Union Budget 2026 Highlights & Key Takeaways present a concise overview of the major announcements, policy priorities, and fiscal measures introduced by the Government of India for the financial year. The budget focuses on economic growth, social welfare, infrastructure development, and fiscal discipline amid evolving domestic and global challenges. These highlights help in understanding the government’s vision, sector-wise impact, and key takeaways relevant for examinations and current affairs analysis.
Union Budget 2026-27
Finance Minister Nirmala Sitharaman presented the Union Budget 2026–27 with a strong focus on growth, inclusivity, and middle-class relief. The budget outlines a roadmap toward “Viksit Bharat” with agriculture, MSMEs, investment, and exports as the four main growth engines.
Deficit Statistics
(₹ करोड़) (In ₹ crore)
| Revised Estimates | Budget Estimates | |
| Fiscal Deficit | 15,58,492 | 16,95,768 |
| Revenue Deficit | 5,26,764 | 5,92,344 |
| Effective Revenue Deficit | 2,18,613 | 9,96,42 |
| Primary Deficit | 2,84,154 | 2,91,796 |
Major Focus Areas
1. Agriculture & Rural Development
Agriculture remains the top priority in this budget with several new missions and financial support measures:
- Launch of PM Dhan-Dhaanya Krishi Yojana covering 100 low-productivity districts to improve irrigation, storage, and credit access.
- Mission for Aatmanirbharta in Pulses with focus on Tur, Urad, and Masoor to reduce imports.
- National Mission on High-Yielding Seeds to boost crop productivity and climate resilience.
- Kisan Credit Card (KCC) loan limit increased from ₹3 lakh to ₹5 lakh.
- Establishment of a Makhana Board in Bihar and support for fisheries, cotton productivity, and vegetable & fruit supply chains.
- A new Rural Prosperity and Resilience Programme to create employment and reduce migration from villages.
2. MSMEs, Manufacturing & Startups
Micro, Small and Medium Enterprises (MSMEs) and startups received a major push:
- Higher classification limits for MSMEs allowing businesses to grow without losing benefits.
- Credit guarantee cover increased for small enterprises and startups.
- Launch of a ₹10,000 crore Fund of Funds to support startups and deep-tech innovation.
- Special loan scheme for first-time women, SC/ST entrepreneurs.
- Focus product schemes for footwear, leather, toys, and food processing industries to boost exports and employment.
- A National Manufacturing Mission to strengthen “Make in India” and promote clean-tech sectors like EV batteries and solar equipment.
3. Education, Skills & Innovation
Strong emphasis was placed on youth development and future skills:
- 50,000 Atal Tinkering Labs to be set up in government schools over five years.
- Expansion of IIT infrastructure and addition of 10,000 new medical seats next year.
- A new Centre of Excellence in Artificial Intelligence for Education with ₹500 crore outlay.
- National Centres of Excellence for Skilling to prepare youth for global manufacturing jobs.
- Broadband connectivity for all government secondary schools and rural health centres under BharatNet.
4. Health & Social Welfare
- Day Care Cancer Centres to be established in all district hospitals within three years.
- Expanded nutrition support under Poshan 2.0 for children and mothers.
- Healthcare coverage for gig and platform workers under PM Jan Arogya Yojana.
- Revamped PM SVANidhi Scheme with higher loan limits and UPI-linked credit cards for street vendors.
5. Infrastructure & Economic Development
Large investments were announced to strengthen infrastructure and urban growth:
- ₹1.5 lakh crore interest-free loans to states for capital expenditure.
- Launch of an Urban Challenge Fund worth ₹1 lakh crore for city redevelopment, water, and sanitation projects.
- Jal Jeevan Mission extended till 2028 to ensure tap water for all rural households.
- Push for nuclear energy, shipbuilding, regional air connectivity (UDAN), and tourism development.
- New Asset Monetization Plan 2025–30 to reinvest capital into fresh infrastructure projects.
6. Exports, Trade & Technology
- Launch of an Export Promotion Mission and BharatTradeNet, a digital trade platform.
- Customs duty relief on life-saving medicines and critical minerals.
- Measures to integrate India into global supply chains and strengthen electronics manufacturing.
- Support for medical tourism and spiritual tourism destinations.
7. Major Income Tax Relief for Middle Class
One of the biggest announcements was personal income tax reform:
- No income tax up to ₹12 lakh annual income under the new tax regime.
- For salaried individuals, the limit effectively rises to ₹12.75 lakh due to standard deduction.
- Revised tax slabs introduced to reduce overall tax burden and increase disposable income.
- Rationalization of TDS/TCS rules to simplify compliance.
8. Fiscal Outlook
- Fiscal deficit target: 4.4% of GDP for 2025–26.
- Continued focus on fiscal discipline while maintaining high capital expenditure and growth momentum.
Overall, the Union Budget 2025–26 aims to balance economic growth with social welfare supporting farmers, empowering MSMEs, investing in youth and innovation, strengthening infrastructure, and offering significant tax relief to the middle class.
Budget 2026 Highlights PDFs
| Budget 2026 Highlights | Download PDF |
| Budget at a Glance | Download PDF |
| Budget Speech | Download PDF |
| Deficit Statistics | Download PDF |
| Transfer of Resources to States and Union Territories with Legislature | Download PDF |
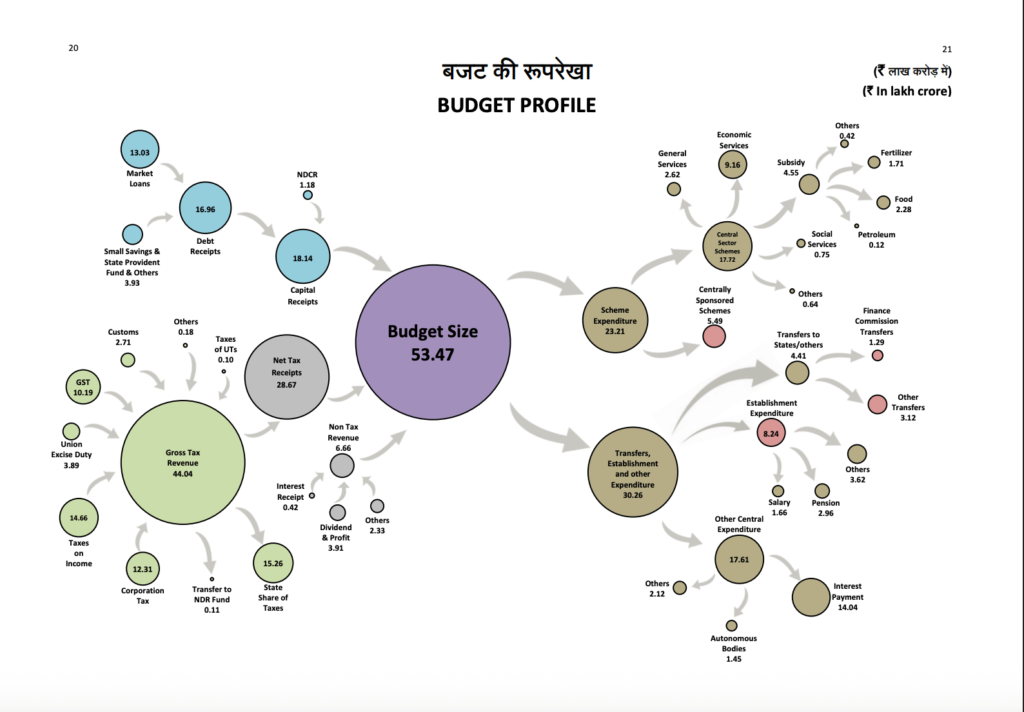
| Budget Profile | Download PDF |
| Receipts | Download PDF |
| Expenditure | Download PDF |
| Outlay on Major Schemes | Download PDF |
| Union Budget 2023 Highlights | Download PDF |