In Rajasthan Geography, Rajasthan’s major rivers and lakes, including the Chambal, Luni, Banas, and Sambhar Lake, shape its arid landscape. These water bodies support agriculture, biodiversity, and cultural heritage.
Previous Year Question
|
Year |
Question |
Marks |
|
2023 |
Sabarmati river flows in which districts of Rajasthan ? Name its tributaries. |
2 M |
|
2018 |
Describe river systems of Rajasthan ? |
5 M |
Major Rivers
- Only 1.16% of surface water of country is available in Rajasthan
- Out of 302 water blocks of Rajasthan 216 are in dark zone
- Aravalli acts as water divide for Rajasthan as it separates drainage system of Bay of Bengal and drainage system of Arabian Sea
- Drainage system of Rajasthan can be divided into three parts
- Rivers flowing towards Bay of Bengal
- Rivers flowing towards Arabian Sea
- Rivers of Inland drainage system
- Churu & Bikaner districts do not have any river


Rivers flowing towards Bay of Bengal
Chambal

- Originates from Janapao Hill Indore (Vindhyachal range).
- Enters into Rajasthan at Chorasigarh, Chittorgarh flows through Chittorgarh, Kota, Bundi, Sawai Madhopur, Karauli and Dholpur . and merges with Yamuna at Etawah
- It is a perennial river.
- 322 km Out of total 1051 kilometre Flows in Rajasthan.
- Major tributaries are Alania Parvan Banas Kalisindh Parvati Bamani Kural Mej and Chhoti Kalisindh.
- Badland topography Due to Gully erosion.
|
Gully erosion |
|
Gully erosion is the removal of soil along drainage lines by surface water runoff. When rills (small channels formed by water flow) increase in size, they become gullies. When a gully bed is eroded further due to headward erosion, it gradually deepens and flattens out, forming a ravine. Ravines can be quite deep, extending to 30 meters or more.Over a large area, gully formation can lead to badland topography, characterized by irregular and deeply eroded landscapes. |
- Notable wildlife includes Gangetic dolphin alligator Otter
- Chambal has been included in Namami Gange Project Phase 3
- Total four dams have been constructed on it
- Gandhi Sagar Dam
- Mandsaur (Madhya Pradesh)
- First and largest dam on Chambal.
- 23×5=115 MW Hydroelectricity is produced.
- Rana Pratap Sagar Dam
- Chittorgarh
- India’s 2nd atomic energy plant
- Rajasthan atomic power station Ravat Bhatta located on it
- 43×4=172 MW Electricity is produced
- Jawahar Sagar Dam
- Borawas Kota.
- 33×3=99 MW Electricity is produced
- Kota barrage dam – kota.
- It leads into two canals –
- left canal provides irrigation facility to Kota and Bundi while right canal provides irrigation to Kota Baran and Madhya Pradesh
- Gandhi Sagar Dam
Tributaries of Chambal
- Parvati – 70 km.
- Originates from Vindhyachal range from Sehore Madhya Pradesh, flows through Baran and Kota and meets Chambal at Pal ghat,Sawai Madhopur-Kota Border.
- Its tributaries are- Andheri, Retri, Bainthli, Bilas.
- Kalisindh– 145 km.
- Originates from the hills of Bagli Village, Devas, Madhya Pradesh.
- Flows through Jhalawar-Kota- Baran and meets Chambal at Naunera ,Kota.
- Harishchandra Sagar Dam (Jaitpur,Jhalawar ) and Navnera barrage Dam (Kota) are located on it.
- its tributaries are ahu(gagron fort is situated at confluence) ,Chandrabhaga, parwan, ujaad, chouli.
- Aahu –
- Originates from Susner, Madhya Pradesh.
- Flows through Kota and Jhalawar and meets Kalisindh at Gagron, forming “Samela”here Gagron Fort is located.
- Parvan–
- Originates from Malwa Plateau Madhya Pradesh by convergence of Ajnaar and Ghodapachad Rivers.
- Flows through Jhalawar and Bara and meets Kalisindh near Ramgarh after passing through Shergarh century
- Nimaaj– Originates from Vindhyachal range from Rajgad Bhanupura Madhya Pradesh. Meets Parvan at Mavasa near Aklera.
- Chakhan– Originates from Bundi and after flowing through Bundii and Sawai Madhopur meets Chambal at Karimpur (Sawai Madhopur)
- Chakan dam has been constructed near Nainwa (Bundi).
- Mej– Originates from Bijoli and meets Chambal at Lakheri Bundi its tributaries are Bajan Kural Mangli.
- Bamani / Brahmani– Originates from Haripura Village in begun,Chittorgarh and meets Chambal near Bhainsrodgarh Fort after flowing through Neemuch Madhya Pradesh. Bamani-Banas project of 89 kilometres is proposed to bring water from Bamanii to Bisalpur Dam.
- Alania– originates from Mukundwada Hills, also called as Chandralohi River. Alania dam is constructed over it.
- Kunu– Originates from Shivpuri plant to Madhya Pradesh.
- Chandrabhaga originates from Seemli, Jhalawar, and merges with the Kalisindh River at Kadia village, Jhalawar.
- Chandrabhaga is famous for the Chandrabhaga Cattle Fair.
Namami gange project – Chambal and Mej rivers are included
Banas

- Origin: Khmanor Hills, Kumbhalgarh (Rajsamand)
- Drainage Area: Rajsamand, Bhilwara, Chittorgarh (Mewar Plain), Ajmer, Tonk, Sawai Madhopur (Malpura-Karauli Plain)
- Confluence: Joins Chambal River at Rameshwar Ghat, Sawai Madhopur
- Catchment Area: Approximately 47,000 sq. km
- With a length of 512 km and a catchment area of approximately 47,000 sq. km, Banas is the longest river flowing entirely within Rajasthan and also the longest tributary of the Chambal River.
- Also called as Varnasha, Vashisti River
- Home to Aahad civilization
- Its tributaries are – Bedach/Ayad, Menal, Kothari, Khari, Daai, Dheel, Morel, Kalisil.
- The river forms 3 Triveni sangam
- Major Dams on Banas and Its Tributaries
- Bisalpur Dam, Tonk – Largest drinking water project in Rajasthan
- Bagheri Ka Naka, Rajsamand
- Nandsamand, Rajsamand (Lifeline of Rajsamand)
- Matrikundiya Dam, Chittorgarh (Haridwar of Mewar)
- Isarda Dam, Sawai Madhopur
- Banas basin expands over districts- Bhilwara, Tonk, Jaipur, Dudu, Ajmer, Dausa, Karauli, Sawai Madhopur, Bundi, Chittorgarh, Pratapgarh, Rajsamand, Udaipur.
Tributaries of banas
- Kothari –
- Originates from Diwer Rajamand and meets banas at Nandhini Shahpura,Bhilwara.
- Meja dam is constructed on it which provides drinking and irrigation water to Bhilwara.
- Bagor civilisation excavated from its banks.
- Khari– Originates from hills of Bijal Village flows through Rajsamand, Bhilwara, Beawar and Tonk. Then meets Banas at Rajmahal (Deoli) after flowing for 80 km.
- Tributary – Mansi.
- Dams – Narayan Sagar Dam (Beawar) and Khari dam (Asind)
- Mansi– Originates from Mandalgad and meets Khaari at Phulia Kalan (Bhilwara)
- Mashi– Originates from Kishangarh (Ajmer) and after flowing through Ajmer & Tonk ;meets Banas River at Devdham, Jodhpuriya (Tonk)
- Daai– Originates from aravalli Hills of Naseerabad and meets Banas at Rajmahal(triveni) after flowing through Ajmer and Tonk
- Dheel– Tributary of Banas, originating from Baawli Village (Tonk) and flows through Tonk and Sawai Madhopur.
- Menal- Originates from Begun (Chittorgarh) and meets Banas at Bigod Triveni Sangam.
- Bedach/Aayad –
- Originates from Gogunda Hills and after flowing 190 kms through Udaipur & Chittorgarh, meets Banas at Bigod Triveni Sangam along with Menal.
- River is called Aayad Prior to Udaisagar Lake and after that it is called Bedach.
- Its tributaries are Gambhiri Gujari Arooi and Baagan.
- Dams – Madaar dam(udpr),Ghosunda dam (chittor)
- Chandrabhaga– Originates from Devado ka Gudha, Amet (Rajsamand) and meets banas at Matrikundiya
- Gambhiri– Originates from Javed Hills Ratlam Madhya Pradesh flows only through Chittorgarh and meets Bedach . Gambhir dam is constructed on it.
- Morel-Originates from hills of Chainpura Village, Bassi and flowing through Dausa and Sawai Madhopur and meets banas at Karauli Sawai Madhopur border.
- Kalisil – Originates from Saputara Karoli and meets banas at Karauli Sawai Madhopur border.
Gambhir
- Originates from hills of Nadothi Village, Saputara Karoli.
- Also called as Uttanga River in Uttar Pradesh and Parvati in Dholpur It meets Yamuna River at Rithvillage Agra.
- Tributaries are Panchna, Parvati, Khaer Machi, Ata, Bhadravati,Barkheda.
- Panchna dam is built over Panchna River (Dam is made of mud with assistance of USA)

Parvati – Originates from Chawar Hills of Karauli and meets Gambhir river at Kharagpur Dholpur, Parvati/ Angai Dam is built on it.
Rivers flowing towards Arabian Sea
These all rivers are seasonal rivers
Luni

- Originates from Nagpahad(Nag hills) Ajmer. After flowing for 495 kilometres, Disappears in run of Kutch Gujarat. Flows for 350 kilometres in Rajasthan through districts ajmer, nagaur, beawar, Jodhpur, Balotra, Barmer and Jalaur.
- Often termed as most polluted river of Rajasthan (NGT has imposed fine on state government for being unable to control river from getting polluted due to dyeing-printing industries of pali and Balotra).
- It is longest river of western Rajasthan.
- Its basin is called “Godwad region”.
- Its other names are Sagarmati (Ajmer) Saraswati, Lavanmati ,Ganga of Marwar half sweet -half salty river(after balotra), “antah salila” by kalidasa.
- Its tributaries are Jojari, Leeladi, Bandi, Guhiya, Sukhdi, Mithri, Jawai, Khari and Sagi
- Ancient civilisation site Tilwada Balotra located on its banks.
- Mallinath cattle fare is organised at Tilwara(Balotra).
Tributaries of Luni –
- JOJARI
- Originates from Pondlu Village, Nagour and meets Luni at Khejarla Khurd, Jodhpur.
- 83 kms long
- Only right side tributary of Luni.
- JAWAI
- Largest tributary of Luni. Originates from the hills of Goriya village,Pali. Meet Luni at Hemaguda Village, Barmer after flowing through Pali, Jalore, Barmer.
- Khari, Bandi and Sukdi are its tributaries
- Jawai dam (Sumerpur,Pali) is constructed on this River Which is called “Amrit Sarovar of Marwar” and is the largest dam of western rajasthan. Sei Canal brings water from Udaipur to Jawai Dam.
- Bandi River Originates from Fulad Village,Pali and meets Loni in Lakhar village. Hemawas dam is constructed on Bandi River in Pali.
- LILADI
- Originates from Jawaja, Ajmer and meets Luni in Beawar district.
- SUKRI
- Originates from Desuri,Pali and after flowing 110km through Pali, Jalor and Balotra confluences with Luni near Samdari Balotra. Bankli dam Jalore is constructed on Sukri River.
- Its tributary is Mathai River (ranakpur jain temples).
- MITHARI
- Originates from Pali and meets Luni at Mangla Village Balotra.
- SAGI
- Originates from JaswantPura, Jalore and flowing through Sanchore, meets Luni at Gandhav village Barmer.
Mahi

- Originates from Mehad Lake, Ameru Hills, Dhar District of Madhya Pradesh.
- 171 km/576 km in Rajasthan.
- Only river which crosses Tropic of Cancer twice.
- Also called as Ganga of Vagad, Ganga of Kanthal, Ganga of Tribals, Swarnrekha of South Rajasthan.
- The plain formed by Mahi River are called
- Kanthal plains in Pratapgarh, and
- Chappan plains in Banswara
- After flowing through Banswara ,Pratapgarh and Dungarpur districts of Rajasthan, it enters Gujarat and later falls into the Gulf of Cambay.
- Mahi’s tributaries Som and Jakham meet it at Navatapra, Dungarpur forming Beneshwar Dham Triveni Sangam (Kumbh of tribals, fair on Magh Purnima).
Mahi dam project
- Joint project of Rajasthan(45%) and Gujarat(55%)
- Total 140 MW hydroelectricity is generated by this project which is totally supplied to Rajasthan
- It is largest dam project of Rajasthan and includes 3 dams
1. Mahi Bajaj Sagar Dam -constructed At Borkheda, Banswara. It is longest dam of Rajasthan (3109 m long)
2. Kagdi pickup dam- Banswara
3. Kadana dam- Constructed at Rampur, Mahisagar District Gujara
Tributaries Of Mahi
- Som
- Originates from Bichhameda Hills, Rishabdev, Kherwara( Udaipur ),flows through Salumbar and Dungarpur. meets Mahi at Beneshwar Triveni sangam
- Its tributaries are Teedi, Gomti, Sarni
- Dams – 1. Som-kagdar dam @ Udaipur, 2. Som-kamla-amba dam @ pratapgarh
- Jakham
- Originates from Bawra maa Hill, Chhoti Sadri (Pratapgarh).
- Meet Mahi at Baneshwar along with Som after flowing through Pratapgarh, Salumbar and Dungarpur
- Jakham dam is constructed in Pratapgarh which is the highest dam of Rajasthan(81m), Sitamata sanctuary. Produces 5.5 MW hydroelectricity.
- Its tributaries are Karmoi and Sookli.
- Anaas
- Originates from Vindhyachal Hills of Ambor, Madhya Pradesh.
- Haran is its tributary
- Moren
- Flows through Dungarpur
- Eru
- Originates from Pratapgarh Hills and meets Mahi at Semeliya Village Banswara.
- Chaap
- Originates from Kalendra Hills Banswara.
- Bhadar
- Originates from Dungarpur and meet Mahi after Kadana Dam in Gujarat.
Sabarmati
- Originates from Padarla Hills Udaipur
- 45 km/416 km Flows in Rajasthan.
- It is the main river of Gujarat. Cities like Ahmedabad, Sabarmati, Gandhi Nagar of Gujarat are located on its banks.
- Its tributaries are Vakal, Hathmathi, Meshwa, Vetrak, Sei, Mansi,Meswa, Madhumati.
- Devas tunnel brings water from Sabarmati to lakes of Udaipur(11.6km), longest tunnel of rajasthan.
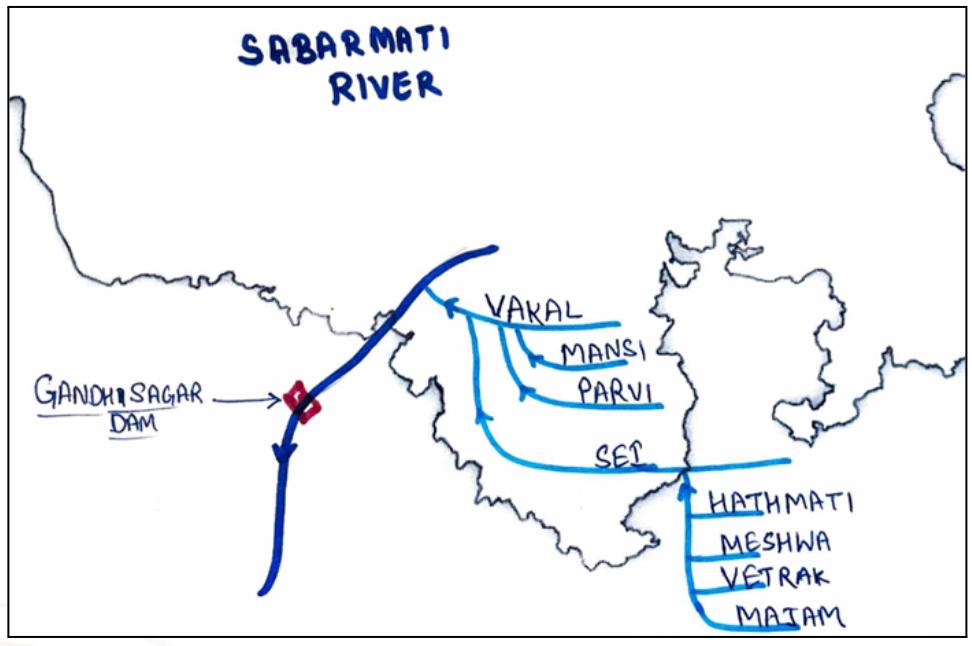
Tributaries Of Sabarmati
- Vakal
- Originates from Gogunda Hills of Udaipur. Mansi and Parviya’s tributaries.
- Water of Wacker River is brought to Udaipur City by 4.6 kilometres long water tunnel from Alsigarh to Undra ghati.
- Mansi Vakal Dam is constructed at Jhadol Udaipur.
- Sei
- Originates from Padarana Village Udaipur.
- Sei dam is constructed which supplies water to Jawai dam Sumerpur via Sei water tunnel (Rajasthan’s first water tunnel).
Western Banas / Paschim Banas
- Originates from the hills of Nia Sanada Sirohi. Flows through Gujarat and falls into Rann of Kutch.
- Its tributaries are Sukhli, Sipu, Bhataria, Suket Balram.
- Sukli Selwara project is constructed on its tributary Sukli.
- Paschim Banas Dam is constructed in Sirohi.
- Abu (Rajasthan) and Deesa (Gujarat) are located at its banks.
Rivers Of Internal Drainage System

Ghaggar River
- Ghaggar River is the longest inland river of the country.
- Originates from Kalka Hills (Shivalik Range, Shimla, Himachal Pradesh).
- Also called Ancient Saraswati, Drishdwati, Dead River, Sorrow of Rajasthan.
- Flows through Himachal, Punjab, Haryana, Rajasthan, Pakistan.
- Flow in Rajasthan – Sriganganagar(entry-Talwara Village (Tibbi, Hanumangarh)
- Home to Ancient Civilizations like – Kalibanga, Pilibanga, Rangmahal (Hanumangarh).
- drainage area is called
- Drain/Paat(Hanumangarh)
- Hakra(Pakistan)
Kantli River
- Originates from Khandela Hill (Sikar) and flows through Sikar, Jhunjhunu, Neem ka Thana,dividing Jhunjhunu into two parts
- Length :-100 km
- Tributaries are Saap, Mavat.
- It is the longest river of internal drainage which flows only in Rajasthan.
- The drainage of the Kantali river is called Toravati.
- Civilizations :-
- Ganeshwar Civilization – Neem Ka Thana (Copper Age)
- Sunari Civilization- Jhunjhunu (Iron Age)
Kakni River
- Kakni is the smallest river of internal drainage system in Rajasthan (17km)
- Also called – Kakaney River, Masurdi River
- Originates from – Kotri village (Jaisalmer)and Extincts at Mithha Khadi
- Flows only in Jaisalmer
- Kakni is the most diverted river in Rajasthan.
- Bujh Lake – It is a sweet water lake situated in Rupsi village, Jaisalmer.
Sabi/Sahibi River
- Originates from – Sewar Hills (Shahpura, Jaipur)
- Ancient civilization – Jodhpura Civilization (jaipur)
Ruparel River
- Originates from – Udainath Hills (Thanagaji, Alwar) and after flowing through Alwar, Bharatpur, Deeg; extincts at – Kushalpur village (Bharatpur)
- Also called as Laswadi River, Varaha River.
- Sikri Dam (Bharatpur) is constructed on it which supplies water to Moti Lake of Bharatpur.
Banganga River
- Originates from Bairath Hills (Kotputli- Behror)and after flowing through Jaipur Rural, Dausa, Bharatpur, Kotputli- Behror; disappears in the plains of Bharatpur
- Also called as
- Arjun ki Ganga
- Tala River
- Rundit Sarita – Due to ending before falling into the main river.
- Ancient Civilization at its banks – Bairath Civilization (Jaipur)
- Tributaries – Gumtinala, Palosan, Suri
- Major Dams –
- Lalpur Dam (Bharatpur)
- Ajan Dam (Bharatpur) – Water supply to Ghana Bird Sanctuary
- Jamwa Ramgarh Dam (Jaipur Rural) – Built by Ramsingh II. -famous for rose cultivation
Rupangarh River
- Originates from – Kishangarh (Ajmer)and after flowing through Ajmer and Jaipur falls into Sambhar Lake
- Nimbark Peeth (Salemabad, Ajmer) is situated on its bank.
Mentha River
- Originates from – Manoharpura (Jaipur)and after flowing through Jaipur, Didwana- Kuchaman,jaipur rural; falls into Sambhar Lake
Kukundu river
- Bandh baretha sanctuary (Bharatpur)
Dravyavati river
- Jaipur (Dravyavati Riverfront Project)
Modified Parbati-Kalisindh-Chambal (MPKC) Link Project (integrated with ERCP)
- Objective: Interlink rivers in the Chambal basin and integrate with the Eastern Rajasthan Canal Project for efficient water resource use.
- Part of: National Perspective Plan (NPP) for interlinking rivers in India.
- MoU Signed: 28th January 2024 (between Government of India, Rajasthan, and Madhya Pradesh).
Note: The Chief Minister of Rajasthan has renamed the Revised Parvati-Kalisindh-Chambal (PKC) Link Project as Ramjal Setu Link Project.
- Benefits in Rajasthan
Barrages and Dams:
- Ramgarh Barrage (Kul River)
- Mahalpur Barrage (Parbati River)
- Navnera Barrage (Kalisindh River)
- Mej Barrage (Mej River)
- Rathod Barrage (Banas River)
- Doongri Dam (Banas River)
- Water Conductor System
- Renovation: Isarda Dam and 26 existing tanks at various points of the ERCP.
ERCP :
- Introduced in the 2017-18 state budget to harvest surplus water from southern Rajasthan rivers and transfer it to water-deficient basins in south-eastern Rajasthan.
- Features
- Chambal Intra-Basin Water Transfer: Utilizes surplus monsoon water from Kalisindh, Parvati, Mej, and Chakan sub-basins, redirecting it to water-scarce regions such as Banas, Gambhiri, Banganga, and Parbati.
- Extensive Coverage: The project will cover 23.67% of Rajasthan’s geographical area and benefit 41.13% of its population.
- Infrastructure Development: Involves constructing barrages, dams, canals, and pumping lines to facilitate water transfer. Key structures include: Ramgarh Barrage at River Kul (Baran), Navnera Barrage at River Kalisindh (Kota), Doongri Dam at River Banas (Sawai Madhopur), Mej Barrage at River Mej (Bundi) etc.
- Phased Implementation: Initially proposed to be completed in three phases over seven years (2017-2023).
- Resource Allocation: The original DPR allocated 50% of the water for supply, 36% for irrigation, and 14% for industrial use.
- Project Cost: The recent Rajasthan budget has increased the project cost from Rs. 37,250 crore to approximately Rs. 45,000 crore.
Benefits
- Water Supply: Ensures a reliable supply of drinking and industrial water for 13 districts (expanding to 17) in Eastern Rajasthan and Malwa and Chambal regions of Madhya Pradesh.
- Benefiting Districts: Jhalawar, Baran, Kota, Bundi, Sawai Madhopur, Ajmer, Tonk, Jaipur, Karauli, Alwar, Bharatpur, Dausa, and Dholpur.
- Enhanced Irrigation: In Rajasthan, the project will provide irrigation to 2,51,000 hectares of new agricultural land and supply additional water for irrigation to 1,52,000 hectares of existing agricultural land, thereby enhancing agricultural productivity.
- Efficient Water Use: Prevents the wastage of surplus water in the Chambal basin.
- Groundwater Recharge: Includes provisions to fill existing enroute panchayat tanks, improving the groundwater table in rural areas.
- Economic Growth: Allocates water for industrial needs, including the Delhi Mumbai Industrial Corridor (DMIC).
- Water Storage: Allows for the storage of water from the Chambal river and its tributaries in dams for 100 days annually, ensuring year-round availability.
- Flood and Drought Mitigation: Helps manage flood and drought conditions in the region.
- Conjunctive Use: Enhances the availability of both surface and groundwater resources.
The ERCP will transform eastern Rajasthan by addressing water needs, supporting agriculture and industry, and boosting socio-economic conditions, thus replicating the success of the Indira Gandhi Canal Project.
Major Lakes
Salt water / brackish lakes
- Sambhar –
- Largest Natural saltwater lake of Rajasthan. created By Vasudev Chauhan (according to Bijoliya inscription) 3rd largest saltwater lake of India (1st Chilika-Odisha and 2nd Pulikat-Andra)
- Salt production is 8% of India, 80-90% of Rajasthan by Sambhar salts ltd. (Hindustan salt ltd.).
- Kayar – Method of salt production by transpiration method.
- Ramsar site (1990)- Kurja and Flamingo
- Formed by inflow of rivers Mentha, Rupangarh, Khandela and Khari.

- Rantmati Sambhar Lake Management Project, 2022 is running for management development and conservation of lake.
- Pachpadra – Balotra
- Best quality salt is produced(98% sodium chloride)
- Salt production by Khairwal caste by air flow method using Morli bush
- Deedwana
- Low quality & non edible salt is produced because of the quantity of sodium sulphate (Na2SO4) more. It is used in the textile,glass, paper, and leather industry.
- Rajasthan state chemical works – 1964
- Lunkaransar
- Bikaner
- Very less salt is produced
- Tal Chhapar
- Churu
- Called home for Black Buck
Other lakes –
- Phalodi lake
- Kavod, Jaisalmer
- Revasa lake, sikar
- Kuchoor lake, sikar
- Baap lake, phalodi

Freshwater Lakes

Jaisamand Lake / Dhebar Lake (Salumber)
- Type:
- India’s second-largest freshwater artificial lake (First – Govind Sagar, Himachal Pradesh)
- Rajasthan’s first artificial lake
- History:
- Constructed between 1685-1691 AD by Mewar Maharana Jai Singh by blocking the Gomati, Jhaveri, and Bagar rivers.
- Features:
- Contains 7 islands, the largest being Baba Ka Magra / Bhangda and the smallest being Pyari.
- Recognized as a habitat for the Bhil and Meena tribes.
- Due to its biodiversity, it is famous as an aquatic habitat.
- Nearby Attractions & Contributions:
- Ruthi Rani Ka Mahal, Chitrit Hawa Mahal, Elephant Rock Statue.
- Two canals originate from Jaisamand Lake for irrigation – Shyampura and Bhat.
- Narmadeshwar Mahadev Temple built by Maharana Jai Singh.
Pichola Lake (Udaipur)
- History:
- Constructed during the reign of Rana Lakha by Pichhu Banjara in memory of his bull at Pichhola village.
- Rivers Feeding the Lake: Sisarma and Bujhra rivers bring water into the lake (inland drainage system).
- Features:
- Contains two palaces within the lake
- Jag Mandir Palace: Located on an island, considered a precursor to the Taj Mahal. Construction initiated by Maharana Karan Singh and completed by Maharana Jagat Singh I.
- During the 1857 Revolt, Maharana Swaroop Singh sheltered British officers.
- Provided refuge to Prince Khurram (Shah Jahan) when he rebelled against his father, Jahangir.
- Jagnivas Palace: Built by Maharana Jagat Singh II.
- Jag Mandir Palace: Located on an island, considered a precursor to the Taj Mahal. Construction initiated by Maharana Karan Singh and completed by Maharana Jagat Singh I.
- Natni Ka Chabutra was built along its banks by Rana Lakha.
- Contains two palaces within the lake
| Doodh TalaiLocated between small hills, on the road leading to Lake Pichola.This small lake nestled among several low hills serves as a major tourist attraction.Nearby scenic spots:Deendayal Upadhyay Park |
Fateh Sagar Lake (Udaipur)
- History:
- Originally constructed as “Devli Talab” by Maharana Jai Singh (1678-1680 AD).
- Reconstructed by Maharana Fateh Singh (1888-1889 AD).
- Features:
- The dam is called Connaught Dam, named after the foundation laid by Duke of Connaught (a British officer).
- Contains three islands:
1️⃣ Largest – Nehru Garden
2️⃣ Second – Solar Observatory (Rajasthan’s largest and India’s first solar observatory)
3️⃣ Smallest – Jet Mountain
- Fateh Sagar Lake is connected to Pichola Lake via Swaroop Sagar Canal.
Udai Sagar-
- On Ayad/ Bedach river by blocking the flow of river.
- By Maharana Udai Singh (1559-1564).
Rajsamand
- The lake was the result of a dam constructed across the Gomati, Kelwa and Tali rivers at the southwestern end by Maharana Raj Singh I, between 1662 and 1676 AD.
- The reason for the dam and lake was to provide employment for victims of a widespread drought and famine (1661), and to provide canal irrigation to local farmers.
- Water supply by Gomati river.
- Nau-choki pal & Dwarkadhish temple are attraction points.
- Ghevar mata temple (It is believed that foundations stone of Lake was laid by Ghevar mata) is also constructed.
- Remains of SUN-DIAL found.
- Raj Singh Prasashti- 25 rock inscriptions on black marble stone, Artist was Ranchod Bhatt Telang
- As large as it is, the lake has been known to disappear in times of severe drought: for instance in 2000 it was merely a huge, empty basin with a surface of dried, cracked mud.
Nakki lake–
- CRATER/tectonic LAKE- located at Mount Abu (Sirohi).
- It is believed that it was dug by gods by their nails.
- Highest (1200m) and deepest lake(35m) of Rajasthan.
- Sacred Lake for Garasia tribe.
- Toad rock ,Nunrock , Nandi rock ,Horn rock
- Freezes in winters.
- Lake is getting polluted because of Karaghas.
Anasagar-
- It is a scenic artificial lake, commissioned and built by Arnoraj Chauhan, son of Ajaypal Chauhan, between 1135 and 1150 AD.
- Mughal Emperor Jahangir added his touch to the lake by laying out the Daulat Bagh Gardens near the lake.
- Emperor Shah Jahan too, contributed to the expansion by building five pavilions, known as the Baradari, between the garden and the lake.
- Water supply is done by Bandi river.
Pushkar–
- crater/volcanic lake- Ajmer।
- Also called as -Panchva tirath,Tirthon ka mama
- Crescent shaped।
- 52 ghats।
- Largest natural freshwater lake of rajasthan।
- “RANGEELA MELA”-Kartik Purnima.
Foy Sagar Lake / Varun Sagar (Ajmer)
- Built in 1892 AD by British engineer Mr. Foy.
- Constructed as a famine relief project to provide employment and support to people during a drought.
Silisedh-
- Situated in Alwar,
- Construction by Vinay Singh
- Located on golden triangle
- Called as “Nanden Kanan”
Ramgarh–
- Baran
- Crater lake- 200th crater
- One of the “geoheritage site” of Rajasthan
Badi Lake
- Surrounded by three chhatris, the Badi Lake is one of the finest fresh water lakes in the country.
- It is an artificial lake that was built by Maharana Raj Singh to help the city counterbalance the devastating effects of drought. He named the lake Jiyan Sagar after his mother Jana Devi.
- During the drought of 1973, the lake proved to be a blessing for the people of Udaipur.
ANAND SAGAR LAKE
- This artificial lake, also known as Bai Talab was constructed by Lanchi Bai, the Rani of Maharaval Jagmal Singh.
- Located in the eastern part of Banswara, it is surrounded by holy trees known as ‘Kalpa Vriksha’, famous for fulfilling the wishes of visitors.
Dialab Lake (Banswara)
- Located on the Jaipur road near Banswara city, this lake is known for its natural beauty.
- The Hanuman Temple on its banks makes it a center of religious faith, attracting devotees throughout the year.
BALSAMAND LAKE
- Built in 1159 AD, it was planned as a water reservoir to cater to Mandore. The Balsamand Lake Palace was built on its shore later as a summer palace.
Kaylana Lake (Jodhpur)
- Built in 1872 AD by Maharaja Sir Pratap Singh as a famine relief project.
- A section of the lake is known as Takht Sagar.
- The Machiya Biological Park, India’s first desert botanical garden, is located on its shore.
Kolayat Lake (Bikaner)
- Kapil Muni Fair is held here on Kartik Purnima.
- Deep Dan (lamp offering) tradition similar to Pushkar Lake.
- The abundance of Peepal trees creates a dry desert garden-like atmosphere.
- Charan community does not visit this lake for religious reasons.
Gajner Lake (Bikaner)
- Mirror-like reflection – The Gajner Palace is beautifully reflected in the lake.
- Gajner Wildlife Sanctuary – Famous for Batbad birds (Demoiselle Cranes).
Other Freshwater Lakes of Rajasthan
| Lake Name | Location |
| Talwara Lake | Hanumangarh |
| Tal Chhapar Lake | Churu |
| Navlakha Lake | Bundi |
| Dugari/Kanak Sagar | Bundi |
| Gaib Sagar | Dungarpur |
| Manasarovar | Jhalawar |
| Kodila | Jhalawar |
| Peethampuri | Sikar |
| Jait Sagar | Bundi |
| Ram Sagar | Dholpur |
| Talab Shahi | Dholpur |
| Mool Sagar | Jaisalmer |
| Amar Sagar | Jaisalmer |
| Gajroop Sagar | Jaisalmer |
| Gadsisar | Jaisalmer |
| Pannashah Talab | Jhunjhunu |
Major Rivers and Lakes / Major Rivers and Lakes / Major Rivers and Lakes / Major Rivers and Lakes / Major Rivers and Lakes / Major Rivers and Lakes / Major Rivers and Lakes / Major Rivers and Lakes / Major Rivers and Lakes / Major Rivers and Lakes / Major Rivers and Lakes / Major Rivers and Lakes / Major Rivers and Lakes / Major Rivers and Lakes / Major Rivers and Lakes / Major Rivers and Lakes / Major Rivers and Lakes / Major Rivers and Lakes / Major Rivers and Lakes / Major Rivers and Lakes / Major Rivers and Lakes / Major Rivers and Lakes / Major Rivers and Lakes / Major Rivers and Lakes
