This is Day 19 | 90 Days RAS Mains 2025 Answer Writing, We will cover the whole RAS Mains 2025 with this 90-day answer writing program
Click here for the complete 90 days schedule (English Medium)
Click here for complete 90 days schedule (Hindi Medium)
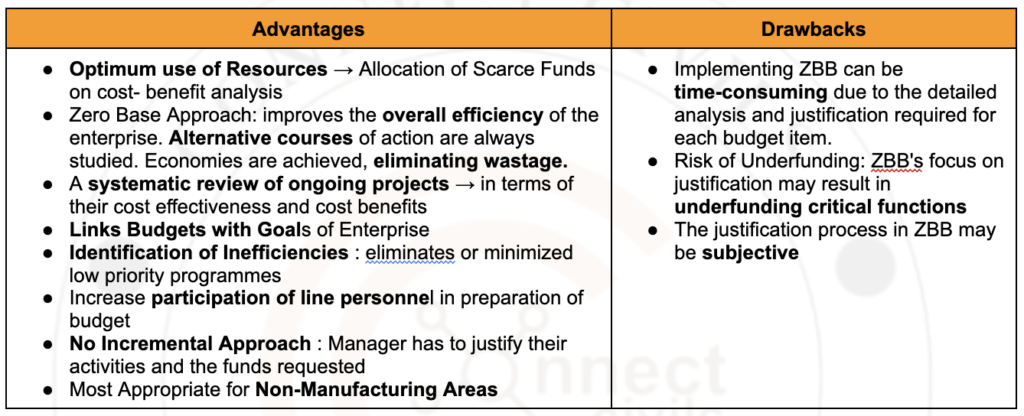
GS Answer Writing – Elementary knowledge of Government Audit, Basic knowledge of Performance Budgeting, Zero-Base Budgeting । पत्र लेखन
Paper 4 (Comprehension part) – कार्यालयी पत्र
Day 19 | 90 Days RAS Mains 2025 Answer Writing