This is Day 70 | 90 Days RAS Mains 2025 Answer Writing, We will cover the whole RAS Mains 2025 with this 90-day answer writing program
Click here for the complete 90 days schedule (English Medium)
Click here for complete 90 days schedule (Hindi Medium)
GS Answer Writing – Federalism, Centre-State relations |Supreme Court, High Courts | Judicial Review, Judicial Activism l Letter and Report
Article 142 provides a unique power to the Supreme Court, to do “complete justice” between the parties,
where, at times, the law or statute may not provide a remedy.
Utility of Article 142 in providing complete Justice:
- Prem Chand Garg case 1967- Art. 142(1) confers upon the Court powers which can contravene the provisions of Article 32 (right to constitutional remedies) in order to provide complete justice.
- Laxmi Devi v. Satya Narayan- The accused to award compensation to the victim with whom he had sexual intercourse with a promise to marry and had later retracted his promise
- Bhopal gas tragedy case 1991- UCC to pay $470 million in compensation for the victims of the tragedy and highlighted the wide scope of Article 142 (1)
- Siddiq v. Mahant Suresh Das– (Ayodhya dispute), the Supreme Court had exercised the powers mentioned under Article 142 of the Constitution.
- Five-judge constitution bench 2023- A court can directly grant divorce under Article 142 of the Constitution, in cases where the marriage has irretrievably broken down, without referring the parties to a family court first, where they must wait for 6-18 months for a decree of divorce by mutual consent.
The Punchhi Commission, chaired by former Chief Justice of India Madan Mohan Punchhi, was constituted by the Union Government in April 2007 to review and examine the functioning of existing arrangements between the Union and States.
Major recommendation to strengthen Cooperative federalism
- Regarding Office of Governor :
- Appointment : adopt the following strict guidelines (i) He/she should be eminent in some walk of life (ii) a person from outside the state (iii)a detached figure etc
- A committee for appointment of governors → it may comprise thePrime Minister, the Home Minister, the Lok Sabha’s speaker and the concerned Chief Minister of the State.
- fixed tenure of 5 years , Removal → impeachment procedure like President
- Discretionary powers should be used sparingly, and must be a choice dictated by reason activated by good faith and tempered by caution.
- Make decision on a Bill within 6 months
- provided clear guidelines on the order of precedence for the appointment of chief ministers, thereby limiting the governor’s discretionary powers in this regard.
- Cooperation
- Amend article 263 : make the Inter-State Council a credible, powerful and fair mechanism for management of inter-state and Centre-state differences.
- Zonal Councils → Meet at least twice a year
- New All India Service → Health, Education, Judiciary
- The Seventh Schedule should be amended to include ‘Environment, Ecology and Climate Change’ under the Union list.
- Political Federalism
- Concurrent list : Some broad agreement should be reached before introducing Bills on Concurrent Subjects by institutionalizing a mechanism under the ISC.
- Emergency : Article 356 should be amended to incorporate guidelines set forth by the SC in S.R. Bommai case (1994) ; Provide a framework for ‘localized emergency’ (Art. 352, 356 → last resort)
- Rajyasabha : Factors inhibiting the functioning of the Rajya Sabha as a representative forum of States should be removed; States should be given equal representation; requirement of domicile status for election to Rajya Sabha should be restored
- Economic Federalism
- All future Central legislation involving States’ involvement should provide for cost sharing.
- Consultation with states in finalizing the Terms of Reference of the Finance Commission.
- Review of all transfers to States to minimize discretionary transfers (like CSSs)
The MHA’s recent initiative to seek states’ comments on the Punchhi Commission reflects a commitment to Cooperative Federalism, fostering collaboration to propel India forward in the era of Amrit Kaal.
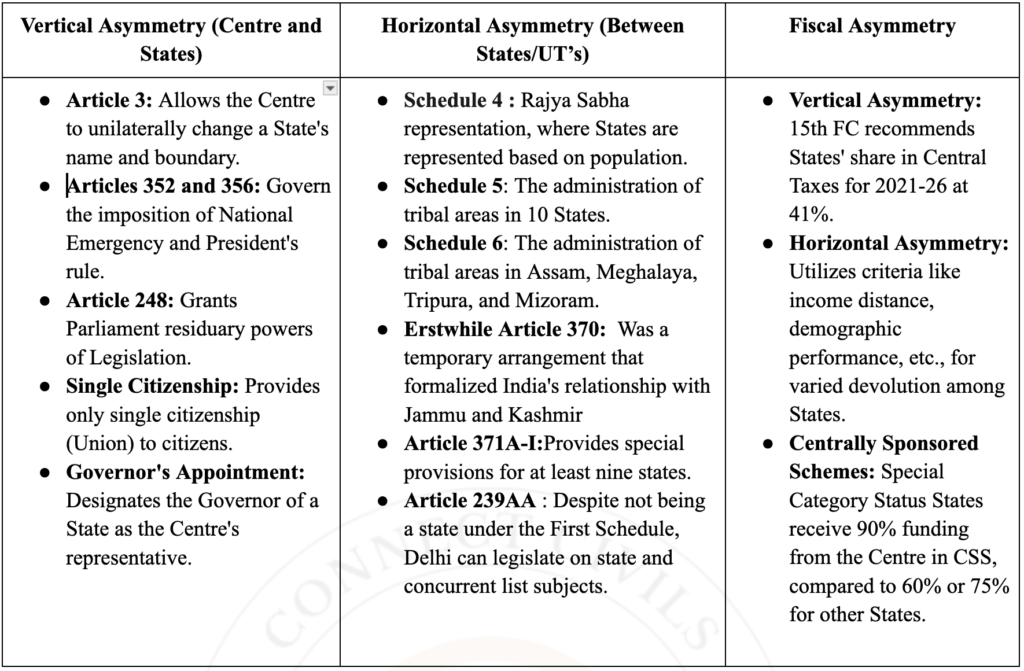
Asymmetric Federalism: It is based on unequal powers and relationships in political, administrative, and fiscal arrangement spheres among the constituent units (States). In India, asymmetry exists both vertically (between Centre and States) and horizontally (among the States).
Existing intrinsic asymmetry :
Asymmetric Federalism: It is based on unequal powers and relationships in political, administrative, and fiscal arrangement spheres among the constituent units (States). In India, asymmetry exists both vertically (between Centre and States) and horizontally (among the States).
Existing intrinsic asymmetry :
Role of Asymmetry in Cooperative Federalism:
- Based on weighted and differentiated equality : Equal treatment of all States while recognizing varying capacities.
- Balancing national unity with regional autonomy : States like Nagaland and Mizoram enjoy negotiated autonomy as a political compromise. Parliament is prohibited from interfering with religious, social practices, land, and natural resources in these states.
- Allows Self-Rule within Shared Rule: Creation of Autonomous District Councils acknowledges historical rights and facilitates self-rule within the shared rule framework.
- Protecting Diversity: Addresses India’s linguistic, cultural and religious diversity by allowing differentiated treatment for states.
- Grants concessions to certain conflict- ridden regions to prevent secessionism and address autonomy demands.
- Special provisions facilitate inclusive decision-making and resource distribution.
However, Concerns have also been raised against asymmetric federalism citing potential for regionalism and separatism.
The recent abrogation of Article 370 also highlights the importance of ensuring that the principles of asymmetric federalism are not misused, emphasizing the ongoing need to balance regional autonomy with national unity.
Despite challenges, asymmetrical federalism remains relevant for accommodating diverse groups and promoting cooperative federalism.It is crucial for sharing governance responsibilities and ensuring inclusive governance in a multicultural society like India.
Paper 4 (Comprehension part) – Letter and Report
Sungleam Society
Indiranagar
Jaipur
24 December, 2023
The Senior Editor
The Hindustan Times
Jaipur
Subject: Compulsory rural posting for doctors.
Respected Sir,
Over 100 million people live in rural India but India’s rural health service is non-existent. Most of the states face an acute shortage of doctors. The doctor-patient ratio in the country is 1: 2000 but most of the doctors are concentrated in towns and cities. The shortfall of surgeons, gynaecologists, physicians and paediatricians in rural areas is as high as 70 percent. It is because of our lopsided development that villages lack basic infrastructure making it difficult for people (doctors) to serve there. But doctors must realize that their profession needs commitment and sacrifice. For them the welfare of patients is above everything else.
On an average the state spends Rs. 15 to 20 lakh per student of MBBS. It is only fair that once doctors get their degrees they should work in rural areas for five years where their services are most needed. They owe it to the state for investing so much in their training. Moreover early exposure to real India will be good training for young professionals and give them invaluable experience. It would be ideal if this is done voluntarily. If it is not, the government will have to make it compulsory. The state will be failing in its duty if it does not provide basic medical facilities for its rural population.
The Government should provide proper infrastructure and basic facilities in primary health centres in rural areas. Utilities like electricity and water and furniture should be made available. The government should arrange to repair and equip the 1,42,655 sub-centres, 23109 primary health centres and 3,222 community health centres. Secondly there should be attractive incentives for doctors to serve in rural areas. Also, serving in rural areas should be made part and parcel of the degree course to sensitise the future set of doctors. Once this is done doctors will willingly opt for rural posting.
Riya Kumari
(A concerned citizen)
Day 70 | 90 Days RAS Mains 2025 Answer Writing
Day 70 | 90 Days RAS Mains 2025 Answer Writing