In World Geography, deserts are arid, expansive landforms characterized by minimal precipitation and sparse vegetation, formed by climatic and geological processes. These second-order relief features, covering vast regions, significantly influence global ecosystems and human adaptations.
Previous Year Question
| Year | Question | Marks |
| 2023 | Write names of any 6 deserts found in Australia. ऑस्ट्रेलिया के किन्हीं 6 मरुस्थलों के नाम लिखिए। | 2 M |
Introduction
- Deserts are dry and extremely arid parts of the landmass. These are mainly found in subtropical high pressure areas, where air descends and thermal inversion is found. Continental location or distance from the coast is also the reason for their origin, because the amount of rainfall keeps on decreasing as we move towards the interior parts. Cold ocean currents are also the reason for their origin.
- On the basis of the amount of rainfall, such areas where rainfall is less than 25 cm are called deserts.
- The world’s dry and semi-arid deserts are mainly found in the western and central parts of the continents, the main ones being Western Australia, Arabia, Thar, Sahara, Libya, Kalahari, Atacama and Arizona and Colorado, Gobi, Sikyang, Taklamakan, Kizilkum, Karakum.
- These dry places can be divided into two parts from the regional point of view –
- Subtropical [hot] deserts
- High latitude [cold] deserts
The reason for most of the world’s deserts being in the west of the continents is
- These dry landmasses are spread in the area of influence of trade winds. Trade winds blow from east to west, which take moisture from the sea and cause rainfall only on the eastern parts of the continents and become completely dry by the time they reach the western parts.
- These deserts are spread in the subtropical high pressure areas from where the winds are attracted towards the centres of low pressure and the counter trade winds descend. Hence, vapour-laden winds are less common in such areas.
- Mountain ranges stand around or on the sides of most deserts as a barrier to the winds, which brings these dry areas into rain shadow regions. Hence, the moist winds blowing from the sea are not able to cause rain in their inner parts. For example, Atacama Desert, Kalahari Desert from Andes, Caucasus Currents from Mountains, Western Australia Desert is affected by Great Dividing Range.
- Cold currents flow in the western parts of these deserts, which make the coastal and the winds passing through them dry and moisture-free, hence there is no rainfall in the western parts of the continents. For example, Venezuelan cold current to the west of Kalahari, Humboldt cold current to the west of Patagonia, Canary to the west of Sahara and to the west of Western Australia, Western Australia cold current, etc.
- These areas come under the influence of dry terrestrial winds or winds blowing from cold latitudes to warm latitudes which have a dry effect and give rise to desert conditions.
- In areas where the atmosphere continuously receives low temperature and as a result there are not many water vapour particles, dryness also occurs there as seen in the Tundra region ‘cold desert’.
Characteristics of desert regions
- Generally the sky is cloudless and the air is particularly dry.
- In desert areas, the temperature is very low at night and reaches 45º during the day. Due to this, the daily temperature difference and annual temperature difference are very high.
- Most deserts are completely affected by the fury of wind. The wind comes from various distances in the form of storm, hurricane, heat wave etc. at a high speed and causes loss of life and property in the affected areas.
- In dry desert areas, there are no large landforms, there are mainly flat areas. This is the main feature of the Gobi Desert.
- Sand dunes are the main feature of deserts.
- Vegetation is sparse in deserts, only those plants are found here which are able to maintain their existence against the dryness.
- Human life is troubled, population and density are found sparse.
Characteristics of desert regions
- Arid and semi-arid conditions are found on about 30% of the Earth’s surface, which does not include cold deserts.
- Desert conditions are found in 43% of the area in Australia, 40% in Africa, 29% in Asia and up to 10% in the New World.
- The Sahara Desert is larger than the total area of the United States. In Europe, aridity is found only near the Caspian Sea.
Types of deserts
1. Rocky desert or hamada –
- In such deserts, bare rocks are seen spread widely. At some places, heaps of sand and rock fragments are also seen. These areas are known as Hammada in the Sahara.
2.Rocky desert or reg –
- In such deserts, angular pebbles and stones are visible in transverse position and sand is rarely seen. In Algeria, they are called ‘Reg’ and in Libya and Egypt, they are called Serire.
3. Sandy desert or erg –
- In such deserts, abundance of sand and absence of rocky surface is mainly observed. From the point of view of common people, these are considered to be the real deserts.
- In the Sahara, they are called Erg and in Turkey, they are called Koum. The Thar desert is mostly of this type.
4. Mountain desert –
- In these deserts, hilly peaks with pointed tops, sharp slopes and deep cut ravines are found. Kyotic of the Sinnerd Desert, Tiwasi of Central Sahara, northern end of Taklamakan etc. are such deserts.
5. Cold desert–
- Due to the prevalence of aridity and lack of water, humans have not yet been able to reside in the North Pole and South Pole of the Earth. These areas fall in the category of deserts due to lack of rainfall, vegetation etc. and temperature difference, but due to extreme lack of heat and temperature, they are always covered with snow or remain cold, so they are called cold deserts.
- Antarctica, Greenland, Baffinland, Lapland, Iceland, Alaska, Northern Canada, Novaya Zemlya and other parts which are located from 66.5 degrees latitude towards the poles are known as cold deserts.
Desert of the world
ASIA
Thar/Great Indian Desert
- Spread between India and Pakistan [85% in India and 15% in Pakistan (Expansion of Thar – Cholistan)]
- Major animals are Great Indian Bustard, Desert Fox, Desert Cat, Black Deer.
- It is the 17th largest desert in the world and the 9th largest hot subtropical desert.
- This desert is of all three types – Arg, Reg and Hammad. It is the most biodiversity-rich desert in the world.’
- Kharam – small desert area, located in Balochistan province [Pak]
Cold Desert of India
- Situated in the Great Himalayas, it stretches from Ladakh in the north to Kinnaur (Himachal Pradesh) in the south.
- The Nubra Valley of Ladakh Union Territory is globally famous for its two humped camels.
Gobi Desert
- Extension in China and Mongolia and cold desert.
- The Gobi Desert extends from the eastern hills of Pamir in the west to the Khingan mountain ranges in the east and from the Altai, Khangai and Yasloi mountain ranges in the north to the Altai and Nanshan hills in the south.
- The western part of the desert is a part of the Tarim Basin.
- This desert is the habitat of the people of the Mongol race.
- The bear species Mazalai lives here.
Takla makan
- It is a cold desert located in China.
- It is surrounded by the Tianshan Hills in the north, the Kunlun mountain range in the south and the Tianshan Hills in the west.
Rub-al-Khali
- Located in Saudi Arabia and falls under the peninsula of the south-east Arabian Sea.
- The world’s largest sand desert area.
- The northern part is called ‘Ad Dahna’, which connects it to the Al-Nafud desert.
Al Nafud Desert
- A hot desert located in western Saudi Arabia.
- North of the Tropic of Cancer
Dasht-e-loot
- It is spread across eastern Iran which is completely surrounded by mountains.
- There is no record of rain in some areas.
Dast-e-kavir
- It is located in southern Iran.
- It is known as the Great Salt Desert.
Maranjab
- Located in Iran.
- One of the most beautiful deserts in Iran.
- There are saxaul forests and high sandy hills.
- There are places like the salty lake of Aran-Bidgol and the Wandering Island (Jazireh Sargardan).
An-Naqb/Negev
- Rocky desert located in southern Israel
Karakum Desert (meaning black sand)
- Located in south-central Turkmenistan and Kazakhstan. Southwest of the Amu Darya River.
- Known for High sand dunes spread in all directions.
Muyun Kum
- A semi-desert region located in Kazakhstan.
- Primarily a dry grassland.
- Important for nomadic tribes and livestock farming.
Kyzyl Kum (meaning ‘red sand’)
- A large desert located in Kazakhstan and Uzbekistan. Northeast of the Amu River.
- Famous for gold and uranium.
- Sheep and camel rearing are the main economic activities.
Badiyat ash-Sham/Syrian Desert
- Part of the Arabian Desert. In Jordan, Syria, Saudi Arabia and parts of western Iraq.
- Very little rain, but Arab nomads use it to raise cattle and camels.
- Oil pipelines and scattered oasis.
Africa
|
Desert |
Characteristics |
|
Sahara Desert |
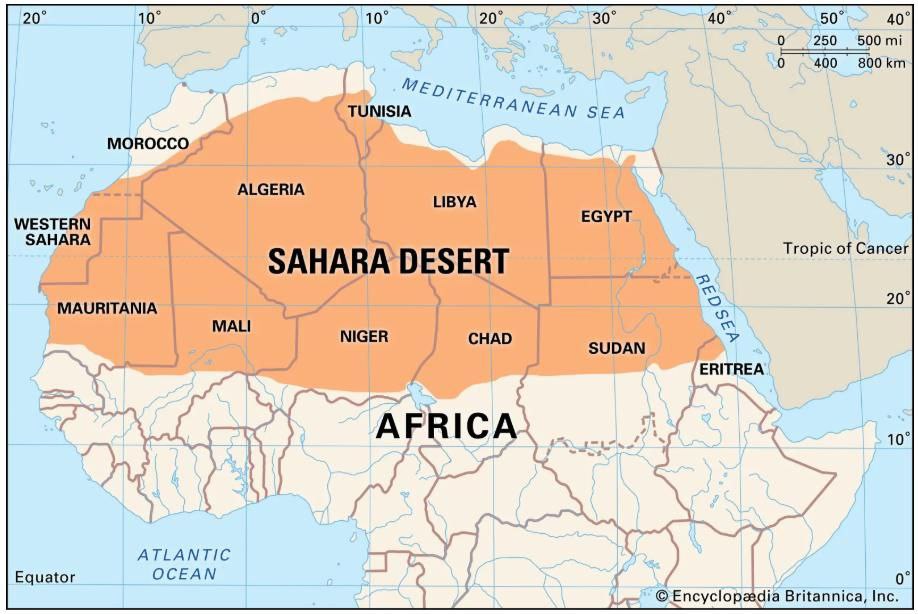 |
|
Western Desert |
|
|
Sahel |
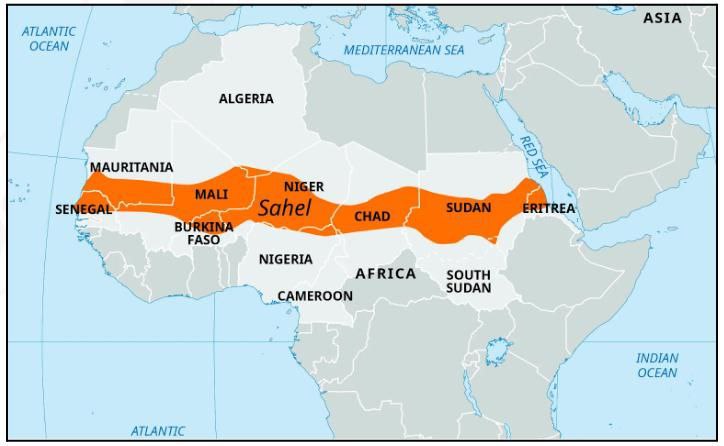 |
|
Namib desert |
|
|
MocamedeDesert |
|
|
Ogaden Desert |
|
|
Danakil Desert |
|
|
Guban Desert |
|
|
Nubian Desert |
|
|
Grand Bara Desert |
|
|
Kalahari Desert [meaning – waterless place] |
|
|
Karoo Desert |
|
|
Chalbi Desert |
|
|
Nyiri Desert |
|
|
Lompol Desert |
|
|
Iguidi Desert |
|
|
White Desert |
|
|
Sinai Desert |
|
North America
|
Desert |
Characteristics |
|
Mojave Desert |
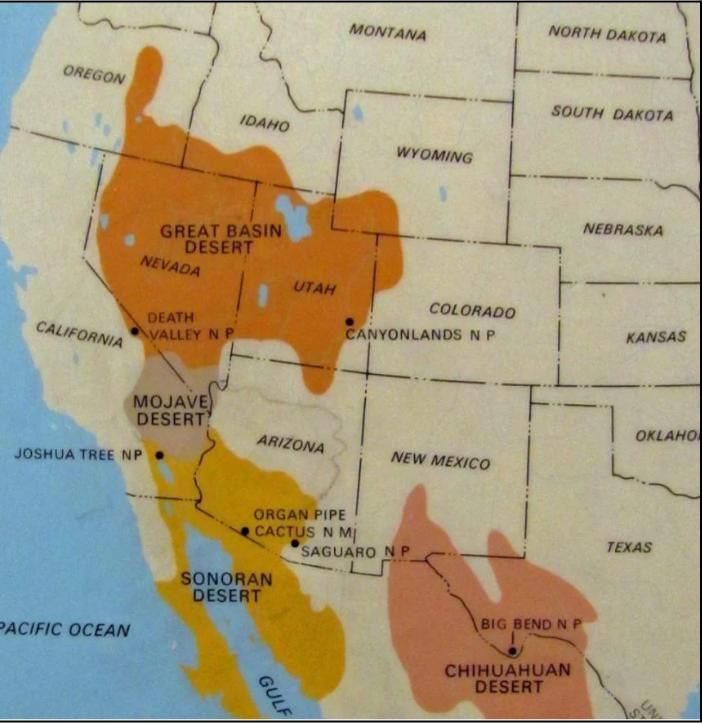 |
|
Great Basin Desert |
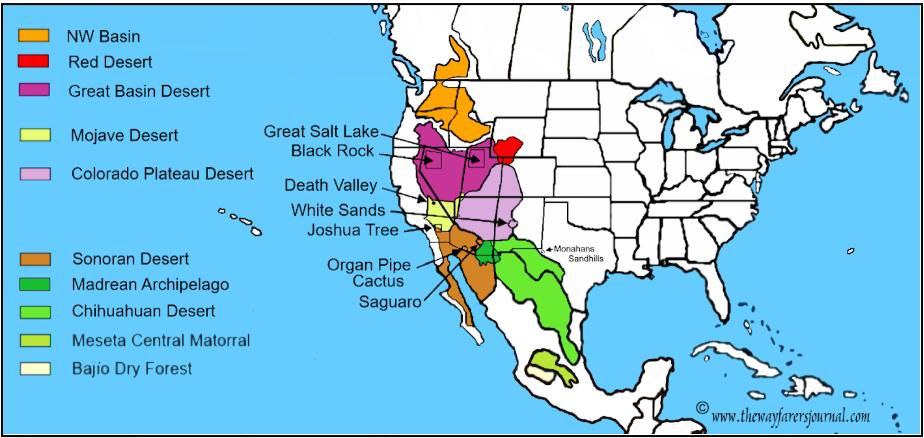 |
|
Chihuahua Desert |
|
|
Sonoran Desert |
Key Features:
|
South America
Atacama Desert
- Located west of the Andes Mountains, primarily in Chile, with some parts extending into Peru.
- It is the driest desert in the world, and Arica (0.08 cm annual rainfall) is the driest place on Earth.
- Major Causes of the Atacama Desert’s Formation:
- Presence of offshore trade winds.
- The Peru (Humboldt) Cold Ocean Current causes dryness along the coast.
- Upwelling of cold water near the Peruvian coast.
- Formation of anticyclones (high-pressure systems).
- Being in a rain shadow region.
Mineral Resources:
- Rich in copper, nitrate, and sulfur deposits.
- Home to the world’s largest nitrate reserves.
- Contains the world’s largest copper mine, “Chuquicamata,” located in Chile.
Climate & Agriculture in Southern Chile:
- Near Santiago, Chile’s capital, a Mediterranean climate exists.
- Chile is known for producing grains and juicy fruits.
- It is also the leading dairy-exporting country in South America.
- The main port city, Valparaíso, is located north of Santiago.
- It is famous for wine production in the Southern Hemisphere.
Petagonia desert
- Located in the rain shadow region of the Andes Mountains.
- Mainly spread across Argentina, with some parts in Chile.
- A temperate and arid desert.
- Formation influenced by the Peru (Humboldt) Cold Ocean Current.
- In the northern part, basaltic lava deposits from the Cretaceous period are found, known as the “Paraná Plateau.”
- Largest desert in South America by area.
- Strong “Pampas Winds” blow here, carrying dust and sand, limiting vegetation growth.
- Rich in minerals like coal, natural gas, oil, and iron. Also contains small deposits of uranium, zinc, and lead.
- Home to camelid species like Llama and Puma.
- Traditional homeland of indigenous tribes like the “Tehuelche” and others.
Oceania
|
Desert |
Characteristics |
|
Tanami Desert |
|
|
Great sandy desert |
|
|
Gibson Desert |
|
|
Great Victoria Desert |
|
|
Other deserts |
|
