Banking and Non-Banking Financial Institutions (NBFIs) are essential components of the financial system, playing a vital role in economic growth and financial management. While banks provide traditional financial services, NBFIs offer specialized solutions to meet diverse financial needs. Understanding their functions helps in effective financial planning and management.
Financial Institutions/Intermediaries
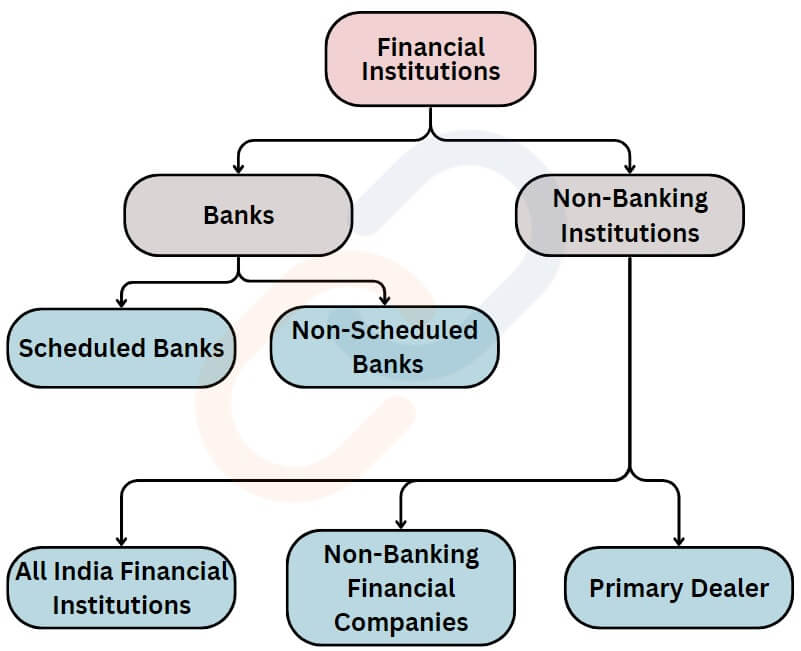
Financial institution (FI)– It is a company engaged in the business of dealing with financial and monetary transactions such as deposits, loans, investments, and currency exchange. FIs can be categorized as –
- Banks
- Non-Banking Financial Institutions
Banking
Bank-
- A company accepting deposits of money, for the purpose of lending or investment, from the public, repayable on demand or otherwise, and withdrawable by cheque, draft, order or otherwise (Banking Regulation Act 1949, Sec 5b
- Important Acts-
- RBI Act 1934
- Banking and Regulation Act 1949
- Payment and Settlement Act 2011
Scheduled Banks and Non-Scheduled Banks
Scheduled Banks-
- These banks are listed in the 2nd schedule of the RBI Act 1934.
- Criteria-
- The bank’s paid-up capital and raised funds must be at least Rs. 5 lakh.
- The bank’s operations are not detrimental to the interest of the depositors.
- Examples- SBI, PNB, ICICI, etc
Non-Scheduled Banks-
- All those banks that are not listed in the 2nd schedule of the RBI Act.
- Examples- Coastal Bank, Subhadra Local Area Bank Ltd, etc
| Scheduled Bank | Non-Scheduled Banks | |
| RBI,2nd sch | Yes | No |
| Borrowing from the RBI allowed? | Yes. RBI Liquidity Adjustment Facility (LAF) Window. | Normally not allowed. Yes, under exceptional circumstances. |
| Requirement of CRR | Yes. Must maintain with the RBI | Yes. Maintain CRR either with RBI or with themselves |
| Requirement of SLR | Requirement of SLRYes. | Requirement of SLRYes. |
| Members of Clearinghouse | Yes, RBI acts as Clearinghouse It enables the banks to settle transactions among themselves | No. Non-scheduled banks are not members of Clearinghouse |
| Examples | Public Sector Banks Private Banks Foreign Banks Regional Rural Banks Payment Banks and Small Finance Banks Primary Urban Cooperative Banks DCCS and StCBs | Local Area Banks Primary Urban Cooperative Banks District Central Cooperative Banks State Cooperative Banks Payment Banks such as Jio and NSDL. |
Universal Banks and Differentiated Banks
Universal Bank-
- These banks offer a wide range of financial services under one roof.
- This includes traditional banking services like lending and deposit-taking, as well as investment banking, wealth management, insurance, and other financial products.
- Example- SBI, HDFC, etc
Differentiated Banks-
- These banks are licensed by the RBI to provide specific banking services and products in selected areas.
- Example-Regional Rural banks, Small finance banks, etc
| Basis | Universal Bank | Differentiated Bank |
| Scope of Activities | No Restrictions. Can provide all the Banking services. | May be restricted. Payment Banks are not allowed to give loansSmall Finance Banks can give loans but at least 50% of the loans should be below Rs 25 lakhs |
| Area of Operation | No Restrictions. Can open branches anywhere across India | May be Restricted. Local area Banks cannot have branches in more than 2-3 districts. The area of Operation of RRBs is restricted through Government’s notification |
| Example | Public Sector Banks Private Banks, etc. | Regional Rural Banks Local Area Banks Payment Banks Small Finance Banks Primary Urban Cooperative Banks |
Digital Banking
100% Digital Bank
- Meaning– Banks have no physical presence. Provide all services on the Internet.
- Recommendation– NITI Ayog recommended issuing the license to 100% Digital Banks.
- Global example-
- UK: Starling Bank, Monese Bank
- China: WeBank
- Present Status in India: No provision, Existing Physical banks provide digital banking services.
- Advantage:
- Low operating cost.
- Credit at lower interest rates.
- Financial inclusion
- Competition among Banks.
Digital Banking Units
- Meaning: Existing banks set up banking units having Cash Deposit Machines, ATMs, free Wifi connections, Bank representative
- Operating Mode: Provide banking 24 x 7.
- Paperless processing: Opening Accounts, Loans, etc.
- Services such as Cash deposits, withdrawals, etc. would be made only through ATMs.
- Product & services:
- Account Opening
- End-to-end digital processing of loans
- Internet Banking Kiosk
- Cash withdrawal and Cash Deposit only through ATM
- Digital Kit for customers: Mobile Banking, Internet Banking, Debit Card, Credit card and mass transit system cards
- Digital enrolment of customers for Atal Pension Yojana, PM Jeevan Jyoti Yojana, etc.
- Eligible Entities: Domestic Scheduled Commercial Banks ( except RRBs, Payment Banks, and Local area Banks)
- Area: No need for a separate license, can be open in both rural and urban areas.
Non-Banking Financial Institutions
All India Financial Institutions (AIFIs)
- AIFIs are established through an act of Parliament for development.
- Does not accept Deposits from the Public.
- Mobilize money from the Government and through the issue of bonds
- AIFIs don’t provide loans to the public. Most of the loans are given to Commercial Banks. For example, NABARD gives loans to RRBs.
- Multi-faceted role in the form of providing hand-holding support and refinancing of loans given by Banks.
- AIFIs are also k/a Development Banks
- At present, there are five AIFIs- NABARD, SIDBI, EXIM, NHB, NaBFID
Non-Banking Financial Companies(NBFC)
- NBFC is a company registered under the Companies Act, engaged in the business of loans and advances, and acquisition of shares /stocks /bonds /debentures /securities.
- NBFC are also k/a Shadow banking institution
- Some NBFCs take only Time-Deposit (no demand deposit)
- Financial activities are their “Principal Business”.
- 50-50 rule of Principal Business:- A company will be registered as NBFC by RBI only if Financial activity is the principal business of the company.
Financial activity is the principal business of the company – when a company’s financial assets constitute more than 50 percent of the total assets and income from financial assets constitutes more than 50 percent of the gross income.
Difference between Banks and NBFCs
| Banks | NBFCs | |
| Source of Funds? | Deposits | Market-based instruments(Larger share) Time Deposits |
| Deposits? | Both Demand deposit and Fixed deposit. | Only Fixed deposit (Time deposit) |
| Deposits insured? | Yes, by DICGC | No |
| Lending? | Yes | Yes |
| CRR? | Yes | No |
| SLR? | Yes | Yes, only for Deposit-Taking NBFCs |
| PSL? | Yes | No |
| CAR? | Yes | Yes |
| Part of Payment and Settlement System? | Yes, Can issue Cheque books | No, cannot issue Cheque books |
| Credit Cards? | Yes | Yes, requires prior permission of RBI. SBI Card, BOB Card |
| Regulation? | Strict Regulation | Partially Regulated or unregulated |
| Transparent? | More transparent | Less transparent |
NBFCs Regulated by the RBI
Investment and Credit Company (ICC)
- Financing of Assets such as automobiles, tractors, etc.
- Lending of loans for other purposes
- Investment in securities
- Shriram Transport; Bajaj Finance; Mahindra
- Finance (Deposit Taking) Aditya Birla Capital (Non-Deposit Taking) ICICI Securities Ltd.
Infrastructure Finance Company (IFC)
- At least 75% of assets are in the form of loans to the infrastructure sector.
- Aseem Infrastructure Finance
- Indian Railway Finance Corporation (IRFC)Power Finance Corporation (PFC)
Core Investment Company (CIC)
- At least 90% of assets in the form of shares, Bonds, Securities
- L&T Finance; Reliance Capital; Tata Capital
Infrastructure Debt Fund (IDF)
- Raise resources through the issue of Rupee or dollar-denominated bonds of minimum 5-year maturity.
- Kotak Infrastructure Debt Fund Limited India Infradebt Limited
Microfinance Institutions
- Provide small-value loans without any collateral
- Muthoot Microfinance Annapurna
Factoring Companies
- Factoring of Trade Invoices of MSMEs
- Siemens Factor Ltd; SBI Global Factors
P2P lending
- Platform to bring together borrowers and lenders
- Lendbox
Account Aggregators
- Aggregate Financial Information about the borrowers to enable Banks to give loans without hassles
- Finvu, OneMoney, etc
Housing Finance Companies
- Offer housing loans, including those that provide loans for purchasing, constructing, repairing, and upgrading homes.
- LIC Housing Finance Limited Bajaj Housing Finance Limited
NBFCs Regulated by the SEBI
Stock Broking Company
- These NBFCs buy and sell stocks and shares for clients.
- Angle One, ICICI Direct, etc
Mutual Fund Company
- This NBFC pools money from investors to buy securities like stocks, bonds, and other assets. Professional money managers run these companies.
- SBI Mutual Fund, HDFC Mutual Fund
Venture Capital Fund
- pools money from investors to buy securities like stocks, bonds, and other assets. Professional money managers run these companies.
- Nexus Venture Partners, Accel
NBFCc Regulated by the Ministry of Corporate Affairs
Nidhi Company
- These companies receive deposits and lend to their members only for mutual benefit.
- Jagriti Nidhi Limited in Rajasthan, Unifirst Mutual Benefit Nidhi Limited in Maharashtra
NBFCc Regulated by the State Governments
Chit Fund Company
- It is a type of rotating savings and credit association that involves a group of people contributing money to a common pool.
- Each month, the collected money is given to one subscriber, who is chosen by auction or lottery. The process is repeated until every subscriber has received their share of the money.
- Gokulam Chits, Government of Kerala Linked Chitty etc
Banking and Non- Banking Financial Institutions (NBFIs)/ Banking and Non- Banking Financial Institutions (NBFIs)
