In Rajasthan Geography, vegetation is classified into distinct types shaped by the state’s arid and semi-arid climate. These include Tropical Thorny/Xerophyte Forest, Tropical Dhonk Forest, Tropical Dry Deciduous/Monsoon Forest, Tropical Teak Forest, and Sub-Tropical Evergreen Forest, primarily distributed across the Thar Desert, Aravalli hills, and southeastern regions.
Previous Year Question
|
Year |
Question |
Marks |
|
2018 |
Explain suitable production conditions of Maize and its main production areas inRajasthan.राजस्थान में मक्का उत्पादन के लिए उपयुक्त दशाओं तथा इसके प्रमुख उत्पादन क्षेत्रों को स्पष्ट कीजिए । |
5 M |
|
2016 |
What do you mean by ‘ Walra’ ?‘वालरा’ से आपका क्या आशय है ? |
2 M |
|
2013 |
Divide Rajasthan into Agro-climatic regions and describe any one in detail.राजस्थान को कृषि-जलवायु क्षेत्रों में विभाजित कीजिए तथा किसी एक का सविस्तार वर्णन कीजिए । |
20 M |
Major Vegetation Types
- National forest policy-1894, 1952
- National forest policy-1988- Targets for forests
- 33% of geographical area
- 60% of mountainous area
- 20% of plains
- State forest policy 18 feb, 2010- targets 20% of state’s geographical area
- State ecotourism policy (1st – 4 feb 2010) (2nd – 15 July 2021)
Forest policy 2023
- Targeted vegetation cover- 20% increase in 20 years (2053)
- Wildlife and biodiversity protection
- Ecological security
- 3R- Reforestation, restoration, rehabilitation measures
- Prevent land degradation and desertification
- Conserve and promote flora and fauna diversity
- Ex-situ, in -situ and circum-situ measures
- Management of biodiversity rich ecosystem viz-grasslands, wetlands, sacred groves and deserts
- Stakeholder participation –to ensure long term sustainability
Forest Report -18th (2023)
- Released on December 21, 2024 by Forest Survey and Research Institution, Dehradun (Uttarakhand)
For India :-
- The forest and tree cover -25.17% (8,27,357 sq. km.) – increased by 1445 sq. km.
- Forest cover – 21.76% (7,15,343 sq. km.) – increase of 156 sq. km
- Tree cover – 3.41% (1,12,014 sq. km.) – increase of 1289 sq. km
- In the current assessment, the total carbon stock in the country’s forests has been estimated at 7,285.5 million tonnes (increase of 81.5 million tonnes as compared to the previous assessment)
Rajasthan secured place in top four states showing maximum increase in forest and tree cover –
- Chhattisgarh (684 sq. km.)
- Uttar Pradesh (559 sq. km.)
- Odisha (559 sq. km.)
- Rajasthan (394 sq. km.)
For Rajasthan:-
- Recorded forest area -9.60%( 32921 sq km)
- Tree and Forest cover – 8.0% (27389.33 sq km ) – 394.46 sq km increase
- Forest cover- 4.84% (16548.21 sq km) – 83.80 sq km decline
- Tree Cover- 3.16% (10841.12 sq km) – 478.26 sq km increase
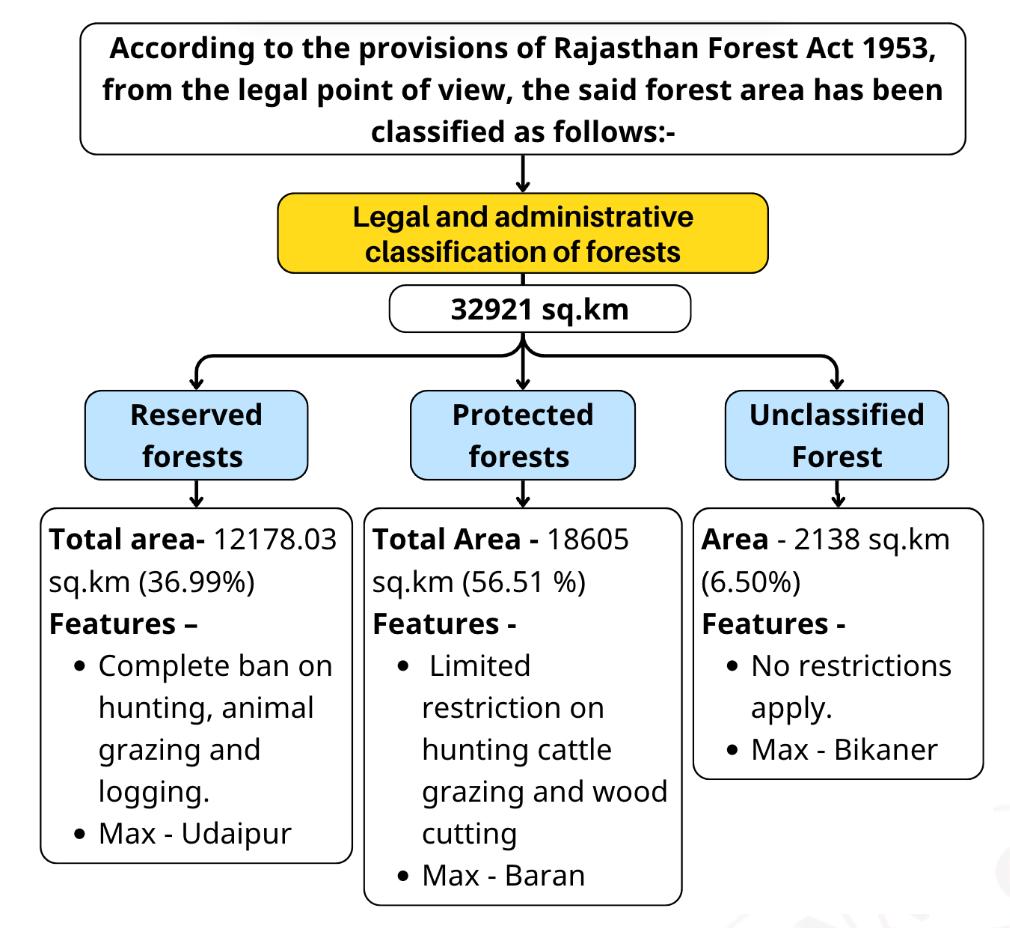
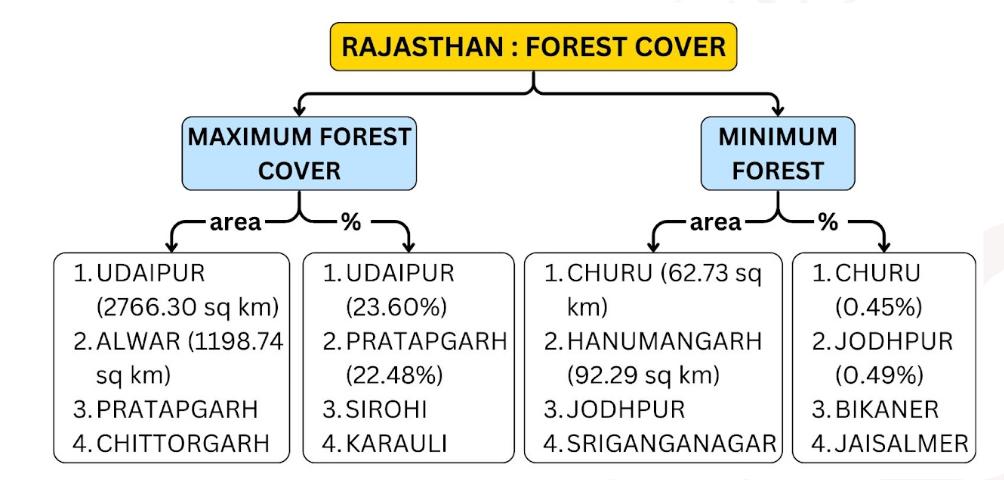
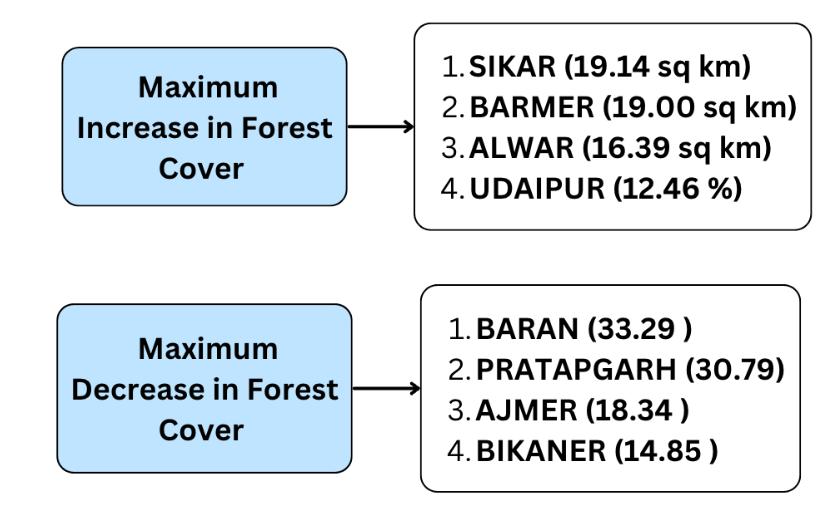
Geographical Classification Of Vegetation
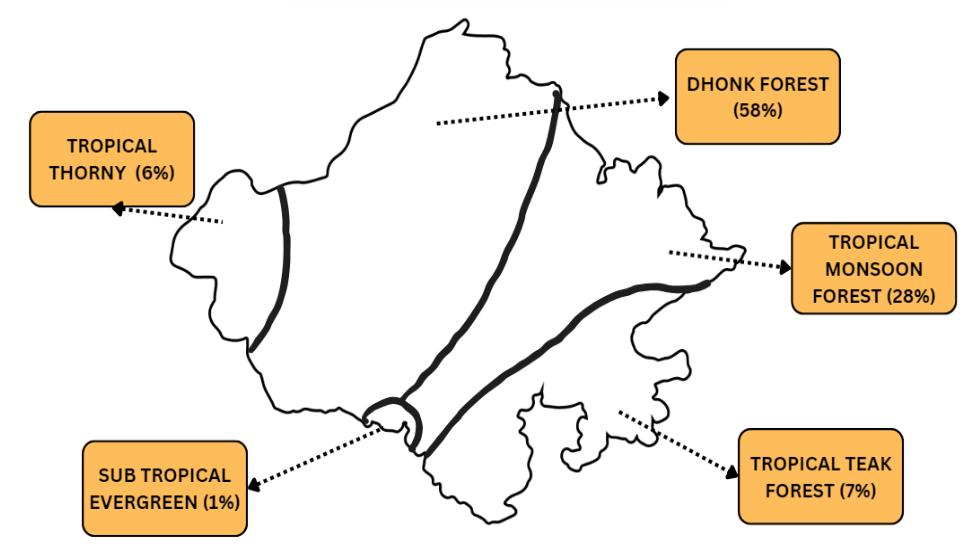
- Tropical thorny/Xerophyte forest-
- 6% of Rajasthan area.
- 0-30 cms rainfall.
- Arid desert area.
- Jaisalmer, barmer, Bikaner, jodhpur.
- Thorny bushes, cactus, aloe vera.
- Prevents desertification.
- Tropical dhonk forest
- 58% of rajasthan area.
- 30-60cms rainfall
- Semi arid areas
- Shekhwati, nagour, luni basin, sawai madhopur, karauli.
- Khejri, rohida, babool, ber, ker
- Fuel wood supply.
- Tropical dry deciduous/Monsoon
- 28% of rajasthan area.
- 50-80cms rainfall
- Alwar, bharatpur, karauli, dholpur, Jaipur, tonk, dausa, Udaipur, Chittorgarh, Bhilwara, rajsamand
- Sal, teak, mango, rosewood,sandalwood,
- Timber of economic importance is supplied
- Tropical teak forest
- 7% of rajasthan area.
- 75-110 cms rainfall
- Banswara, Dungarpur, pratapgarh, kota, Jhalawar
- Mahua, gular, tendu, palash
- Industrial use
- Sub- tropical evergreen forest
- 1% of rajasthan area
- About 150cms rainfall
- Mountabu, sirohi
- Jamun, bamboo, ambartari(dicleptera abuensis)
- Highest biodiversity
- Grasses
- Sevan/leelan (Lasiurus scindicus), western Rajasthan (maximum in Jaisalmer), nutritious grass, shelter of godawan
- Dhaman- (Cenchrus ciliaris )- maximum in Jaisalmer, for milching animals
- Bamboo- (Bambusa vulgaris)- banswara, called as green gold
- Khas- bharatpur, sawai madhopur, tonk, ajmer; fragrances, syrups and perfumes are made
- Bur- Bikaner, fragrance
- Mochia- churu, tal chhapar; black buck feeds on it.
Afforestation programmes
- Desert afforestation program (1977-1978)
- 10 districts
- 75:25 (Center : State)
- State forest action plan (1996-2016)
- Aravali afforestation plan- with aid of Japan
- Rajasthan forestry and biodiversity project(2003-2018)- with aid of JICA
- Aim- to promote forestry and biodiversity, soil and underground water conservation, poverty alleviation and livelihood program
- phases (8+8 YEARS)
- I – 2003-2010 – 18 Districts
- II- 2011-2018- 15 Districts (10 desert+05 non deserts)+07 wildlife sanctuaries
- Harit rajasthan yojana
- Van-dhan yojana (2015)-
- Alternate livelihood to people living near forests
- Employment opportunities
- Protect forests and wildlife
- Ghar-ghar aushadhi yojana (2021)
- To promote local medicinal plants use to improve immunity
- Tulsi, giloy, kalmegh, ashwagandha
Major Vegetation Types / Major Vegetation Types / Major Vegetation Types / Major Vegetation Types
