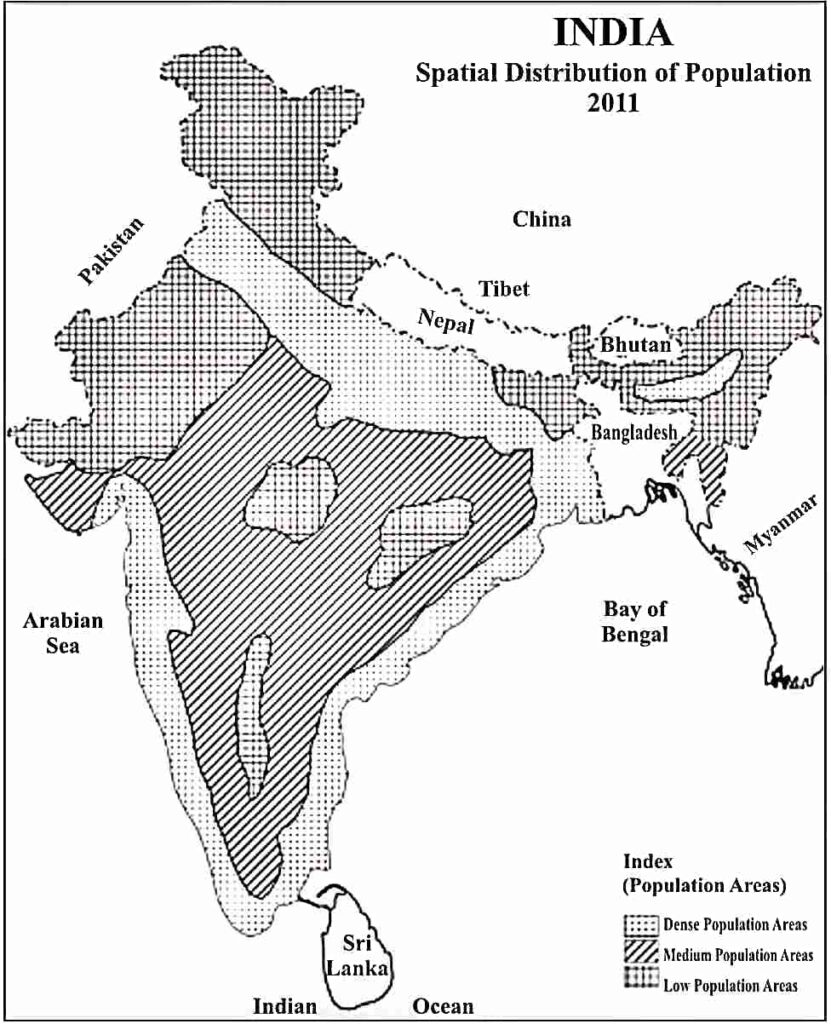
In Indian Geography, India’s population distribution varies widely, with dense concentrations in the Gangetic plains and sparse settlements in hilly and desert regions. Factors like climate and economy shape high-density states like Uttar Pradesh and low-density areas like Ladakh.
General Introduction
- The distribution of population in India is uneven.
- In five states like Uttar Pradesh, Bihar, West Bengal, Maharashtra and Andhra Pradesh, about 50% of the population lives on 30% of the country’s area, whereas in the northern and north-eastern hilly states, less than 4% of the population lives on 16% of the area.
- The Indian economy is agriculture-based, factors that help in the development of good agriculture also control the population distribution.
- According to Clark, factors like economic system, technological development, social organization, government policy, etc. play a more important role in population distribution.
Factors controlling population distribution
- Climate – Extremely cold, extremely hot and extremely humid climate is unsuitable for human habitation and activities. The mountainous regions of Himalayas, the dry desert of Rajasthan and the Eastern Himalayas are sparsely populated. The Terai regions are sparsely populated due to unhealthy climate.
- Surface – In areas with uneven surface, the population is less due to lack of cultivable land, difficulty in agricultural work, obstacles in transportation and isolated situation.
- Water availability – In northern India, the population density decreases from east to west with the amount of rainfall. In the dry northwestern part of Rajasthan, relatively dense population is found due to water supply through canal.
- Mineral resources – The excellent possibilities of industrial and economic development in mineral-rich areas attract people. Population concentration became possible in mineral areas like Damodar valley, Chota Nagpur plateau, Kolar region, etc.
- Transport facilities – Transport facilities are more available in plain areas than in mountains and plateaus, hence plains are more densely populated.
- Socio-psychological factors – Social, psychological, religious and cultural factors also play a definite role in population concentration. These factors include social organization, social structure, customs, education, medicine, casteism, religious structure, social and religious values.
- Political and economic factors – Political turmoil, dissatisfaction, insecurity etc. are political factors and industrialization, urbanization etc. are economic factors. Due to increase in terrorism in the border states of India like Jammu-Kashmir, Punjab, Assam, the rate of population migration has increased.
Population distribution on geographical basis
- Areas with dense population – India’s plains and coastal regions have the highest population density because they offer better water availability, agriculture, transportation, and employment opportunities.The northern plains (Punjab, Uttar Pradesh, Bihar, West Bengal, Assam, Delhi, Haryana, Chandigarh, North Eastern Rajasthan) and coastal areas (South India) are prominent.
- Areas with medium population – Plateau regions are in second place in terms of distribution. Minerals are found in plateau regions. Hence, industrial development is more in these regions and population resides near industrial centres. This region includes South Eastern Rajasthan, Madhya Pradesh, Gujarat, Chhattisgarh, Orissa, Jharkhand, Maharashtra, Andhra Pradesh and Karnataka.
- Areas with low population – Due to natural and topographic differences, population resides less in the northern and north eastern hilly states and western Rajasthan.