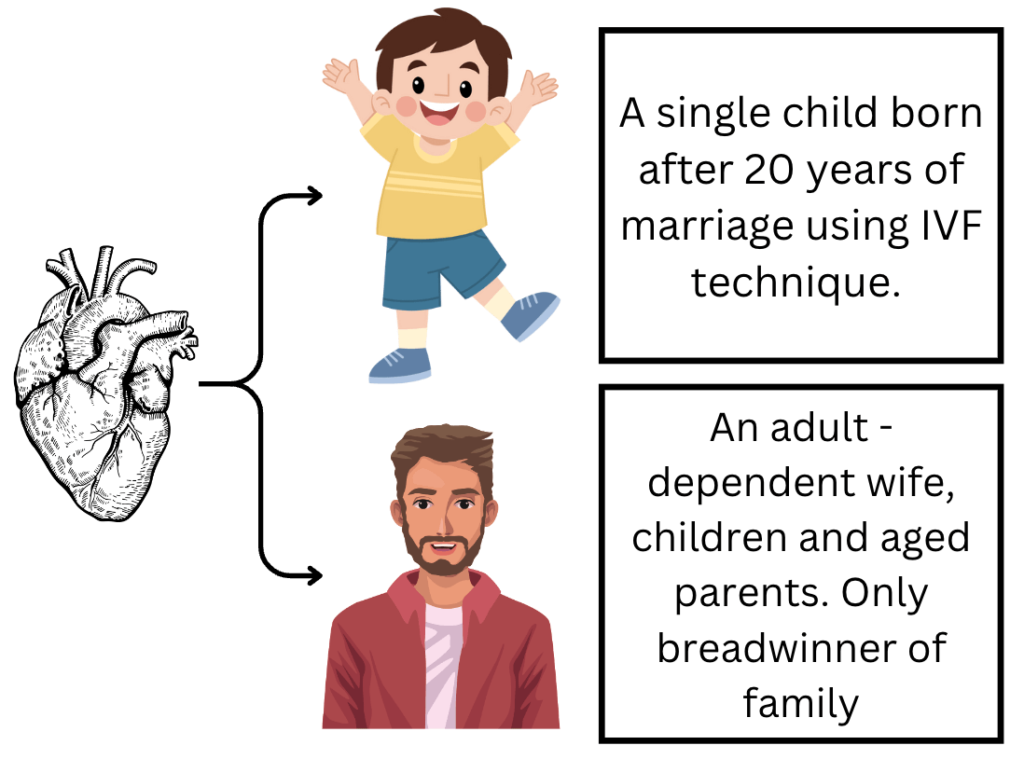
- You are a heart surgeon. You have the two conditions as described in the image. Whom will you transplant this heart to ?
Crisis of conscience
A Crisis of conscience is the strong form of ethical dilemma in which the moral agent needs to fight with inner beliefs and external circumstances. This creates a deeper inner tension or conflict and hence a great deal of mental pain.
How to handle it ?
- Inner development (Meditation/spirituality – Apple founder Steve Jobs visited India in 1974)
- External knowledge (Geeta helped J. Robert Oppenheimer)
- Knowledge of relevant laws, rules and regulations
- Emotional intelligence (Self awareness, Social awareness and management)
- Developing Strong value system
Example
Conflict of Interest
The Situation when decisions taken in public capacity have some vested interest in the private sphere of life.
Examples –
- Insider trading (Rajat Gupta case)
- Cricket selector (His/her son came for trial)
- Chanda kochhar (Misused her position as CEO of ICICI bank for personal banks)
How to avoid
- Clear rules and regulation
- Transparency in system
- Proper Audit mechanism
- Value development programs
Types of Ethical dilemma
There are mainly three types of ethical dilemmas.
- Private cost dilemma
- Ex – Principle Vs preservation or Professional life Vs personal life
- Right vs Right Dilemma
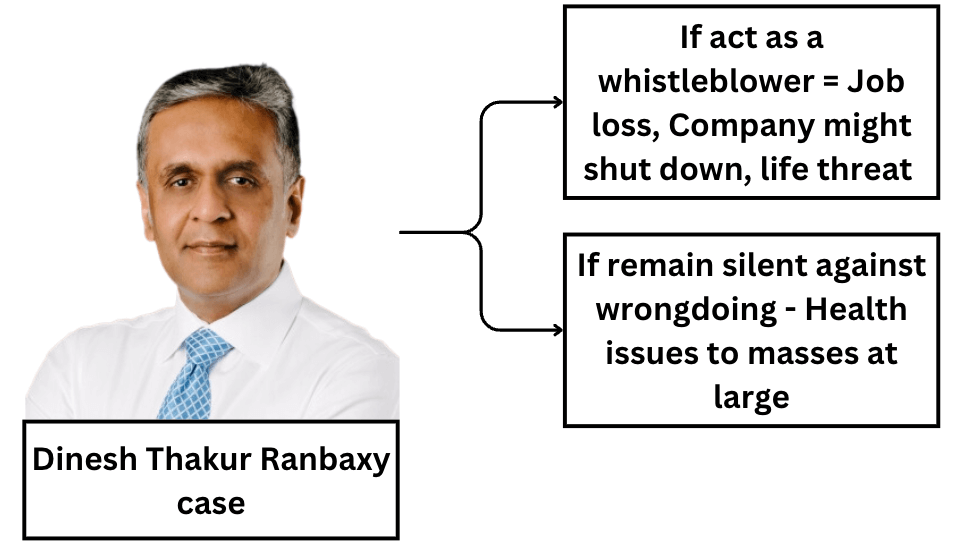
- Loyalty vs Humanity (Ex – Dinesh Thakur Ranbaxy case)
- Conjoint ethical dilemma
- End Vs means dilemma
Ethical dilemmas in Administration
Trick – PP PEARL LANDLESSNESS CJ
| Dilema | Example in administration |
| Principle Vs preservation | IES Satyendra dubey exposed corruption in highway development – Was killed |
| Professional life Vs Personal life | IPS officer 24*7 Duty – Less time to family members |
| Profit vs Social responsibility | Social ethics vs Economic ethicsAn IAS officer heading DISCOM – Dilemma to bring it out of loss vs govts commitment to give free electricity |
| Preferential treatment vs non discrimination | Eg – Jharkhand tribal girl death from hunger due to denial of PDS (Biometric didn’t work) – Such a case demand preferential treatment |
| Punishment vs Reward | Offering of flowers to those violating traffic rules (Means) = Change of heart (End) |
| End vs Means | End – To make a bridge for better traffic managementMeans – Need to break a temple = Religious sentiments might get hurt |
| Autonomy vs Accountability | Autonomy to take CL (Casual leave), PL (privilege leave) and other leaves Accountability – Incharge of office to get the work done on timeEg – Shri Satish dhawan gave autonomy to APJ Abdul kalam for Rohini Satellite launch but when the launch failed, he made himself accountable for the failure |
| Rules vs Discretion | Rules – Don’t provide PDS to anyone without proper documents Discretion – Someone dying from hunger must be provided relief, going beyond the rules |
| Loyalty vs Honesty | Loyalty – Towards govt in powerHonesty – Expose wrongdoing if required |
| Automation vs Employment | Eg – Govt to promote AI, ML, Robotics and other cutting edge technology, on the other hand 69% jobs are at threat due to automation |
| National interest vs Humanity | Officer investing Ajmal Kasab |
| Development vs sustainability | Mumbai Metro Rail Corporation Ltd (MMRCL) to cut trees in Aarey forest, MumbaiSC allowed to cut 177 trees [Penalty above than that] |
| Letter of law vs Spirit of law | A traffic police challaned a car carrying critical patient for overspeeding |
| External accountability vs inner responsibility | A juvenile thief get caught for petty crimesExternal accountability – trial and Jail Inner responsibility – Rehabilitate him/her |
| Speed vs accuracy | Attempting RAS paper – Students in dilemma to maintain speed or quality In administration – CM needs to inaugurate a bridge in 2 months. Speed must not compromise the safety standards |
| National security vs Privacy | Taking someone’s fingerprint or Narco test |
| Equality vs Equity | Reservation in administrative jobs |
| Senior’s oder vs public good | When superior direction is against public good.Eg – A Junior can’t or shouldn’t be rebel against his/her senior (Otherwise work culture gets spoil) but also he/she shouldn’t get succumbed to wrong advice |
| Secrecy vs Transparency | Someone demanding information of national importance in RTI (RTI act section 8) |
| Centralization vs Decentralization | Too much Centralization = Imposing decisions on stakeholder = Poor resultToo much decentralization = Inefficiency and Poor implementation |
| Justice vs mercy | Eg – Nirbhaya rape case – One of the culprit was juvenile. He was convicted to only 3 years sentence (Juvenile Justice Act)Release of A.G. Perarivalan, a convict in the former Prime Minister Rajiv Gandhi assassination case Seeing His satisfactory conduct in jail, his medical condition and his education qualification acquired during incarceration |
How to solve ethical dilemma
ALIR Model – Accountability, Legality, Integrity, Responsiveness
- Democratic Accountability – An administrator should be accountable to government of the day
- Principle of legality – Decision should uphold constitution and judicial laws
- Professional integrity – Adhering to ethical principles of organization
- Responsiveness to civil society – Ultimately welfare attitude
Different approaches to solve Ethical dilemmas
| Approach | Focus on |
| Utilitarian Approach | The Greatest Good for the Greatest Number – Hence take such a decision which benefit more number of people and harm less number of people |
| Rights Approach | Every human being has right to live with dignity |
| Justice/Fairness approach | All equals should be treated equallyFavoritism should not be promoted |
| Common Goods Approach | What is good for society is good for an individual. Hence decisions should be beneficial for all members of society. |
| Virtue Based Approach | The act done by a virtuous person is always right. Hence the decision maker should focus on character developmentEx – Lord Krishna |
| Deontological Approach | Follow duty irrespective of the result |
| Nehruvian Approach | National interest must be at the top |
| Vivekanadan Approach | Service to the mankind is the ultimate goal |
| Gandhian Approach (Talisman) | The decision must be useful for the poorest and weakest person |
| Legal Approach | The action must follow the legal principles and hence must withstand the court’s trial |
Ethical Decision Making
Which decision is called ethical ?
Socrates
- A decision is called ethical if it is taken by a knowledgeable person.
- The only virtue is knowledge and the only evil is ignorance.
- Example – Knowledge of Code of conduct, Code of ethics, Rules and regulation, Laws etc.
Geeta
- LokSamgarah – A decision is called ethical if it promotes social welfare
- Example – Implementation of social welfare policies
- Nishkam Karma – A decision is called ethical if the action taken is selfless or desireless and without any expectations.
- Example – Hemant karkare sir laid his life during mumbai attack of 26/11
Plato –
- A decision is called ethical if it follows any of these 4 values – Wisdom, Courage, Temperance and Justice
- Wisdom – Surender kumar solanki (DM of Dungarpur) used wisdom to solve 2 problems with single scheme – Solar man
- Courage – Durga Shakti Nagpal (exposed a land scam)
- Temperance – Gandhi ji,
- Justice – Poma tudu ma’am traveled 2 hours on a hill to meet tribes and deliver justice.
Jeremy Bentham –
- A decision is called ethical if it is taken under Quantitative Utilitarianism.
- Example – Universal basic income (UBI)
John Stuart Mill –
- A decision is called ethical if it is taken under Qualitative Utilitarianism.
- Some pleasures are intrinsically better than others, even if they are less intense or less immediate
- Higher pleasures – Intellectual, moral, and aesthetic pleasures (Spiritual discourse, Reading etc)
- Lower pleasures: Bodily or sensual pleasures (e.g., Carnal desires, eating, drinking, resting)
- Example – Targeted basic Income or Universal basic capital
Hinduism –
- A decision is called ethical if it follows the Dharma, Arth, Karma and Moksha.
Steps involved in Ethical decision making
Ethical decision making involves five basic steps :-
Step 1:
- Recognize the moral aspect of the problem
- Example – Violation of right, Not following duty, Violating Ethical good, Involved in vices
Step 2:
- Describe the factual details
- Example – How many stakeholders involved
Step 3:
- List down all the moral/ethical values at stake
- Ex – Ethical Values like Impartiality, Accountability, Transparency, Empathy, Temperance, Integrity etc at stake
Step 4:
- Visualize all the possible alternatives to rescue the values at stake
- Alternatives Should Not violate canons of Justice (Like give him/her opportunity to represent)
- Avoid personal bias
- Procedural formality < Developmental objectives
Step 5: Analyzing the consequences of the alternatives
Final outcome is assessed on various Tests and approaches
- The Rights approach – Whether the final outcome respect the rights of all stakeholders
- The Justice Approach – Is the final outcome treats everyone fairly or it is discriminatory
- The Utilitarian approach – Greatest good for greater number
- The common good approach – Is the final decision serving the community as a whole or just some members ?
- The Virtue approach – Would it help me become a better person
- Care Ethics Approach – Does this decision take into account the relationships, concerns, and feelings of all stakeholders ?
- Harm test– Least harm to people or environment
- Reversibility test – What if I was in that situation
- Publicity test – What if this decision is published in Newspaper ?
- Defensibility test – Should not violate any law
- Time test – Timely decision
Contributing factors for making ethical decisions
At Individual level
| Factors | Example |
| Attitude | If Prime minister of a country have good attitude towards a particular gender = Better policy decision |
| Knowledge | Knowledge of Good/bad [Ex – If I have knowledge of lokasamgraha principle, My decisions would not be self centric but for social welfare] Ex – Nobel laureate Kailash Satyarthi |
| Individual values | Values like Honesty, Truthfulness, Ahimsa [Ex – Ahimsa led Gandhi ji to call back non cooperation movement after Chori Chora kand] |
| Legal Awareness | Awareness about Domestic violence act 2005 – Decision to behave humanely towards female members in family |
| Emotional intelligence | An RPS officer with emotional intelligence – Take decision to solve the matter by talking rather than by force |
| Accountability | An elder sibling is accountable for any wrongdoing (In absence of parents) = better decision making in life Accountability of Thana Incharge (CI) for crime = Decision to have regular meetings with Inspectors and Thanedars |
| Conflict of Interest | A father in cricket selection committee -> May take wrong decision to select incompetent son |
| Conscience | Gandhi’s conscience led him to take decision of not eating non veg ever |
Organizational level
| Factors | Example |
| Audits and transparency | Social audit in MGNREGA, RTI in govt office = Better decision makingWhen a civil servant picks up a pen to decide anything, He/she has RTI in her mind – Aruna Roy |
| Board of directors (Leadership) | Diverse and competent board of directors in companies like TATA, Wipro = Better decision making = Good profit and strong corporate governance Dr Samit Sharma IAS – As a special secretary to health and family welfare department, he brought out reforms in generic medicine |
| Employees participation (Management in industries) | Success of Hero cycle (O P Munjal) In 2020, OYO announced that it would make all employees shareholders by offering them deeply discounted employee stock ownership plans (ESOPs) |
| Process Integrity | Selection through UPSC/RPSC → Rigorous training → Field posting → Subordinate postings = better decision making in administration |
| Organizational values | Like in civil services, Values like Integrity, empathy, Transparency, Accountability are must for good governance |
| Legal Sanctions, Rules and Regulations | IPC (1860)CrPC 1973The Central Civil Services (Conduct) Rules, 1964THE ALL INDIA SERVICES (CONDUCT) RULES, 1968 etcThe Rajasthan Civil Services (Conduct) Rules, 1971Better decision making in administration |
| Discretionary power | Officers at the level of Joint Secretary and above |
| Training programs | Mission Karmyogi – The National Programme for Civil Services Capacity Building |
| Hierarchy or Centralization/decentralization | Too much Centralization = Imposing decisions on stakeholder = Poor result Too much decentralization = Inefficiency and Poor implementation For better decision making = Detailed codification of laws/policy + discretionary power at lower level + accountability + use of tech to get instant feedback |
Social level
| Factors | Example |
| Social Values | Harmony, Tolerance, Compassion, Empathy, Kindness etcEg, India society = Vasudev Kutumbakam = Peace and prosperityEg, Syria – Religious intolerance among kurds and sunnis |
| Modern concepts | Feminist ethics – Better decision regarding women genders in societyEg, In October 2022, the BCCI announced that female cricketers would receive the same match fees as their male counterparts. This includes ₹15 lakh for a Test match, ₹6 lakh for an ODI, and ₹3 lakh for a T20.#Metoo MovementBlack ethics – Black people have equal right to live with dignity as their counterpartsBlack Lives Matter movement in 2020 after the murder of George Floyd in USA |
| Legal sanctions | PCPNDT act – Decision for gender equality RTE Act 2009 – To make the article 21A as binding a binding law |
| Judicial interpretation | SC judgment on Sabarimala, triple talaq etc |
| Govt. Policies | Eg. – Kalibai Bheel Medhavi Chhatra Scooty Yojana = Many parents decide to continue their child’s studies |
Some other factors
- Availability of alternative
- Awareness of circumstances [Ex – A person with sound mind will take better decision]
- Freedom of will [Ex – Capability and opportunity will lead to better decision making]
- Past experiences [Ex – Dr Samit sharm’s past MBBS experience or Dr. Ravindra Goswami (Bundi collector) treated patients during doctor‘s strike]
- Environmental factors – Peer group, Friends, Family members, teachers etc shape the decision making ability of a person
- Support system – Better the support system, better decision making.
Practice Questions related to Ethical concern, dilemma and decision making in administration
| What is a crisis of conscience and how is it different from conflict of interest ? Explain with examples | 5M |
| Enlist different types of ethical dilemmas faced by an administrator and give remedies for each of them. | 10M |
Ethical concern, dilemma and decision making in administration / Ethical concern, dilemma and decision making in administration/ Ethical concern, dilemma and decision making in administration/ Ethical concern, dilemma and decision making in administration / Ethical concern, dilemma and decision making in administration / Ethical concern, dilemma and decision making in administration / Ethical concern, dilemma and decision making in administration
FAQ (Previous year questions)
Situation when there is conflict between two or more moral principles and moral agents need to pick one at the cost of another.
Moral agents need to optimize the benefit.
In most cases, professional ethics must take precedence –
Professional Duty Ensures Impartiality & Rule of Law – Personal ethics may be shaped by emotions, biases, or culture, while professional ethics are standardised and aligned with constitutional values
To avoid a conflict of interest
To avoid personal prejudice at work
To Avoid nepotism, favoritism and Crony capitalism
Protects Public Interest over Private Interest –
Ex -A civil servant must cancel an illegal tender won by a friend if it violates the procurement rules.
Creates Accountability and Trust in Public Institutions
Ex: Neutral behaviour in recruitment or election duties is essential, regardless of personal preferences.
It is not wise to apply to public administration the sort of moral and ethical norms we apply to matters of personal conscience – Max Weber
Example – An RPS officer might need to give up non-violence if the law requires him/her to do so.
But in some special circumstances, personal ethics might take over –
In case of discretion, an officer might violate professional ethics like strictly following rules and regulations, and can take decision out of compassion and empathy
Ex – During the crowd control, an IAS officer protected refugees against mob violence by violating protocol, guided by personal morality
Few Personal values, like compassion, Integrity etc have positive spillover effects
Ex – These values motivate an officer to behave decently with his/her subordinates and hence strengthen professional bonds
Public choice theory – For better governance, we need to adopt values like user-friendly practices, empathy, Appreciation etc
While a complete separation of private and public life is neither feasible nor always desirable, a public servant must uphold professional ethics as the guiding force, using emotional intelligence to harmonize personal values with institutional integrity for the greater good.
Situation when there is conflict between two or more moral principles, and moral agents need to pick one at the cost of another.
Moral agents need to optimize the benefit
Ex – You are an employee in a company, and your boss leads the company to make a profit from losses. Your boss’s attitude towards his wife is very harsh, and he exhibits domestic violence. What decision will you take? Will you directly complain to the police?
The minimum basic needs of an individual
Administrators’ responsibility
Physiological needs like Food, Clothes, Shelter, Clean Drinking Water and sanitation
Effective implementation of various government schemes like Annapurna Rasoi Yojana, Pradhan Mantri Awas Yojana, Mid-Day Meal Scheme, ICDS for children and mothers, Swachh Bharat mission, etc
Following the principle of utilitarianism
Ex – Operation Sulaimani is a free food programme introduced in the city of Kozhikode
Healthcare and education
Equity and Inclusion – Ensuring that vulnerable groups like SC/ST, minorities, women, and the disabled are not left behind
Ayushman Bharat for free secondary and tertiary healthcare
Ensuring proper implementation of the Right to Education Act and the Samagra Shiksha Abhiyan
Regular inspection of the health center and schools
Safety needs
Maintain law and order through active policing and community engagement.
Implement the Vishaka Guidelines, women’s helplines, and night shelters for the homeless.
Emergency services, disaster preparedness, and cyber safety initiatives.
Ex – Exercising power under the Disaster Management Act 2005
Organising community events, grievance redressal platforms like Ratri Chaupal
Social needs
Belongingness, care, and community support are fundamental.
Inclusive approach towards senior citizens, persons with disabilities, tribals, and minorities.
Ex – IAS officer Poma Tudu traveled hours on foot to reach remote tribal areas, ensuring services reach the last mile
Self esteem
Inculcation of values like empathy so that citizens are treated as subjects of rights rather than objects of charity
Promote citizen participation in governance through platforms like MyGov, RTI, and social audits
Encourage skill development and entrepreneurship for self-reliance
Lack of administrative attitude or acumen – When administrators lack the necessary cognitive, emotional, and behavioural alignment to their duties, it creates cognitive dissonance
Ex – A young officer posted in a rural area may feel demotivated and frustrated if they hold elitist or urban-centric attitudes
Conflict of interest – When personal interests – financial, political, or familial, clash with official duties, it creates a dilemma that hampers decision-making and leads to internal stress
Ex – An officer overseeing tender allocation might face pressure from relatives or politicians to favour certain contractors
Conflict in private and public values – An administrator may face moral conflict when their private ethical values (e.g., non-violence, pacifism) clash with the professional need for strict action (e.g., evictions, arrests)
Ex – An officer with Gandhian ideals may feel disturbed while overseeing forced land acquisition, even if it’s legally required
Hedonistic tendencies/Poor Value system/lack of Integrity – If the administrator is guided by materialism or shallow pleasures (desire for fame, comfort, or money), stress arises when those desires are unfulfilled or are challenged by ethical demands.
Wealth without work is a sin according to Gandhiji and such sins ultimately leads to mental stress
Ethical dilemma and Crisis of conscience – In morally grey situations, choosing between two ‘rights’ creates immense internal pressure and guilt.
Poor work life balance (Overburnedned) – long hours, staff shortages, and public/political pressure = little time for self-care and family = mental stress
Lack of power/authority or discretion – Often, officers are held responsible without being given sufficient autonomy or are micromanaged by seniors and politicians. This helplessness leads to frustration and stress
Example: An honest officer may face frequent transfers or political interference when trying to take tough decisions (Ashok Khemka, who faced over 50 transfers)
Not following the karm yoga – Inaction in administration leads to accumulated pendency, loss of public trust, and internal guilt and hence causes mental stress
Cultivating emotional intelligence, ethical grounding, and karmic detachment is essential for long-term mental well-being and effective governance.
Ethical decisions are those decisions which adheres to the moral principles and values.
Factors essential –
At the individual level –
Attitude, Knowledge, Individual values. Legal Awareness, Emotional intelligence, Accountability, Conscience etc plays role in ethical decision making
At the organizational level –
Audits and transparency, Board of directors (Leadership), Employees participation (Management in industries), Process Integrity, Organizational values, Legal Sanctions, Rules and Regulations, Discretionary power ,Training programs etc
At the Social level –
Social Values, Modern concepts, Legal sanctions, Judicial interpretation, Govt. Policies etc
Other factors –
Availability of alternatives
Awareness of circumstances [Ex – A person with sound mind will take better decision]
Freedom of will [Ex – Capability and opportunity will lead to better decision making]
Past experiences [Ex – Dr Samit sharm’s past MBBS experience or Dr. Ravindra Goswami (Bundi collector) treated patients during doctor‘s strike]
Environmental factors – Peer group, Friends, Family members, teachers etc shape the decision-making ability of a person
Support system – Better the support system, the better is decision-making.
Harmonising decisions –
Taking help of bona fide action – If an act is legally questionable but done with honest intent for public welfare, courts often provide relief.
Ex – During the COVID-19 lockdown, many IAS officers distributed food and essential supplies to migrant workers without waiting for formal approvals. Though these actions bypassed certain bureaucratic protocols, they were considered bona fide due to their intent to serve public interest in an emergency
Clear Dissent – When following orders may result in unethical outcomes, record dissent with clear justification
Ex – A civil servant refusing political pressure to approve an illegal tender
Balancing Rule with Spirit of Law – Rigid adherence to rule may harm public interest; applying its spirit ensures ethical governance
Ex – Bypassing procedure temporarily to save a critical patient in an ambulance
Ethical decision-making is a delicate balance between rules and values. An administrator must be morally upright, legally aware, and emotionally intelligent to harmonise ethical and administrative responsibilities, ensuring justice and trust in governance.
