Urbanisation is an important theme in Rajasthan Geography, describing the growth and expansion of towns and cities along with the shift of population from rural to urban areas. In Rajasthan, urbanisation reflects changes in economic structure, industrial development, infrastructure, and service-sector growth. The pattern of urban centres also shows strong links with trade routes, administrative functions, and regional resource distribution.
Trend and Growth of Urbanisation in Rajasthan
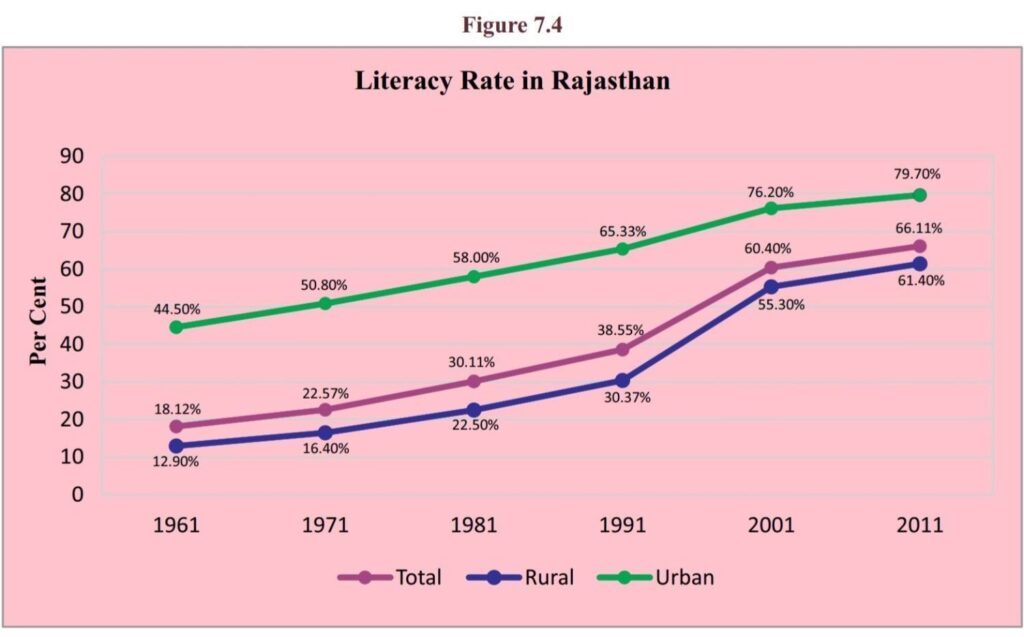
- Urbanisation refers to the migration of people from rural to urban areas, marked by a steady increase in the proportion of the population living in cities.
- The trend of urbanisation in Rajasthan has been following a similar pattern to the national level.
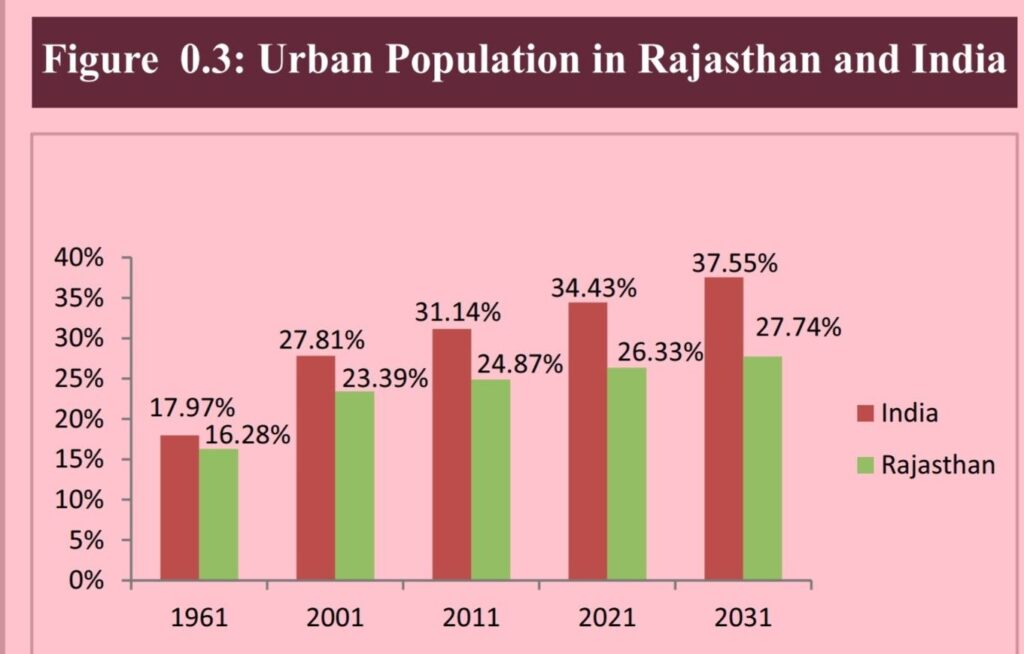
- The share of India’s urban population in the total population increased from 17.97 per cent in the year 1961 to 31.14 per cent in the year 2011.
- A comparable trend is seen in Rajasthan, where the percentage of the urban population in the State’s total population rose from 16.28 per cent in 1961 to 24.87 per cent in the year 2011.
- In Rajasthan, the share is projected to be 26.33 per cent in 2021 and increase to 27.74 per cent by 2031.
- The total population living in urban areas of Rajasthan in 2001 was 132 lakh, comprising 70 lakh males and 62 lakh females. This is expected to reach 242 lakh, including 126 lakh males and 116 lakh females, by 2031.
Districts with the maximum population growth rate
| Rural | Urban |
| Jaisalmer | Alwar |
| Barmer | Dausa |
| Banswara | Baran |
Districts with Minimum population growth
| Rural | Urban |
| Kota | Dungarpur |
| Sri Gangamnagar | Pratapgarh |
| Jhunjhunu | Banswara |
Districts with the Highest and Lowest Rural Population
|
Highest |
Lowest |
|
|
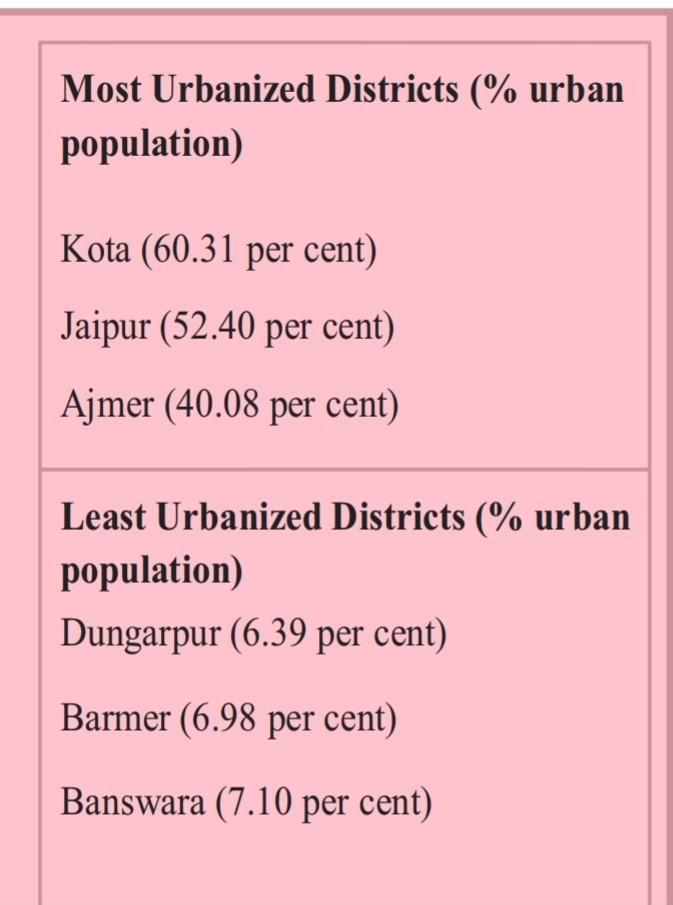
Districts with the Highest and Lowest Urban Population
|
Highest |
Lowest |
|
|
Urban and Rural Population Percentage
| Rural (75.1%) | Urban (24.1%) |
| Highest – Dungarpur | Highest – Kota |
| Lowest – Kota | Lowest – Dungarpur |
Urban population in Rajasthan as per economic survey -2024-25
|
Maximum |
Minimum |
|
|
Sex Ratio
- In Rajasthan, about 75.1% of the state’s population lives in rural areas.
- The rural sex ratio of Rajasthan is 933, and the urban sex ratio of Rajasthan is 914.
- The sex ratio in rural areas of the state is 933. Pali district of the state ranks first on the basis of the rural sex ratio of 1003. It is followed by Rajsamand (998), Dungarpur (996) and Pratapgarh (984).
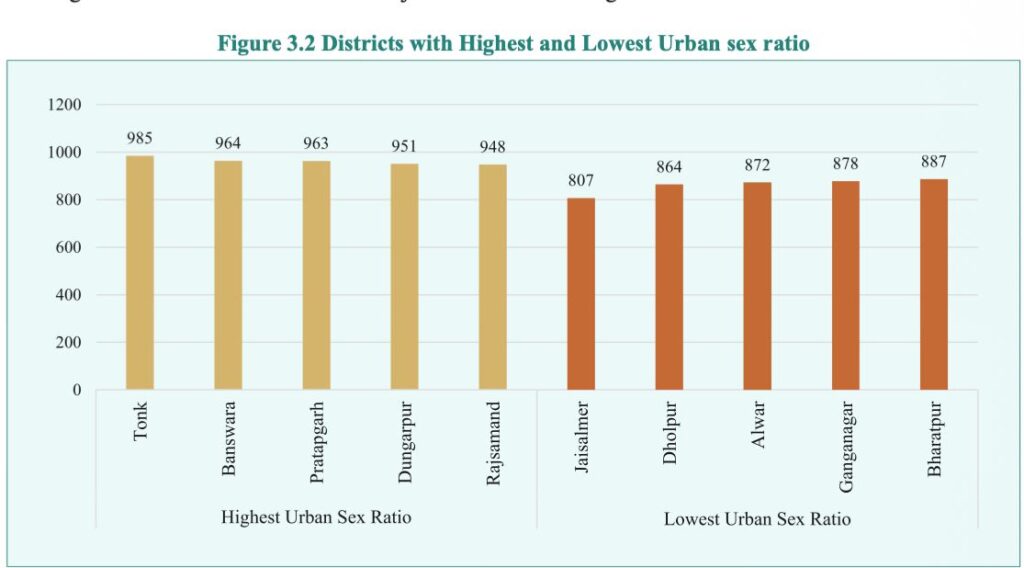
- Tonk district has the highest sex ratio in urban areas at 985, followed by Banswara (964), Pratapgarh (963) and Dungarpur (951). Jaisalmer district has the lowest sex ratio in urban areas at 807.
Rural Area sex Ratio
| Maximum | Minimum |
| Pali -1003 Rajsamand-998 Dungarpur -996 | Dholpur-841 Karauli-856 Jaisalmer-859 |
Urban Sex Ratio
| Maximum | Minimum |
| Tonk-985 Banswara-964 Pratapgarh-963 | Jaisalmer-807 Dholpur-864 Alwar -872 |
Child Sex Ratio
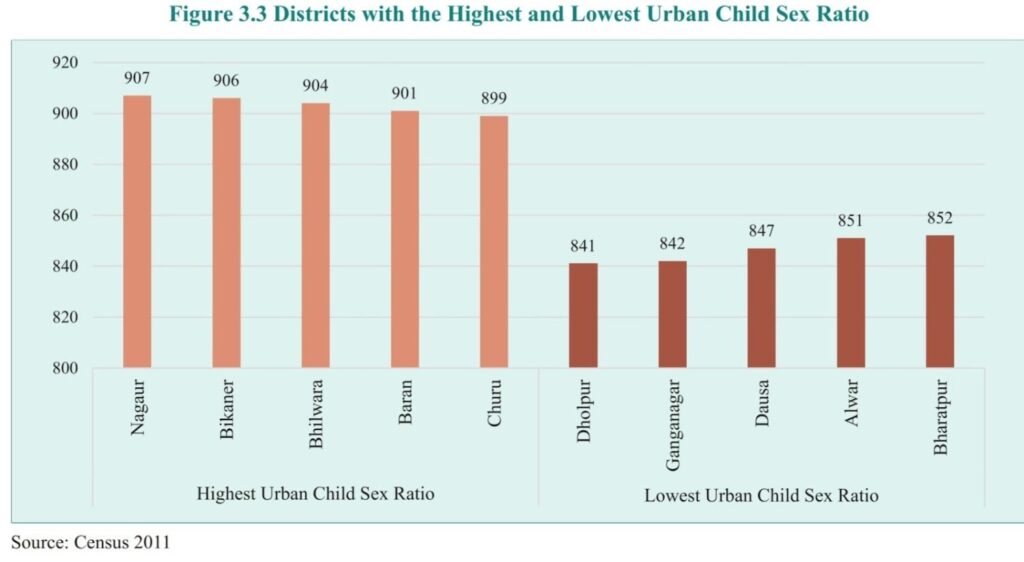
- A similar trend is observed in the Child (0-6 years) Sex Ratio across urban and rural areas of Rajasthan. While rural areas have performed better than urban areas, both regions experienced a decline in the Child Sex Ratio in the year 2011 compared to the year 2001.
- In urban areas, the Child Sex Ratio decreased from 887 girls per 1,000 boys in 2001 to 874 girls per 1,000 boys in 2011. In rural areas, it declined from 914 girls per 1,000 boys in the year 2001 to 892 girls per 1,000 boys in the year 2011.
Rural Child Sex Ratio
| Maximum | Minimum |
| Banswara- 937 Pratapgarh-936 Bhilwara- 933 | Jhunjhunu-832 Sikar-843 Karauli-850 |
Rural literacy rate (61.4%)
| Maximum | Minimum |
| Jhunjhunu -73.4% Sikar – 70.8% Kota – 68.6% | Sirohi – 49% Pratapgarh – 53.2% Jalore – 53.3 % |
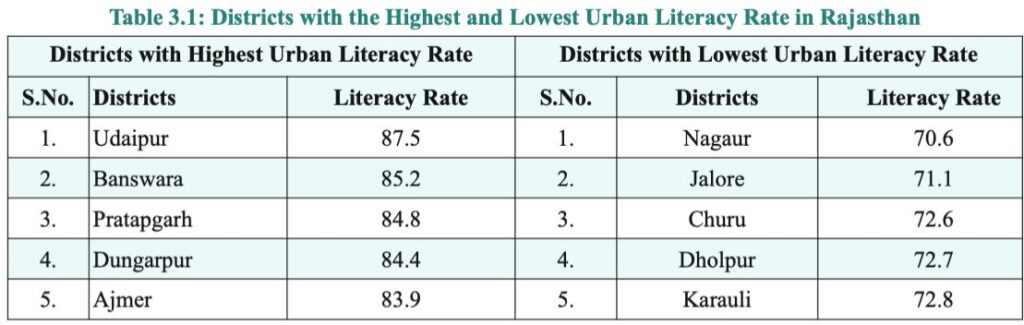
Urban Literacy rate (79.7%)
Urban agglomeration population of 1 lakh and above
- Jaipur – 30.46 lakh
- Jodhpur- 11.38 lakh
- Kota – 10.02 lakh
- Bikaner – 6.44 lakh
- Banswara (1.01 lakh), an urban Agglomeration has the smallest population size.
Spatial Variation in Urbanisation
Migration in Rajasthan (Rural-Urban)
- According to the 2011 Census data, males in Rajasthan mainly migrate from rural to urban areas in search of employment opportunities. 49.16 per cent of the male migrant population in Rajasthan moved for better work opportunities,
- Females primarily migrate due to marital reasons. 59.11 per cent of the female migrant population migrated due to marriage.
Urban salum Dwellers in Rajasthan
- Jaipur
- Kota
- Jodhpur
- Bikaner
- Ajmer
- Udaipur
- Sri-Ganganagar
- The highest percentage of salum dwellers relative to the total population in Rajasthan
- Pilibanga
- Jahazpur
- Kesrisinghpur
Seven Urban development authorities, namely (Jaipur, Ajmer, Jodhpur, Kota, Bharatpur, Bikaner and Udaipur), 10 urban improvement trusts, namely (Alwar, Abu, Barmer, Bhilwara, Chittorgarh, Jaisalmer, Pali, Sri Ganganagar, Sikar and Sawai Madhopur)
Real Estate Regulatory Authority, Rajasthan (RERA):
- To facilitate the growth and promotion of a healthy, transparent, efficient and competitive real estate sector, the Government of Rajasthan has constituted the Rajasthan Real Estate Regulatory Authority (RERA) and the Real Estate Appellate Tribunal on 6 March, 2019.
State Government initiatives for Urban development
Master Plans
- A master plan for any city provides a vision and a legal framework for its development over a period of around 20 years. Of the 300 municipal towns in Rajasthan, master plans for 194 have been prepared and approved by the government.
Mukhyamantri Shahari Rojgar Guarantee Yojana
- The scheme provides economic support to urban families by offering unskilled labour employment for members aged 18-60 years.
- In 2023-24, the number of employment days was increased from 100 to 125.
Rajasthan Urban Development Fund-II (RUDFII)
- The Rajasthan Urban Development Fund-II was established on 25 August 2021 with provisions to secure loans from Housing and Urban Development Corporation Limited (HUDCO), financial institutions and banks, as well as to receive special or additional grants from the State Government.
Central government initiatives for urban development
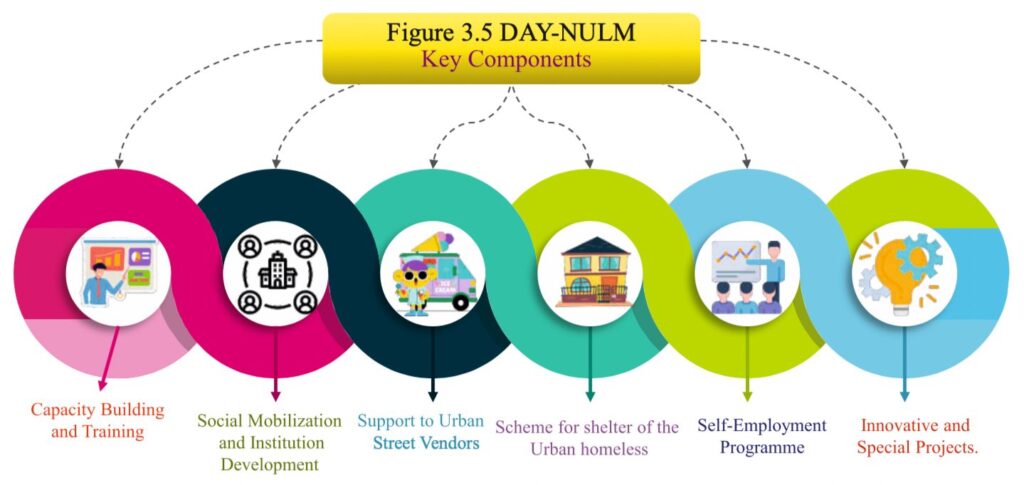
Deendayal Antyodaya Yojana-National Urban Livelihood Mission (DAY-NULM)
- The mission is being implemented in 213 urban local bodies of Rajasthan.
Urban Infrastructure Development Scheme for Small and Medium Towns (UIDSSMT)
- The Ministry of Urban Development (MoUD) revised the funding pattern to 60:20:20 (GoI: State: ULB) in alignment with the AMRUT funding structure for 11 ongoing projects.
Smart Cities Mission
- Launched by the Government of India in June, 2015.
- Aims to develop cities that offer core infrastructure, ensure a high quality of life for residents, maintain a clean and sustainable environment and utilise ‘Smart Solutions’ for urban development.
- The mission targets 100 cities, with funding of ₹100 crore per city per year provided.
- In Rajasthan, four cities-Jaipur, Udaipur, Kota and Ajmer were selected for development as Smart Cities.
Atal Mission for Rejuvenation and Urban Transformation (AMRUT 2.0)
About AMRUT
- Ministry: Ministry of Housing and Urban Affairs
- Type: Centrally Sponsored Scheme
- About: Launched in selected 500 cities and towns, focusing on the development of basic infrastructure in the sectors of Water supply, Sewerage and septage management.
- AMRUT 2.0
- AMRUT 2.0 focuses only on water and sewerage and aims to provide tap water to all households in statutory towns and improve sewerage management in 500 AMRUT cities.
Swachh Bharat Mission
- Launched on 2nd October, 2014 (birthday of Mahatma Gandhi) as a national movement.
- Objective: Accelerate the efforts to achieve universal sanitation coverage and to put the focus on sanitation.
- Sub-missions: It has 2 Sub-missions (Both are Centrally Sponsored Schemes)
- Swachh Bharat Mission (Gramin): Under the Ministry of Jal Shakti
- SBM (G) Phase-II (2020-21 to 2024-25) is under implementation.
- Swachh Bharat Mission (Urban): Under Ministry of Housing and Urban Affairs (MoHUA)
- SBM-U 2.0 Phase II is under implementation till 2026.
- Swachh Bharat Mission (Gramin): Under the Ministry of Jal Shakti
Swachh Bharat Mission (Urban) 1.0
- The Swachh Bharat Mission (Urban) aims to enhance cleanliness across India through public participation, focusing on the construction of Individual Household Latrines (IHHL), community/public toilets, urinals, and effective solid waste management.
Swachh Bharat Mission Urban 2.0
- The Swachh Bharat Mission (Urban) 2.0 was launched in October 2021 for five years. Its key components include toilet construction (Individual Household Latrines (IHHL), community/public toilets (CTs/PTs) and urinals), solid waste management, used water management, and Information, Education, Communication & Capacity Building (IEC&CB).
Pradhan Mantri Awas Yojana (Urban)
- Launched: June 25, 2015
- Ministry: Housing and Urban Affairs
- Public expenditure (40%) and private investment, including beneficiary contribution (60%).
- Beneficiary – Economically Weaker Section (EWS): Annual household income up to Rs. 3 Lakh.
- Low Income Group (LIG): Annual household income from 3-6 Lakh.
- Middle Income Group (MIG): Annual household income from Rs. 6-18 Lakh.
- The beneficiary family should not own a pucca house in his/ her name or in the name of any member of his/her family in any part of India.
Urban programs run by externally aided agencies
Rajasthan Urban Infrastructure Sector Development Program (Phase III)-ADB
- Under the project, works worth ₹3,930.45 crore are being implemented across 12 cities.
