Agriculture, Horticulture and Animal Husbandry form the backbone of the primary sector and play a crucial role in ensuring food security and rural livelihoods. These allied activities support sustainable development by providing employment, nutrition, and raw materials for agro-based industries. Together, they contribute significantly to economic growth and balanced rural development.
Agriculture horticulture and animal husbandry
Agriculture Development in Rajasthan
Agriculture institutions
|
Name of Institution / Centre |
Location & Establishment Details |
|
Central Arid Zone Research Institute (CAZRI) |

|
|
Arid Forest Research Institute (AFRI) |
|
|
National Research Centre on Rapeseed-Mustard |
|
|
Central Wool Development Board (CWDB) |
|
|
Central State Farm, Suratgarh |
|
|
Central Institute for Arid Horticulture (CIAH) |
|
Other Agriculture institutions
| Central Sheep & Wool Research Institute (CSWRI) | Avikanagar (Tonk) – 1962 |
| Central Institute for Research on Goats (CIRG) | Avikanagar (Tonk) – 1962 |
| Sheep and Wool Training Institute | Jaipur |
| Sheep Disease Research Laboratory | Jodhpur |
| NBPGR Regional Station (National Bureau of Plant Genetic Resources) | Jodhpur |
| National Research Centre on Seed Spices (NRCSS) | Tabiji, Ajmer – Established 2000 |
| Rajasthan Poultry Research & Training Institute | Ajmer – 1988–89 |
| Central Agricultural Research Station (IARI Regional Station) | Durgapura, Jaipur – 1943 |
| Central State Farm – 2, Jaitsar | Jaitsar, Ganganagar – With assistance from Canada |
| Ber & Date Palm Research Centre | Bikaner – 1978 |
| Bull Rearing Centre | Nagaur |
| Central Wool Testing Laboratory | Bikaner – 1965 |
| Sheep Breeding Farm (Merino Breed Production Centre) | Fatehpur, Sikar – 1973; Produces “Merino Breed” |
| National Research Centre on Camel (NRCC) | Johadbeed, Bikaner |
| Cotton Research Station | Sri Ganganagar |
| Central Livestock Breeding Farm (CLBF) | Suratgarh (Ganganagar) |
| Fodder Seed Production Farm | Mohangarh (Jaisalmer) |
| Pearl Millet (Bajra) Research Centre | Barmer |
| Sorghum (Jowar) Research Centre | Vallabhnagar (Udaipur) |
| Rice Research Centre | Banswara |
| Maize Research Centre | Banswara |
| Rajasthan State Institute of Educational Research & Training (SIERT) | Udaipur |
| Manikya Lal Verma Tribal Research & Survey Institute | Udaipur |
| National Bureau of Soil Survey & Land Use Planning (NBSS&LUP) – Western Regional Centre | Udaipur |
| Buffalo Breeding Centre | Vallabhnagar (Udaipur) |
| Anthropological Survey of India – Western Regional Centre | Udaipur |
| India Meteorological Department Observatory | Jaipur |
| National Institute of Ayurveda (NIA) | Jaipur |
| Central Electronics Engineering Research Institute (CEERI) | Pilani (Jhunjhunu) |
| National Pig Farm | Alwar |
| Ceramic Electrical Research & Development Centre (CERDC) | Bikaner |
| Goat and Fodder Research Center | Ramsar (Ajmer) |
| Buffalo Breeding and Research Center | Vallabhnagar (Udaipur) |
| Fisheries Survey and Research Center | Udaipur |
| Wildlife management and desert ecosystem training institute | Tal Chhapar, Churu |
| Millet Research Center | Mandore (Jodhpur) |
| Maize Research Center | Bosawat (Banswara) |
| Rice Research Center | Banswara |
| Isabgol Research Center | Mandore (Jodhpur) |
| Rajasthan Agricultural Research Institute (RARI) | Durgapura (Jaipur)1943 |
| Agricultural Research Center (ARC) | Bikaner |
| Chaudhary Charan Singh National Institute of Agricultural Marketing | Jaipur |
| Rajasthan State AYUSH Research Center | Ajmer |
| Central Dry Area Horticulture Research Center (NRCAH) | Beechwal (Bikaner) |
| Rye Research Center | Sewar (Bharatpur) |
| Medicinal Plant Research Center | Mount Abu (Sirohi) |
| Irrigation Management and Training Institute | Kota |
| Agro-ecology Tourism and International Flower Research Center | Mount Abu (Sirohi) |
| Goat Development and Pasture Production Project | Ramsar, Ajmer – With support from Switzerland |
Livestock Breeding and Research Centers in Rajasthan
- Harit Muniya Breeding Center – Udaipur
- Sheep Breeding Center: Fatehpur (Sikar). One unit of this center is located in Bankaliya (Didwana Kuchaman).
- Buffalo Breeding Center: Dag (Jhalawar), Kumher (Deeg)
- Horse Breeding and Research Center: Keru (Jodhpur
Center of excellence in Rajasthan
| Center of excellence | Location |
| Citrus | Nanta, kota |
| Pomegranate | Bassi, Jaipur |
| Date Palm | Sagra Bhojka, Jaisalmer |
| Guava | Devrawas, Tonk |
| Orange | Jhalawar |
| Mango | Khemri, Dholpur |
| Vegetables | Bundi |
| Flowers | Sawai Madhopur |
| Custard Apple | Chittorgarh |
| Dates (खजूर) | Sagara Bhojka (Jaisalmer) |
| Papaya | Dausa |
| Fig | Sirohi |
| Maize | Banswara |
| Rare earth elements | Udaipur |
| Medical genetics | JK loan Hospital Jaipur |
| Mati kala | Jaipur |
| Olive | Bassi Jaipur |
| Blockchain Technology | Bhamashah Data Centre, Jaipur. |
| Dr. Ambedkar CoE | Rajasthan university |
| Internet of things | Swami keshwanand institute of technology Jaipur |
| Ceramics | Bikaner |
| Millets | Jodhpur agriculture university |
| Swayamsiddha | Jaipur |
| Vastu and Astrology | Jaipur |
| Apiculture | Bharatpur |
| Millet | Jodhpur |
Horticulture Development in Rajasthan
- Separate Directorate of Horticulture established in 1989–90.
- Headquarter – Jaipur
- Purpose – To increase area, production, and productivity of Fruits, Vegetables, Spices, Flowers, Medicinal plants. To exploit Rajasthan’s large potential for horticulture
- 1990–91: State schemes and centrally assisted schemes started.
- 1992–93: World Bank-assisted Agricultural Development Project launched.
- An international level Date Tissue Culture Laboratory has been established at Jodhpur.
Horticulture Development Schemes
National Horticulture Mission (NHM)
- To increase the area, production and productivity of different horticulture crops like fruits, spices and flowers.
- This scheme is being implemented in selected 31 districts.
Rashtriya Krishi Vikas Yojana (RKVY)
- The scheme includes initiatives such as date palm cultivation, horticulture development in districts lacking NHM support and vegetable clusters in urban areas.
- It also focuses on strengthening centers of excellence in Jhalawar, Dholpur, Tonk, Bundi, Chittorgarh, Sawai-Madhopur, Bassi (Jaipur) and Nanta (Kota) for promoting protected farming and developing nurseries.
Rajasthan Govardhan Jaivik Urvarak Yojana (2024)
- Objective – To promote organic farming in Rajasthan by encouraging farmers to produce organic manure/fertilizer.
- Key Feature – One-time financial assistance is provided to farmers.
- Subsidy is given for setting up units to produce organic manure/fertilizer.
- Farmers receive ₹10,000 or 50% of the unit cost, whichever is lower.
- Launch Year – 2024
Rajasthan Pashudhan Bima Yojana / Mukhyamantri Mangala Pashu Bima Yojana (2024)
- Objective – To protect livestock owners from financial losses due to the death or disease of animals and to improve animal health.
- Key Features – Free insurance coverage for all livestock of the state.
- Free vaccination for all insured animals.
- Coverage available for dairy animals and other livestock species.
- Aims to reduce economic vulnerability of livestock farmers and increase productivity.
- Beneficiaries – Livestock rearers/cattle owners in Rajasthan.
- Launch Year – 2024
Rajiv Gandhi Krishak Saathi Sahayata Yojana (Compensation Details)
- Objective – To provide financial assistance to farmers in cases of accidents.
- Benefits – ₹2,00,000 in case of accidental death.
- ₹5,000 to ₹50,000 in case of disability (depending on severity and disability level).
Knowledge Enhancement Program
- 100 farmers of Rajasthan will learn the tricks of farming in these 4 countries.
- Under the program, FPO farmers will visit the Netherlands, Australia, New Zealand and Brazil.
- The tour will start from November 2025.
- Ten farmers each from ten agricultural divisions were selected from the state for the seven-day tour.
- In this exposure visit, farmers will get information about the latest technologies and innovations.
- Selected farmers were trained in different batches between November 2025 to March 2026.
- During the tour, farmers will learn how to do better farming and animal husbandry in polyhouse and off season in less land and less water.
Agriculture in Rajasthan
- Agriculture in Rajasthan is mainly dependent on rainfall. Since the state receives insufficient and inadequate rainfall due to weak monsoon, therefore agriculture production is also affected.
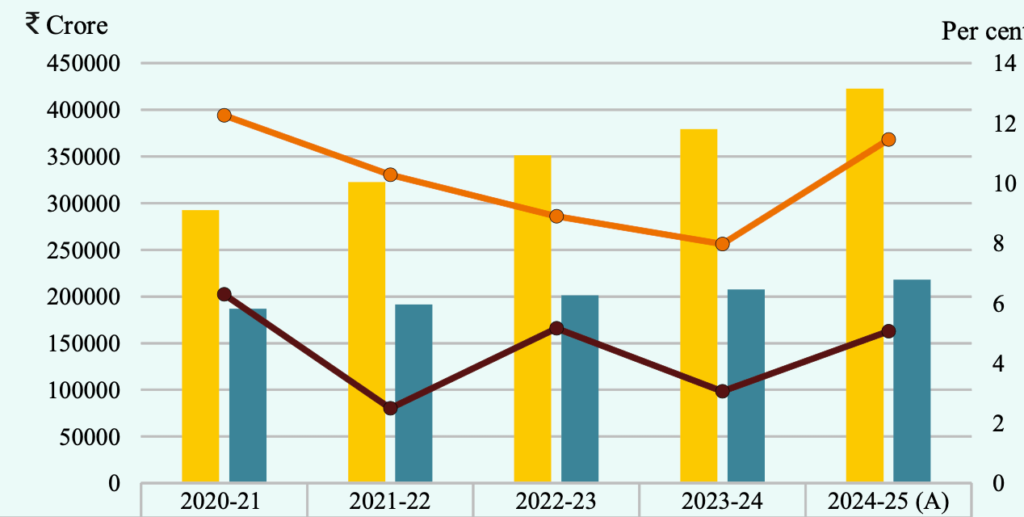
- Contribution of Agriculture in GSVA (Gross State Value Added) – Rajasthan
- At Constant Prices (2011-12): 26.54%
- At Current Prices: 26.92% (Higher than the all-India contribution of 17.77% in this sector)
- Key Observation:
- The agricultural sector’s value has increased from ₹1.19 lakh crore in 2011-12 to ₹2.18 lakh crore in 2024-25.
- This reflects a Compound Annual Growth Rate (CAGR) of 4.76% at constant (2011-12) prices.
- Agriculture and allied sectors remain key constituents of the State economy.
- Rajasthan with 10 agro-climatic zones has the potential to produce a wide variety of food grains, cash crops and horticulture crops.
Old vs New Agro-Climatic Zones of Rajasthan
| Zone / Region | Old Districts | New Major Districts |
| Arid Western Region | Barmer, parts of Jodhpur | Barmer, Jalore |
| Irrigated Region | Sri Ganganagar, Hanumangarh | Sri Ganganagar, Hanumangarh |
| Partially Irrigated Region | Bikaner, Jaisalmer, Churu | Bikaner, Churu |
| Inland Drainage Region | Nagaur, Sikar, Jhunjhunu | Sikar, Jhunjhunu, Jaipur |
| Luni Basin Region | Jalore, Pali, Sirohi | Ajmer, Pali, Sirohi city, Revdar, Shivganj |
| Arid and Semi- Arid Region | (New Zone) | Jodhpur, Nagaur, Jaisalmer |
| Flood-Prone Region | Alwar, Dholpur, Karauli, Bharatpur, Sawai Madhopur | These 5 + Tonk + Ajmer |
| Sub-Humid Region | Udaipur, Sirohi, Bhilwara, Chittorgarh | Udaipur, Bhilwara, Chittorgarh, Rajsamand, Sirohi (only Abu Road & Pindwara) |
| Humid Region | Dungarpur, Banswara | Dungarpur, Banswara |
| Humid Hadoti Region | Kota, Jhalawar, Baran, Bundi | Kota, Baran, Bundi, Jhalawar, Pratapgarh |
Major Changes in Agro-Climatic Zones of Rajasthan
- Tonk and Dausa have been shifted to the Flood-Prone Zone, and removed from the Arid & Semi-Arid Zone.
- Jaipur has been included in the Inland Drainage Zone along with Sikar and Jhunjhunu.
- Sirohi has been divided into two zones, allowing maize cultivation recommendations in the hilly/mountain areas.
- Udaipur and Chittorgarh’s rice-growing areas have been excluded from their earlier zone.
- Due to the presence of the Narmada River canal, Barmer-Jalore now has a separate climatic identity, distinct from Godwar region (Pindwara, Abu Road etc.).
- In the Hadoti region, Pratapgarh has been added. Now, crops like mustard, soybean, and jowar will also be recommended here.
- The extremely arid zone of Jaisalmer has now been merged with new clusters of Jodhpur and Nagaur.
- In the year 2024-25, Agriculture and allied sectors contributed to 26.92 % of Rajasthan’s Gross State Value Added (GSVA) at current prices which was 28.56 % in the year 2011-12.
Sectoral Contribution of Agriculture Sector at Current Prices
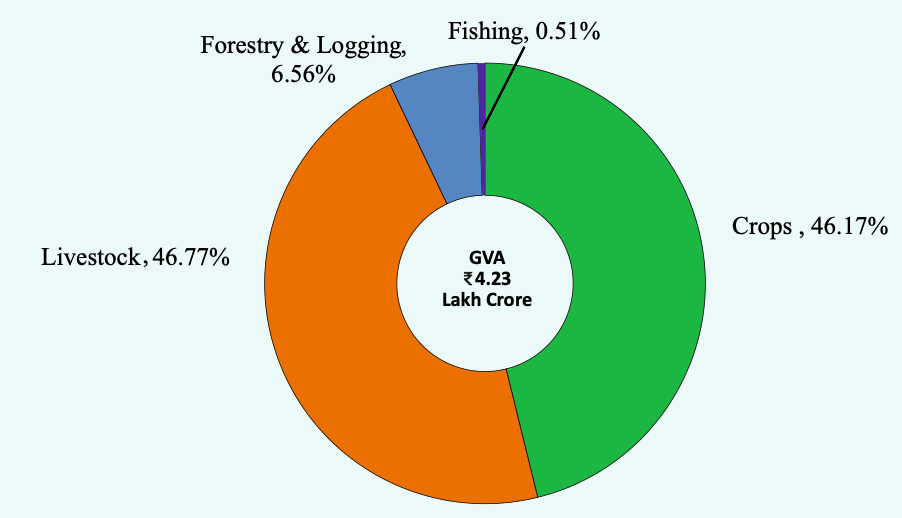
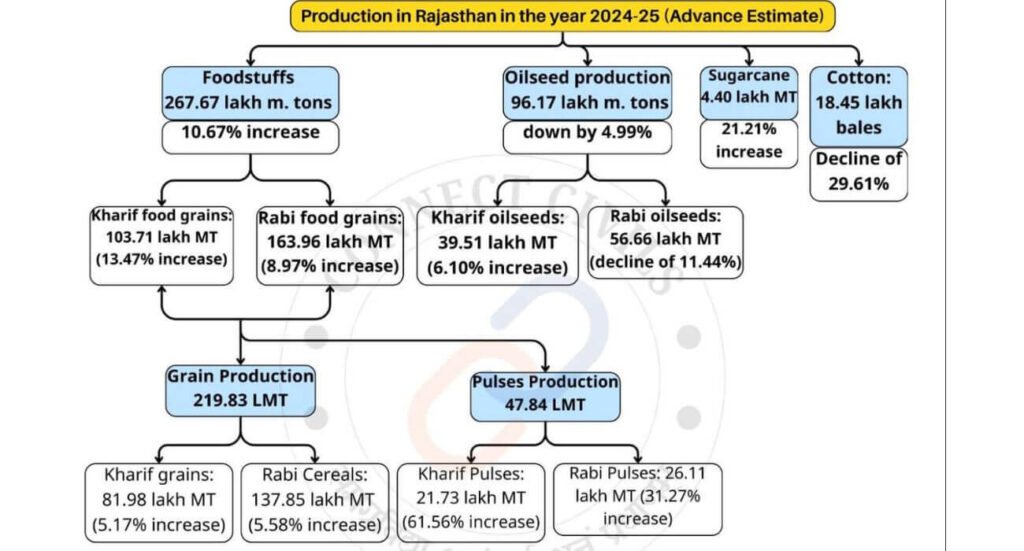
Production of Kharif and Rabi Crops in the State
- As per advance estimates for the year 2024-25, the total food grain production in the State is expected to be 267.67 lakh tonnes with an increase of 10.67 % as compared to previous year.
- The kharif food grain production in the year 2024-25 is expected to be 103.71 lakh tonnes (increase of 13.47 %)
- Production of kharif cereals for the year 2024-25 is expected to be 81.98 lakh tonnes compared to 77.95 lakh tonnes for the previous year representing a growth of 5.17 %.
- The production of Kharif pulses is estimated to be 21.73 lakh tonnes in the year 2024-25
- The production of oilseeds in the year 2024-25 are estimated at 96.17 lakh tonnes against 101.22 lakh tonnes for the year 2023-24, with a decrease of 4.99 per cent.
- Production of Sugarcane is estimated 4.40 lakh tonnes in the year 2024-25 as against 3.63 lakh tonnes for the year 2023-24, with an increase of 21.21 %.
Comparative Position of Rajasthan in Major Agriculture Crops
| Crop | Rank of Rajasthan | Contribution (%) |
| Rapeseed & Mustard | 1st | 46.13% |
| Bajra | 1st | 44.66% |
| Total Oilseeds | 1st | 22.78% |
| Nutri-Cereals | 1st | 15.66% |
| Guar | 1st | 90.36% |
| Groundnut | 2nd | 18.76% |
| Jowar | 3rd | 14.87% |
| Gram | 3rd | 14.75% |
| Total Pulses | 3rd | 13.88% |
| Soyabean | 3rd | 8.05% |
Budget 2025-26 for agriculture
- A Mini Food Park will be established in Anupgarh (Sriganganagar).
- Agro Food Park in Sanchore (Jalore).
- The agricultural produce markets proposed in the budget are Bidasar (Sujangarh, Churu), Bhinay, Rupangarh (Ajmer), Tapukda (Khairthal Tijara), Ramgarh Pachwara (Dausa), Nawan, Khatu Khurd (Didwana Kuchaman), Simalwara (Dungarpur) and Rajakheda (Dholpur)
- Mandi/Centre of Excellence – Location
- Fruit-Vegetable Mandi – Jaitaran (Byavar), Sirohi
- Subordinate Agricultural Mandi – Banetha (Tonk), Mandar (Sirohi)
- Garlic Centre of Excellence – Baran
- It is also proposed in the budget to organize Global Rajasthan Agri-Tech Meet (GRAM) in the coming year.
- Under the Gopal Credit Card Scheme, 2.50 lakh cow-rearing families will be provided interest-free loans.
- Purchasing-selling cooperative societies will be established in the newly established 8 districts.
- Under Mahatma Jyotiba Phule Mandi Shramik Kalyan Yojana, it has been proposed in this budget to increase the assistance amount for marriage up to the limit of two daughters of licensed workers from ₹ 50 thousand to ₹ 75 thousand per marriage.
Other news in current affairs
- For the conservation and promotion of indigenous animals, the state’s first Centre of Excellence Indigenous Farm will be established in Pali. (Amount: ₹10 crore).
- Taking inspiration from Prime Minister Narendra Modi’s concept ‘Catch the Rain’, it is proposed to construct 5000 water recharge structures through CSR under the ‘Karmabhoomi se Mathrubhumi’ campaign.
- Residential school for migrant animal herders will be opened in Rajsamand.
- New conservation reserve in Mokla Parevar – Jaisalmer and Vuchara Man-Jaipur
- Establishment of a biological park in Bharatpur and works will be done in biological park, Nahargarh-Jaipur.
- For better conservation of the state bird Great Indian Bustard, various works will be done in a 2 thousand hectare area in National Desert Park-Jaisalmer.
Budget 2025-26 for Animal husbandry
- New Bypass Protein Animal Feed Plants will be set up in Rajsamand (Nathdwara) and Udaipur.
- Centre of Excellence-Rajasthan Institute of Veterinary Sciences Polyclinic, Panchbatti (Jaipur)
- ‘Eye Care Specialty Center’ for Animals – Hingonia, Jaipur and Rajuvas Bikaner
- Animal Prosthetic Centre – Multipurpose Animal Hospital, Sanganer.
- ‘Sex Sorted Semen Lab’ will be established in Bassi (Jaipur).
- Mukhyamantri Mangala Pashu Bima Yojana: double the number of insured livestock farmers in each category by expanding the scope of this scheme.
- 10 lakh livestock farmers will be benefited by giving 75% subsidy on the first two AIs (Artificial Insemination) for “Sex Sorted Artificial Insemination” and 50 percent subsidy for the remaining 2 AIs.
- New milk plants will be set up in Alwar, Udaipur, Banswara, Bharatpur and Sawai Madhopur.
- Under ‘Mukhyamantri Dugdh Utpadak Sambal Yojana’ A target of 13 thousand lakh liters has been set for milk collection.
- Animal Grant: It has been announced that the grant per animal for the Gaushalas and Nandishalas operating in the state will be increased by 15% to ₹ 50 per day.
Livestock for Prosperous Farming
The State, animal husbandry is not merely a subsidiary to agriculture but it is a major economic activity, especially in arid and semi-arid areas.
- The livestock Census-2019 placed total livestock population of the State at 568.01 lakh and poultry birds at 146.23 lakh.
- The State is home to about 10.60 per cent of the livestock of the country.
- It accounts for about 7.24 percent of cattle, 12.47 per cent of buffaloes, 14.00 per cent of goats, 10.64 per cent of sheep and 84.43 per cent of camels of the country.
- The State contributed 14.44 per cent of milk and 47.98 per cent of wool to the nation’s production in the year 2022-23.
Livestock Development
Focuses on improving animal health, productivity, and welfare through various government schemes and initiatives
- Foot-and-Mouth Disease Control Program: An intensive vaccination campaign led to the administration of free disease prevention (FMD vaccines) to 200.13 lakh cows and buffaloes across the State.
- Sex Sorted Semen Scheme: The subsidy for improving milch animal breeds increased from 50 percent to 75 percent, benefiting approximately 2 lakh cattle farmers.
- Pashumitra Yojana: It aims to deliver animal husbandry services such as tagging, vaccination, insurance, artificial insemination for improving the breed of animals, pregnancy testing etc. directly to farmers’ doorsteps. Under this scheme, 5,000 young unemployed trained livestock assistant will be provided fixed honorariums, based on their work performance.
- Camel Conservation Grant provides financial assistance of ₹20,000 in two installments (for each calf newborn at 0-2 months of age and at 1 year of age) to camel farmers.
- Livestock Free Health Scheme (Pashudhan Nishulk Aarogya Yojana) provides free treatment for livestock through veterinary institutions and camps.
Livestock farmer’s welfare initiatives
National Livestock Mission (NLM)
- It is an Entrepreneurship Development Program, with the aim of motivational animal farmer to establish enterprises in the field of Animal Husbandry.
Raj Saras Suraksha Kavach Bima Yojana (8 th Phase):
- A personal accident insurance scheme has been implemented with effect from 1 st February, 2024 Under this scheme a sum of ₹5.00 lakh is payable in case of accidental death/total permanent disability and ₹2.50 lakh in case of partial permanent disability. 1,53,508 milk producers have been insured under this scheme.
Chief Minister Dugdh Utpadak Sambal Yojana:
- Under this scheme grant in aid has been increased from ₹2 per liter to ₹5 per liter to the milk producers in the year 2022-23.
PM Kisan Yojana:
- Farmers across India get ₹6,000 per year from the Central Government.
- Rajasthan’s Addition (2025 Budget by FM Diya Kumari): State government will give ₹3,000 extra to farmers.
- Total Benefit for Rajasthan Farmers: ₹9,000 per year (₹6,000 from Centre + ₹3,000 from State).
Rajasthan Mahatma Jyotiba Phule Mandi Shramik Kalyan Yojana
- Prasuti Sahayata (Maternity Assistance)
- 45 days wage loss to license holder women labourer will be compensated financially during pregnancy.
- 15 days wage loss will be compensated to male beneficiaries.
- Benefits applicable for two deliveries.
- Medical Reimbursement
- ₹20,000 medical expenses reimbursed by the Government.
- Applicable for serious illnesses like Cancer, Heart Attack, etc.
- Marriage Assistance
- ₹75,000 assistance for marriage of female Hammal or Palledar (earlier 50,000)/or marriage of two daughters.
- Application mandatory at least 90 days before marriage.
Pradhan Mantri Dhan Dhanya krishi yojna:
- Approved on July 16, 2025, the scheme targets 100 low-performing agri-districts with an annual outlay of ₹24,000 crore for 6 years.
- It aims to enhance productivity, promote crop diversification, improve irrigation and storage, and ensure credit access. The focus will be exclusively on agriculture and allied activities.
- The scheme ensures saturation-based convergence of 36 schemes from 11 ministries, benefiting 1.7 crore farmers directly.
- District-level plans will be prepared by district collectors with support from agricultural universities and NITI Aayog.
- A digital dashboard, farmer app, and district ranking system will ensure transparency, access, and accountability.
- The convergence will also include state schemes and local partnerships with the private sector. Rather than introducing new schemes, PMDDKY ensures coordinated delivery of existing programmes to the last-mile farmer, avoiding duplication and enhancing impact.
- The scheme identifies 100 districts based on:
- Low productivity
- Low cropping intensity
- Less credit disbursement
- Each selected district under PMDDKY will establish a District Dhan-Dhaanya Krishi Yojana (DDKY) Samiti, chaired by the District Collector or Gram Panchayat.

Gopalan Department
- The State promotes the conservation and development of native cattle breeds, focusing on sustainable growth through gaushalas and Nandishalas under the Govansh Sanrakshan and Samvardhan Nidhi Rules, 2016
Gaushala Development Initiatives
Gaushala Vikas Yojana:
- State Government is providing financial assistance of maximum ₹10 lakh on 90:10 (Government:Public) basis, for the development of basic infrastructure (Cattle shed, fodder store, Gopalak Awas Grih, water tank etc.) in registered Goshalas.
Panchayat Samiti Stariye Nandishala Jan Sahbhagita Scheme
- Aimed at addressing stray male cattle issues, by establishing Nandishalas at the Panchayat Samiti level with a funding ratio of 90:10 from government and public contributions.
Gram Gaushala/Pashu Ashraya Sthal Jansehbhagita Scheme
- This scheme focuses on sheltering stray animals by establishing Gaushalas or Pashu Ashray Sthals at the Gram Panchayat level, with an estimated setup cost of ₹1 crore (90:10 funding).
Dairy Development
- Up to December 2024, a total of 19,054 Dairy Cooperative Societies have been affiliated with 24 District Milk Producers’
- Cooperative Unions a State level Apex Body – Rajasthan Cooperative Dairy Federation (RCDF) Limited, Jaipur.
Developed hybrid varieties
- Wheat = Lal Bahadur, Raj 1482, Raj 3077, Raj 3765, Raj 3777, Raj 4037, Raj 4079, Raj 4083, Raj 4120, Raj 4238, Raj Molya Rodhak-1, MG Nabi, Lerma , Kalyan sona, Malvika, Kohinoor, Chambal-65
- Barley = RDB-1, BL-2, Rajkiran, RD 2035, RD 2552, RD 2503, RD 2668, RD 2624, RD 2660, RD 2715, RD 2786, RD 2794, RD 2849, RD 2899, RD 2907, Kailash, Kedar, karan, Jyoti
- Pearl Millet (Bajra) = Raj 171, RHB 90, 121, 127, 154, 173, 177, 223, 228, 233, 234 Nutrition twins = 233 & 234 (bio-fortified).
- Muskmelon = Durgapura Madhu, RM 50, MHY 3, MHY 5
- Watermelon = Durgapura Kesar, Durgapura Lal “
- Rice – Basmati, Mahi Sugandha, Parmal, Padma, Jamuna
- Sugarcane – CO-1007, CO-1111
- Maize – Mahi kanchan, Mahi dhawal, Arun, Parbhat, HM-8
- Thar Shobha – Khejri