Supply Chain & Logistics Mix: E-Commerce & E-Marketing Strategies play a vital role in modern business success. Effective supply chain management ensures smooth operations, while strategic e-marketing enhances customer engagement and sales. This page explores how these elements integrate to optimize business performance and drive growth.
Supply Chain Management
- Supply Chain Management (SCM) is the process of managing the flow of goods, services, information, and finances from raw material sourcing to the final delivery of products to customers.
- It involves coordinating various activities such as procurement, production, logistics, and distribution to improve efficiency, reduce costs, and enhance customer satisfaction.
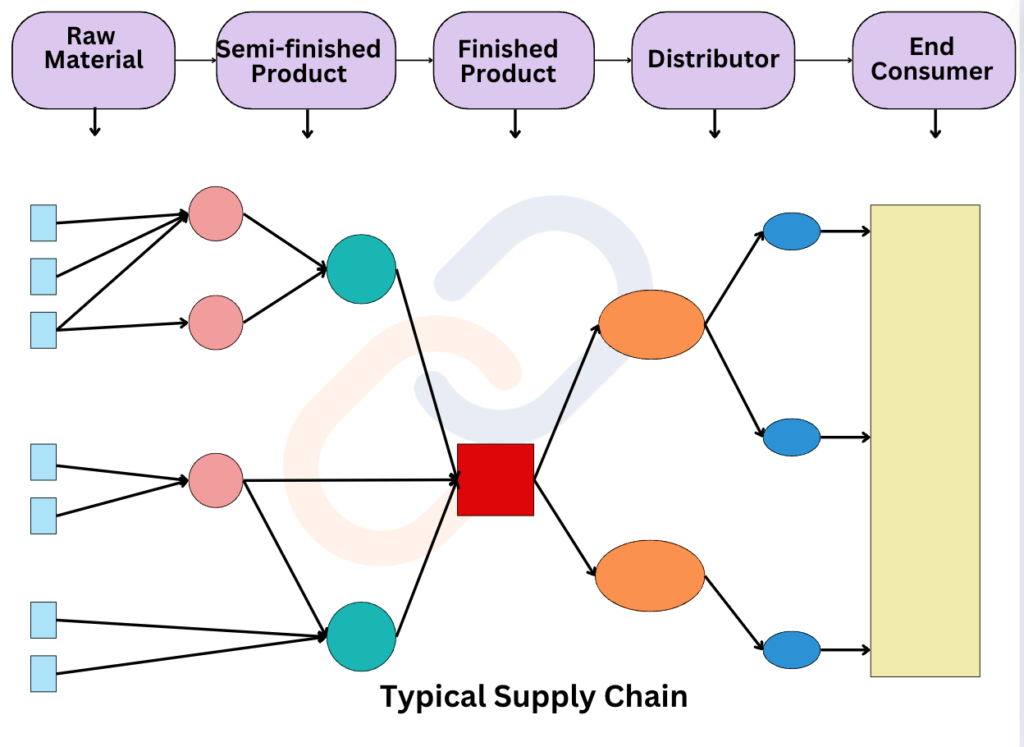
Components of Supply Chain Management:
Planning
- Involves demand forecasting, inventory management, and production scheduling.
- Helps align supply with customer demand to avoid overproduction or shortages.
- Tools: ERP (Enterprise Resource Planning), demand forecasting software.
- Example: Walmart uses advanced data analytics to forecast demand and optimize inventory levels.
Sourcing (Procurement & Supplier Management)
- Involves selecting suppliers for raw materials and negotiating contracts.
- Focuses on cost-effectiveness, quality, and supplier relationships.
- Example: Amul Procures milk from over 3.6 million dairy farmers across India. Uses a cooperative model for direct sourcing, ensuring fair pricing.
Manufacturing (Production)
- Converting raw materials into finished products.
- Includes assembly, quality control, and packaging.
- Focuses on efficiency, minimizing waste, and maintaining high quality.
- Example: Toyota uses Just-in-Time (JIT) manufacturing to reduce inventory costs and increase efficiency.
Logistics (Transportation & Warehousing)
- Involves transportation, warehousing, and distribution.
- Uses supply chain networks and third-party logistics providers (3PL).
- Example: Flipkart (Walmart-owned) has a strong warehousing and delivery network in India.
- Uses AI and automation in fulfillment centers.
Delivery (Distribution & Retailing)
- Ensures products reach customers efficiently.
- Involves last-mile delivery networks.
- Example: Zomato & Swiggy uses real-time tracking and logistics for food delivery. Ensures fast delivery with AI-driven route optimization.
Returns (Reverse Logistics)
- Handles returned or defective products.
- Focuses on recycling, refurbishing, or disposal.
- Example: Amazon India has an efficient return and refund policy for customers. Uses logistics partners for product pickups.
Information & Technology (IT Integration)
- Uses AI, blockchain, IoT, and ERP systems for supply chain efficiency.
- Example: TCS (Tata Consultancy Services) develops AI-driven supply chain management software for businesses.
- Example: Lenskart uses AI to track inventory and optimize logistics.
Logistic Mix
The logistics mix refers to the combination of activities involved in planning, executing, and controlling a company’s physical flow of goods and services from the point of origin to the destination.
- It is a subset of supply chain management, contributing to the creation of time and place utility.
- Ensuring the right product, in the right quantity, at the right time enhances the overall efficiency and effectiveness of the supply chain.

The essential elements include:
- Order Processing : Receive, confirm, and prepare customer orders and prepare them for shipping.
- Inventory/stock management : maintaining optimal stock levels, tracking product movement, and preventing stockouts or overstock situations.
- Warehousing : Storing goods in a proper manner so that they can be accessed easily and quickly when required.
- Material Handling during loading, unloading, stacking, and organizing inventory.
- Packaging : to ensure their protection during transportation, convey necessary information, and influence consumer perception.
- Transportation and distribution to the point of consumption.
- Information Handling- supporting functions such as real-time tracking, inventory management, and communication.

E-Commerce
- Term E-Commerce is an abbreviated term for ‘electronic commerce’, which refers to the process of undertaking business transactions over the Internet.
- Generic e-commerce portals – any product, ranging from furniture to flowers. E.g.- FlipCart, Amazon
- Specific e-commerce web portal – only specific category products. E.g- Big Basket.
- It is an internet-based business ecosystem that comprises an e-commerce web portal, e-commerce software, an e-commerce app allowing various buyers and sellers to undertake business transactions comfortably and securely.
- M-Commerce and Multi-channel Commerce –The purpose is to interact in multiple ways with the buyers. It consists of an App, web portal, email, social media, etc.
- Use of Emerging Technologies in e-Commerce –
- Use of AI/ML in sorting of products and services for personalized experience to customers.
- Use of Augmented reality (AR) and virtual reality (VR) in Man-Machine-Interface.
- Use of Blockchain technology in record maintaining.
Types of E-Commerce:
- B2B (Business-to-Business): Companies involved in the supply chain, like manufacturers selling to wholesalers, and wholesalers to retailers, all use a common portal to conduct business.
- B2C (Business-to-Consumer): Businesses sell products directly to consumers, e.g., Amazon, Flipkart.
- C2C (Consumer-to-Consumer): Consumers sell to each other on platforms like Quikr, OLX.
- C2B (Consumer-to-Business): Consumers promote products via their social media (e.g., blogs) and link back to the company’s e-commerce site, earning rewards, e.g., affiliate marketing.
- B2G (Business-to-Government): Businesses provide products or services to the government, e.g., Government e-Marketplace (GEM).
- C2A (Consumer-to-Administration): Consumers interact with government agencies for payments or information, e.g., paying utility bills or taxes online.
- P2P (Peer-to-Peer): Individuals transact directly with each other without intermediaries, e.g., cryptocurrency, ridesharing.
- D2C (Direct-to-Consumer): Brands sell directly to consumers online, bypassing intermediaries, e.g.Mamaearth,BoAt,Pepperfry.
Difference between Inventory and Marketplace Model
| Aspect | Inventory Model | Marketplace Model |
| Inventory Ownership | Platform owns and manages inventory. | Platform connects buyers with third-party sellers. |
| Product Selection | Platform decides on the product selection. | Diverse product selection from various sellers. |
| Logistics & Fulfillment | Platform manages the entire supply chain. | Sellers handle their own logistics, fulfillment. |
| Pricing Control | Platform has direct control over product pricing. | Sellers have control over the pricing of their products. |
| Customer Relationships | Platform manages customer service and support. | Customer relationships may be shared between platform and sellers. |
| Brand Identity | Platform’s brand is prominent. | Individual sellers have their own brand identity. |
| Risk & Investment | Higher risk, significant investment in inventory. | Lower risk, investment in platform development. |
| Scalability | Scaling may be challenging due to physical constraints. | Scalability is often more straightforward by onboarding more sellers. |
| FDI in INDIA | FDI is not allowed. | 100 % FDI under automatic route allowed. |
Advantages of E-Commerce:
- Speed up the shopping process: E-commerce platforms allow customers to browse, compare and buy products faster, eliminating the need to visit a physical store.
- Personalized shopping experience: Through data analytics, e-commerce platforms can provide personalized product recommendations based on customer preferences, thereby increasing satisfaction.
- Reduced operational costs: E-commerce businesses can reduce overhead costs through functions such as outsourcing, allowing them to operate in multiple locations without a physical store.
- Customer retargeting: E-commerce platforms can easily retarget customers who have shown interest in products, using coupons, email marketing and personalized ads, thereby increasing the likelihood of conversion.
- Encourage accidental purchases: The convenient and simplified purchase process in e-commerce often promotes accidental purchases, thereby increasing sales.
- Access to reviews before buying: Customers can read product reviews and ratings from other buyers, helping them make informed purchase decisions.
- Detailed product information: E-commerce platforms provide product descriptions, specifications, and images, making it easier for customers to understand the product before buying.
- Making high-quality service affordable: E-commerce businesses can provide high-quality customer service with lower operating costs due to automation and digital tools.
- Fast and affordable marketing: Digital marketing strategies, such as social media campaigns and search engine optimization (SEO), help e-commerce businesses reach a wider audience quickly and at a lower cost.
- Flexibility of 24/7 service: E-commerce platforms are always available, allowing customers to shop at any time, increasing convenience and sales opportunities.
Disadvantages of E-Commerce:
- Lack of personal touch: E-commerce lacks the personal interaction and customer service that physical stores can provide, which can impact customer satisfaction.
- Uncertainty about quality: Customers cannot be sure about the quality of the product without physically inspecting it, leading to potential dissatisfaction.
- Delayed delivery: E-commerce often involves shipping, which can delay product delivery, especially to remote areas or during peak shopping seasons.
- Trust issues with high-value items: Customers may hesitate to buy high-value items like gold or furniture online, as there are doubts about their authenticity, quality and after-sales service.
- Site crashes: Technical issues, such as website crashes or slow loading times, can disrupt the shopping experience and lead to lost sales.
- Cybercrime and data privacy concerns: E-commerce platforms are vulnerable to hacking, data breaches and other cyber threats, posing risks to both businesses and customers.
Challenges to E-Commerce in India
- Lack of digital infrastructure: Inadequate digital infrastructure in many parts of India limits the reach and efficiency of e-commerce platforms.
- Low internet penetration in many areas: Limited internet penetration in rural and remote areas hampers the growth of e-commerce.
- Policy uncertainty: The absence of a specific and comprehensive e-commerce policy creates uncertainty for businesses operating in the sector.
- Taxation issues: Inconsistent taxation laws and issues such as Base Erosion and Profit Shifting (BEPS) pose challenges for e-commerce companies in India.
- Lack of digital literacy: Many potential customers lack the digital literacy needed to effectively navigate and use e-commerce platforms.
- Cybersecurity concerns: E-commerce platforms face significant cybersecurity risks, including credit/debit card data breaches and ransomware attacks.
- Language barriers: Limited availability of services in local languages restricts access for non-English speaking customers.
- Limited coverage in remote areas: E-commerce companies often face logistical challenges in delivering products to remote and rural areas.
- Quality variations: There may be significant differences between the product shown online and the product delivered, leading to customer dissatisfaction.
Recent Developments:
- Consumer Protection (E-Commerce) Rules 2020: These rules were introduced to ensure fair practices, transparency and protection of consumer rights in the e-commerce sector. They aim to protect consumers from unfair trade practices, misleading advertisements and ensure authenticity of products being sold online.
E-Marketing
E-Marketing uses the internet and digital tools to promote products or services to a target audience.
Examples:
- SEO (Search Engine Optimization): Enhancing website visibility on search engines like Google.
- Social Media Marketing (SMM): Promoting products on platforms like Facebook, Instagram, and Twitter.
- Email Marketing: Sending promotional emails to subscribers.
- Content Marketing: Creating blogs, videos, or infographics to engage customers.
- PPC (Pay-Per-Click) Advertising: Running paid ads on Google or social media.
- Affiliate Marketing: Partnering with affiliates who earn commissions by promoting your products.
- Influencer Marketing: Collaborating with social media influencers to reach their followers.
- Mobile Marketing: Targeting customers via mobile apps or SMS.
- Video Marketing: Using YouTube or social media to share promotional videos.
- Online PR: Managing your brand’s online reputation through press releases and social media.
Benefits of E-Marketing:
- Wider Reach: Reaching audiences across the world.
- Cost-Effective : Lower costs than traditional marketing.
- Measurable Results: The effectiveness of campaigns can be measured through tools such as Google Analytics.
- Personalization: Customizing the content as per each customer.
- 24/7 Availability: Customizing the content as per each customer.
- Flexibility and Agility : quick adjustments to campaigns in response to market changes.
- Detailed Targeting: Marketers can target specific demographics, interests, and behaviors, improving the effectiveness of campaigns.
Limitations of E-Marketing:
- High Competition : The online marketplace is highly competitive, making it difficult for brands to stand out.Competitors can easily copy marketing strategies, forcing businesses to constantly innovate.
- Security & Privacy Issues : Customers are concerned about data breaches and misuse of personal information.
- Dependence on Technology : Requires stable internet access and digital devices, limiting accessibility for some users. Technical issues like website crashes, slow loading times, or platform outages can impact sales.
- Trust Issues : Online fraud, phishing scams, and misleading ads make some consumers hesitant to engage with e-marketing.Lack of face-to-face interaction can make it harder to build customer trust.
- High Advertising Costs : Paid advertising (Google Ads, Facebook Ads, etc.) can be expensive, especially in competitive industries. Continuous investment is required to maintain visibility and engagement.
- Ad Fatigue & Consumer Resistance : Overexposure to digital ads can lead to ad fatigue, reducing engagement.
- Many users install ad blockers, further limiting the reach of online marketing efforts.
- Negative Publicity Spreads Fast : Negative reviews, customer complaints, or social media backlash can go viral quickly.A single mistake in an ad campaign can lead to significant brand damage.
FAQ (Previous year questions)
Supply Chain & Logistics Mix / Supply Chain & Logistics Mix/ Supply Chain & Logistics Mix/ Supply Chain & Logistics Mix /Supply Chain & Logistics Mix
Supply Chain Management (SCM) is the process of managing the flow of goods, services, information, and finances from raw material sourcing to the final delivery of products to customers.
It involves coordinating various activities such as procurement, production, logistics, and distribution to improve efficiency, reduce costs, and enhance customer satisfaction.
