In World Geography, a plateau is a significant landform characterized by its elevated, flat, or gently rolling surface, often formed by tectonic activity or volcanic processes. These expansive, table-like regions, found across various continents, play a crucial role in shaping climate, ecosystems, and human activities.
Previous Year Question
| Year | Question | Marks |
| 2016 | Define Mesa ? मेसा को परिभाषित करें ? | 2 M |
Introduction
- Plateaus are the second order reliefs of the earth.
- Plateaus are spread over 33% of the total land surface.
- Areas which are uplifted from their surroundings, having a flat and a broad top, having more than one, steep slopes are called plateaus.
- Some plateaus are up to 100 meters high and some extensive plateaus are up to several thousand meters high. Generally, their height ranges from 300 meters to 1000 meters above sea level.
Classification of Plateaus
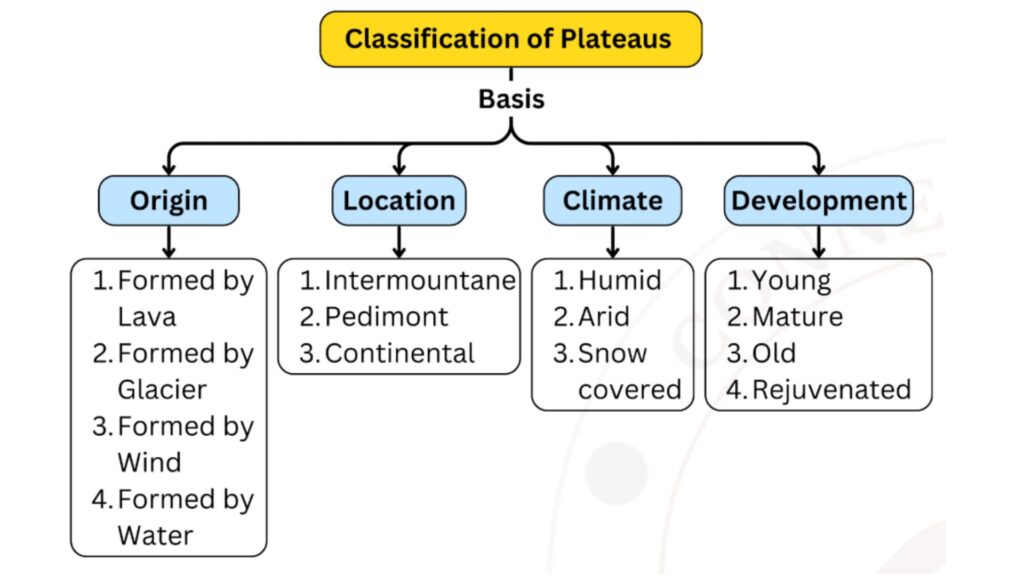
A. Classification of plateaus based on their origin
- Lava plateaus – Lava from the interior of the earth when overflows over an area, forms a Lava plateau. Example – Deccan Plateau (India), Columbia Plateau (USA)
- Glaciated Plateaus – Plateaus formed by the erosion and depositional activities of glaciers are called glacial plateaus. Glaciers erode mountainous regions through various processes, gradually wearing down the landscape and shaping flat plateaus.
These are found in high latitudes Eg. Labrador, Scandinavia, Alaska etc. In lower regions, small plateaus are formed by the deposition of moraines. Example – Garhwal Plateau of India and the Puchia Plateau in Germany.
- Aeolian plateau – These plateaus are formed by the excessive deposition of soil brought by the winds. Potwar of Pakistan and Loess Plateau of China are examples of this.
- Aquiferous or Aqueous plateau – The sediments which have been constantly being deposited in the oceanic regions or geosynclines, causing upliftment in sea beds due to endogenetic forces, resulting in formation of aqueous plateau. Hence, an aquiferous plateau is formed by both the processes of deposition by the river and upliftment due to the vertical movement of the earth. Example – Shan Plateau (Myanmar)
B. Classification of plateaus based on Location
- Intermountain Plateau–
- Due to their location between mountains, these are called intermountain plateaus.
- These plateaus form along with folded mountains due to endogenous forces. As mountain ranges develop along the edges of a tectonic plateau, the central parts may also rise.
- The highest, most extensive and highly complex plateaus of the earth’s surface fall in this category.
- Example – Tibetan plateau between the Himalayas and Kunlun mountains, Bolivian plateau, Mexican plateau.
- Piedmont Plateau – These plateaus are formed on the foothills of the mountains, having mountains on one side and sea or plain on the other. The slope of the plateau towards the plain is steep and fast. Example – Patagonia Plateau of Argentina, the mountain at the foot of Andes Mountains and Piedmont Plateau situated to the east of Appalachian Mountains in the United States.
- Continental Plateau – These types of Plateaus are extended in the entire area of a country or a continent.These plateaus are usually located away from the mountainous regions. For example, the Deccan Plateau , the plateau of Greenland and the plateau of Antarctica.
C. Classification of plateaus based on climate
- Humid Plateau – These plateaus mostly have 50% of humidity and good rainfall. For example plateaus of Meghalaya and Malagasy are included under this category.
- Dry or Arid Plateau – The amount of evaporation exceeds the amount of rainfall received thus dryness prevails on these plateaus, for example Tarim, Gobi and Potwar Plateau.
- Iced Plateau –Higher regions and higher latitudes are mostly covered with perpetual snow because of lower temperatures example Greenland and Antarctic plateaus
D. Classification of plateaus based on stage of development
- Young Plateau – These types of plateaus are separated from its nearby region with a steep edge. The rivers flowing on these plateaus create deep valleys. The process of erosion is very active on these types of plateaus. On the Colorado Plateau, the river creates Grand canyons.
- Mature Plateau – These plateaus have caves and ridges with highly uneven surface . The margins of these plateaus appear to be terrace form like Appalachian plateau
- Old Plateau – The relief features of these plateaus are converted into flat Plains example plateau of Ranchi.
- Rejuvenated Plateau – Due to the endogenetic forces the old plateaus sometimes get uplifted and erosion begins again.
Mesa –A sloping plateau or a hill with a flat top is called a mesa. In Jharkhand, mesa is called pat in the local language. Mesa is formed by the physical weathering of the plateau and over time, butte is formed by the weathering of mesa. Butte is a smaller topography than mesa.
Importance of plateau
- Economically, plateaus are more populated than mountains.
- Intensive agriculture is done on their fertile soil.
- They are storehouses of precious minerals.
- Rivers descending from their steep slopes form waterfalls.
- Reservoirs are constructed on their hard surface.
- Means of transport are more developed on plateaus than on mountains. Although plateaus are found to be much less developed than plains.
Importance of plateau
- Storehouse of mineral wealth – Plateaus are storehouses of non-metallic (sand, gypsum, coal, limestone) and metallic minerals (iron ore, copper, gold). Minerals are found in abundance in the Canadian Shield [Canada], Chhota Nagpur Plateau of India, Hazaribagh Plateau etc. The Brazilian plateau is important for manganese, the South African plateau is important for gold, copper, diamond deposits etc.
- Limited contribution in agriculture – Due to the rough and rocky surface of the plateaus, their role in agriculture is limited. Red and laterite soil is found in these rocks which is usually infertile but due to the presence of black or regur soil on the lava plateaus, it is suitable for the cultivation of cotton and wheat.
- Development of forest and animal husbandry – The availability of vegetation on the plateaus depends on the climate there. Small grasses grow on the plateaus of arid and semi-arid climate areas, which are suitable for animal husbandry. Dense forests and wood business and related industries develop on the plateaus of humid regions. India’s Chhota Nagpur Plateau is the world’s largest lac producing region.
- Effect on traffic and transportation – Development of traffic and transportation is easy in flat and plain plateau regions. On the contrary, traffic and transportation cannot develop in rugged plateaus.
- Population distribution – The plateaus on which mineral mines and industries are developed have a higher population. On the contrary, the plateaus with dense forests, rugged and rocky terrain have less population.
Plateau of the world
Asia Plateaus
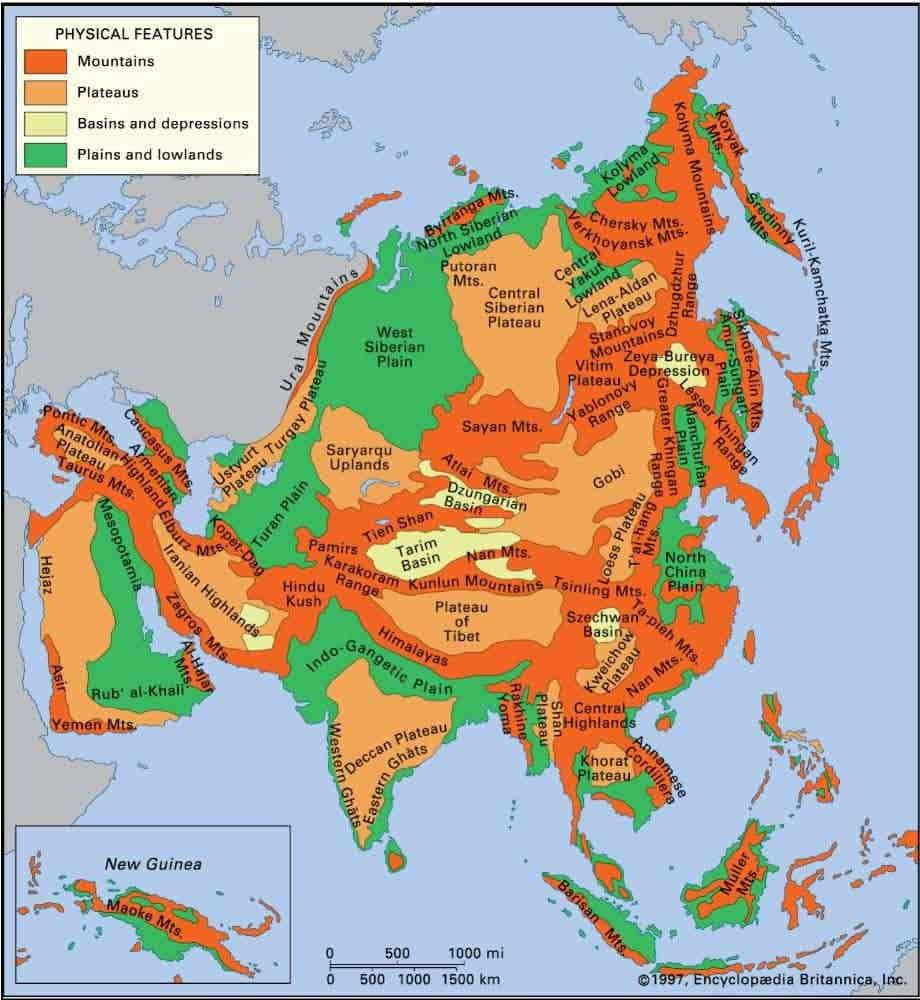
Tibet plateau
- The world’s largest and highest plateau.
- Intermountain plateau [Located between the Kunlun Shan mountain range and the Himalayan mountain range.]
- Located in China.
- It is also called the third pole.
- Many glaciers are found on this plateau from which many rivers of Asia originate. Such as – Sutlej, Brahmaputra, Yangtze ,Indus etc.
- There are many big and small lakes, the main ones being Mansarovar Lake and Rakshasa Lake.
Pamir Plateau (Roof of the World)
- Tajikistan, Afghanistan, China and Kyrgyzstan
- It is the meeting point of various mountain ranges of the Asian continent, hence it is also called the Pamir Knot.
- Major mountain ranges originating from it: Hindukush, Himalayas, Karakoram, Tienshan, Kunlun.
Anatolia Plateau
- An intermountain plateau, situated between the Pontic and Taurus mountain ranges.
- It is called Asia Minor.
- A dry climate is found here.
- The capital of Turkey, Ankara, is situated on this plateau. The world’s saltiest lake, Lake Van, is situated here.
- This plateau region is famous for Angora goats which produce high quality wool.
Armenian highlands
- This plateau region is spread across Armenia, Southern Georgia, Western Azerbaijan, Turkey, North Western Iran.
- Its highest peak is Mount Ararat.
- Sevn, Vahan and Urmia lakes are located in this plateau region.
- Evidence of volcanic activity is found here.
- The major mountain ranges of Western Asia are shaped in this plateau region, hence it is also called the Armenian knot.
- Rich in minerals – Iron ore, gold, chromite etc. are found here.
- Climate – Continental.
Iran Plateau
- Situated between the Zagros and Elbrus mountain ranges.
- A region with a dry climate.
- Iran’s deserts Dasht-e-Lut and Dasht-e-Kavir are located in this plateau region.
- This plateau region has reserves of fossil fuels like petroleum, natural gas, oil etc.
Arabian Plateau
- Situated in South-West Asia.
- This plateau is bordered by the Persian Gulf to the east, the Arabian Sea to the south, the Red Sea to the west and the Mediterranean Sea to the north-west.
- The slope of this plateau is from south-west to north-east.
- Remains of ancient Gondwanaland
- This plateau is made up of ancient hard rocks which, due to being dry, have formed a thick layer here due to the breaking of the stones. Large mounds of which are visible here and there.
- In its northern part lies the Sham Plateau
Potwar Plateau
- Located in East Pakistan.
- This plateau has reserves of natural gas, coal, oil etc.
- Islamabad and Rawalpindi are major cities located on the plateau.
Deccan Plateau
- The Deccan Plateau is a part of the ancient GondwanaLand. It is located in Southern India.
Chota Nagpur Plateau
- It is the north-eastern part of the Deccan Plateau located in India. It is also called the Ruhr region of India.
Shan Plateau
- Spread in eastern Myanmar.
- Located between the Irrawaddy and Salween rivers.
- Precious stones such as sapphire, ruby and emerald and many minerals such as zinc, lead, silver etc. are found in the plateau.
Da Lat/Lam Vien Plateau
- Vietnam
Loess Plateau
- Spread in China.
- Also known as Yellow Land Plateau or Huangtu Plateau.
- Formation – Due to deposition of wind.
- Huang Ho River flows through this plateau.
- The plateau is highly eroded and the soil of this plateau is very fertile.
- Due to erosion of the plateau, silt gets deposited in the drainage path of Huangho River, which causes floods in the Huangho River.
Yuan Plateau
- High and extensive region located in southwest China.
- Karst landforms (such as caves, sinkholes) are widely found here.
- It is dotted with deep and narrow valleys of rivers like Salween, Mekong, Sikyang etc.
- It is also important for mineral resources such as copper, zinc and tin
(Ustyurt Plateau)
- Stretches between Kazakhstan, Turkmenistan, and Uzbekistan.
- Located between the Caspian Sea and the Aral Sea
- Reserves of natural gas and petroleum
- Was also part of the Silk Road.
Plateau of central siberia
- Situated between the Yenisei and Lena rivers.
- It is a highland situated in the middle of the Siberian plain.
- The Siberian lowland is situated to the north of the plateau, mountains to the south, plains of Western Siberia to the west and Yakutian lowland to the east.
- The Tunguska River flows through this plateau.
- Many types of minerals are found here. Such as – diamond, gold, natural gas, coal and iron ore etc.
- Climate – Continental.
- Coniferous (Taiga) forests are found.
Mongolian Plateau
- Located in the Republic of Mongolia in the north central part of China.
- The dry plateau is spread in the eastern part of Mongolia, which is very rough.
- The southern part of the Great Khingan range is located to its east.
- Minshan and Holan mountains are located in its middle.
- The eastern part is desert.
Khorat Plateau
- The plateau is in the Isan region of northeastern Thailand.
- It is also called the Nekhen Ratcha Range.
- Wolframite ore (tungsten) is found.
- Known for animal husbandry and fishing.
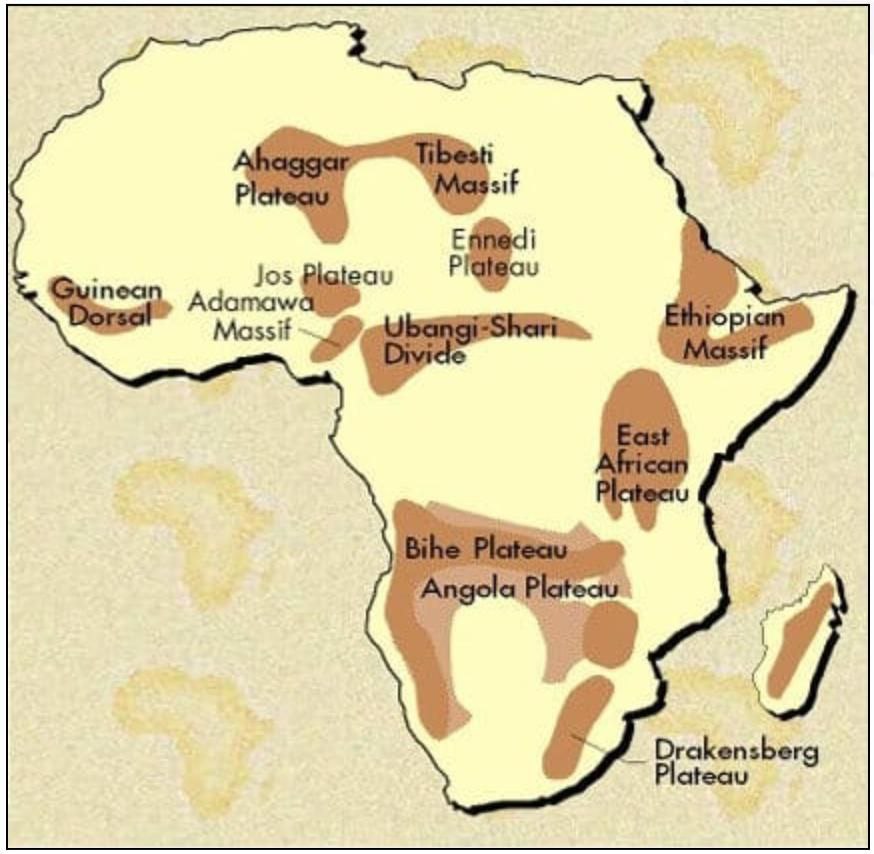
Africa Plateaus
|
Plateau |
Characteristics |
|
Bie plateau |
|
|
Ethiopian Highlands |
|
|
East African Plateau |
|
|
Jos Plateau |
|
|
Tassili Plateau |
|
|
Ahaggar Plateau |
|
|
Guinea highlands |
|
|
Fouta Jallon Plateau |
|
|
Great Karoo Plateau |
|
|
Adamawa Plateau |
|
|
Ubangi Plateau |
|
|
Katanga Plateau |
|
|
Malagasy Plateau |
|
|
Tanganyika Plateau |
|
|
(Ennedi Plateau) |
|
|
Tademait Plateau |
|
|
Aïr Massif |
|
|
Makonde/Mewala Plateau |
|
|
DarfurPlateau |
|
 |
North America Plateaus
|
Plateau |
Characteristics |
|
Canadian Shield / Laurasi-an Shield |
|
|
Columbia Plateau |
|
|
British Columbia Plateau |
|
|
Great Basin Plateau |
|
|
Colorado Plateau |
|
|
Chiapas Plateau /Mexico Plateau |
|
|
Allegheny and Cumberland Plateau |
|
|
Piedmont plateau |
|
|
Ozark Plateau |
|
|
Yukon Plateau |
|
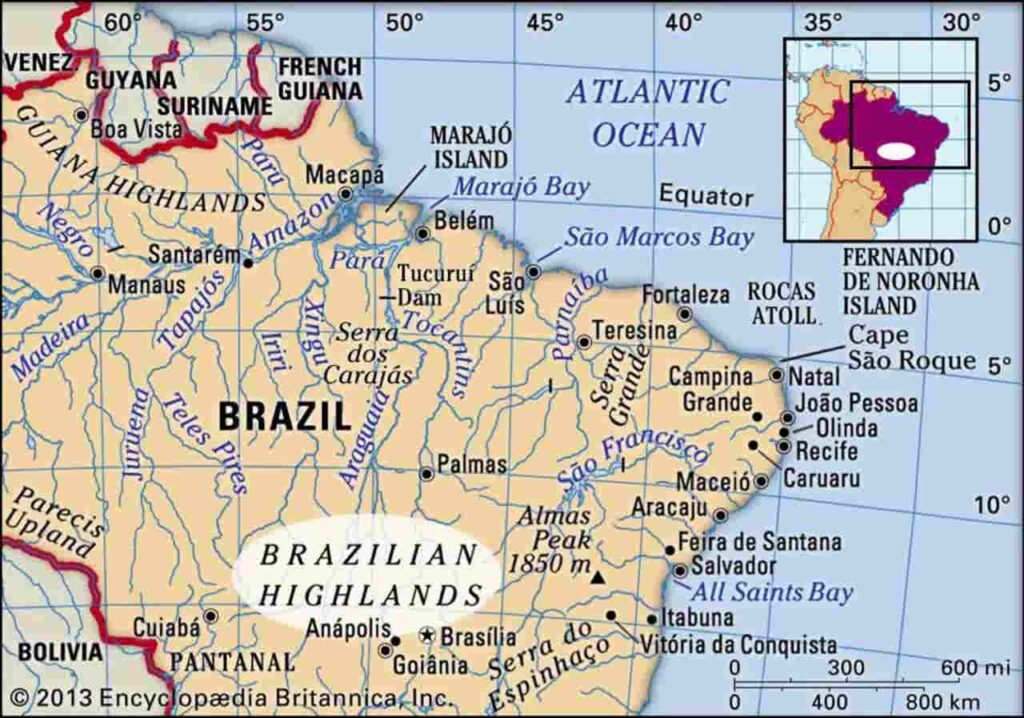
South America Plateaus
Guiana Plateau
- It is one of the oldest landforms of the world. Hence, it is an example of a shield.
- It is located in the northern part of South America and is spread across Guyana, Suriname, French Guiana, Brazil, Venezuela and Colombia.
- The highest point of this plateau is ‘Pico da Neblina’ which is located in Brazil.
- This plateau region is located near the equator, hence, there is high rainfall and abundant biodiversity is found here.
- The world’s highest waterfall ‘Angel’ is situated in the Guyana plateau, which is located on the ‘Churun’, a tributary of the Caroni River (Caro in some sources). The Caroni River is a tributary of the Orinoco River. Angel Falls is located in the south-eastern part of Venezuela.
- Many types of minerals are found in this plateau region such as iron, gold, manganese, bauxite, silver etc.
- The world’s largest reserves of laterite soil and bauxite are found here.
Brazilian Plateau / Brazilian Highland
- It is spread in Brazil and is one of the oldest landforms in the world.
- The highest point of this plateau is Pico da Bandeira. Many types of minerals are found here like iron, gold, copper.
- Its height is more towards the Atlantic coast and the slope is gentle towards the Amazon basin.
- Red soil (Terrarosa) has developed in the highland areas of Brazil, so coffee is produced on a large scale in Brazil. Brazil holds the first place in the world in coffee production.
- Mato Grosso and Minas Gerais, located in the western Brazilian Highlands, are important regions for iron ore and manganese.
- Itabira is the largest iron ore mine in South America.
Plateau of Mato grosso
- This plateau is located in Brazil. It is spread in the south and west of Brazil.
- This region has been highly eroded.
- The Tapajos River, a tributary of the Amazon, flows northward from here, while the Paraguay River originates here and flows southward.
- It is also a center for gold and diamond mining.
- It serves as a major watershed region.
- South of the Mato Grosso Plateau, extensive coffee plantations are found, known as “Fazenda.”
- Brazil is the world’s largest producer and exporter of coffee.
- Santos Port is used for coffee exports and is also known as the “Coffee Port.”
Borborema Plateau
- Located in northeastern Brazil.
- Connected to the Brazilian Plateau.
- Contains gold deposits.
- One of the world’s largest sugarcane-producing regions.
- The Sao Francisco River is nearby.
Bolivian Plateau
- There is a vast inter mountainous plateau between the Andes mountain ranges.
- It is mainly spread in Bolivia, but it is also spread in Peru, Chile and Argentina.
- The main vegetation of this plateau region is shrubs and grass, because dry conditions exist here.
- This is a plateau formed by volcanic activity, hence a layer of lava is spread on it.
- Lake Poopo and Lake Titicaca are located on this plateau. Lake Poopo has dried up and Lake Titicaca is a freshwater lake which is the highest navigable and fishing lake in the world. The high plains around Lake Titicaca are called Altiplains.
- Being a plateau region with a semi-arid climate, an inland drainage system is found in this region.
- The capital of Bolivia is ‘Lapaz’, the world’s highest capital on the plateau.
- Mining of tin and tungsten minerals from the plateau.
- The plateau of Bolivia is also called ‘Alti-Plano’.
Petagonia Plateau
- Extends from the Andes Mountains to the Atlantic Ocean.
- Mainly spread across Chile and Argentina.
- Lava layers are found on this plateau.
- Located in the rain shadow region of the Andes Mountains, resulting in an arid climate.
- The Colorado River forms its northern boundary.
- The cold Patagonian Desert, the largest desert in South America by area, is located here.
Europea Plateaus
|
Plateau |
Characteristics |
|
Bohemia Plateau |
|
|
Fanno–Scandia Shield |
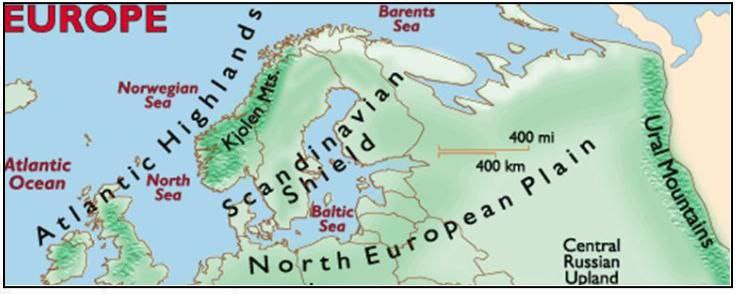 |
|
Greenland Plateau |
|
|
Bavarian Plateau |
|
|
Meseta Plateau / Meseta Central |
|
|
Ukraine Plateau |
|
|
Massif central |
|
Oceania Plateaus
|
Plateau |
Characteristics |
|
Western plateau region |
|
|
Kimberley Plateau |
|
|
Other |
|
|
Otago Plateau |
|
Plateau of the world / Plateau of the world / Plateau of the world / Plateau of the world / Plateau of the world / Plateau of the world / Plateau of the world / Plateau of the world / Plateau of the world / Plateau of the world / Plateau of the world / Plateau of the world / Plateau of the world / Plateau of the world / Plateau of the world
